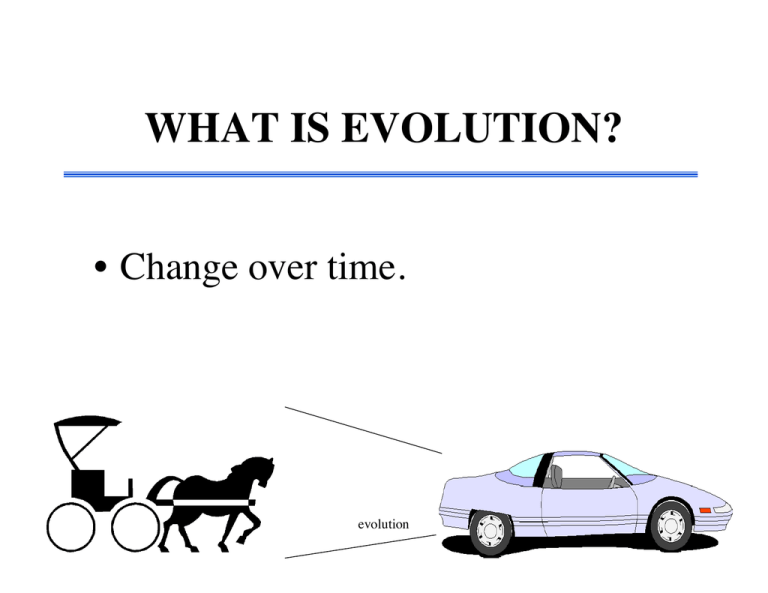
WHAT IS EVOLUTION?
• Change over time.
evolution
1
WHAT IS BIOLOGICAL
EVOLUTON?
• Changes in the genetic makeup of a
population of organisms over time !
evolution
2
A FACT
• Biological organisms evolve
evolution
3
A FACT
• Biological organisms evolve
evolution
4
A FACT
• Biological organisms evolve
• The details are under discussion
evolution
5
ANOTHER FACT
• Nature does not have a plan; it is more
like a blind watch maker
evolution
6
WHAT IS ADAPTATION?
Def’n - properties of an organism
that allow it to survive and
reproduce.
evolution
7
ANOTHER FACT
• At present, evolutionary theory is the
ONLY unifying theory in biology
evolution
8
WHAT IS A THEORY?
• A coherent system of general
propositions.
evolution
9
FATHERS OF THEORY OF
NATURAL SELECTION
• Charles Darwin
• Alfred Russell Wallace
• Patrick Matthew
evolution
10
THEORIES GET ACCEPTED
AS A FUNCTION OF:
• Supporting evidence
• Current views on the matter
evolution
11
DEFINING SPECIES
Def’n - a group of actual or potentially
interbreeding organisms
evolution
12
REMEMBER:
• When we speak of evolution, we mean
change across but not within
generations. The latter is referred to as
ontogeny.
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World
Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL 60661. All rights reserved. "
World Book illustration by Richard Lewington, The Garden Studio, London
1952
evolution
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World
Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL 60661. All rights reserved. "
World Book illustration by Richard Lewington, The Garden Studio
1990
13
DARWINIAN DEFINITION
OF EVOLUTION:
• Def’n - Descent with modification.
evolution
14
THE FIVE STAGES OF
EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY
•
•
•
•
•
Pre- Darwinian
Darwinian
Eclipse of Darwin
Modern Synthesis
Post-Modern
evolution
15
LAMARCK’S
TRANSFORMATION THEORY
Species changed due to :
• “Programmed” internal forces
• Acquired characteristics
evolution
16
LAMARK’S INTERNAL
FORCES THEORY
Trait
Value
sp 1
sp 2
time
17
LAMARCK’S INHERITANCE
OF ACQUIRED CHARACTERS
• Effects of unique events
get passed on to
offspring.
evolution
18
CUVIER’S APPROACH
• Whole species were frequently wiped
out by catastrophe and then,
miraculously, new ones appeared
evolution
19
DARWIN’S VOYAGE 1831-6
evol_2
20
UNDENIABLY SIMILAR
evol_2
21
GALAPAGOS
MOCKINGBIRDS
evol_2
22
GALAPAGOS FINCHES
evol_2
23
ONE GREAT IDEA!
• Various finches evolved from
a common ancestor
evol_2
24
FROM HIS READINGS,
DARWIN KNEW
• Earth is very old - lots of time for change
• Enormous reproductive potential for
organisms - why aren’t we covered in
flies?
• Extant variation can be selected artificially
evol_2
25
A QUOTE:
• “… Darwins’ view of Nature… kept faith
with the competitive, capitalist,
Malthusian dynamics of a poor-law
society and that his theory would make
him an ally of the middle and upper
class “
evol_2
26
A PROPOSAL
• When together in a habitat, two similar
species do better when each specializes
on different resources
Seed
Size
Beak Size
evol_2
27
EVIDENCE FROM FINCHES
• Compare alone vs. shared
evol_2
28
STICKLEBACKS
• They come in different shapes and sizes
SHALLOW
DEEP
evol_2
29
INTERESTING PATTERN
• When alone in lakes each species is
intermediate in size
• When together in lakes each species
displays much more size extremes - benthic
species is much bigger and feeds deep and
the limnetic species is smaller and feeds
shallow
• Coincidence?
evol_2
30
IS BEING EXTREME
BENEFICIAL?
evol_2
31
HOW THE STONEFLY GOT
ITS WINGS
evol_2
32
MISSING LINK?
evol_2
33
WEISMANN SHOWED
• Acquired characters are NOT heritable
evol_2
34
THE BIG PROBLEM:
• Linking Mendelian inheritance to natural
levels of within-population variability
evol_2
35
LEADERS OF THE MODERN
SYNTHESIS
• R. Fisher
• J. Haldane
• S. Wright
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia
Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc.,
525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL 60661. All
rights reserved. "World Book illustration
by Shirley Hooper, Oxford Illustrators
Limited
evol_2
36
BIG ACHIEVEMENT
• Demonstration that it was that it was
mathematically possible to achieve
everyday patterns of variation without
having to resort to acquired
characteristics or hopeful monsters
evol_3
37
INDUSTRIAL MELANISM
• evol_3
38
POST-MODERN FEATURES
• Demonstration of inheritance mechanism
(birth of molecular biology)
• Better integration of evolutionary and
ecological theory
• Studies on the adaptive nature of behavior
(in the broad sense)
• Studies on phenotypic plasticity
• The species concept
evol_3
39
SCPECIES CONCEPT
• OLD - A set of similar organisms
(measured against some time)
• NEW - A group of interbreeding
organisms
evol_3
40
DARWIN’S THEORY IS
ELEGANT
• It requires no demons to make it work!
evol_3
41
A SUMMARY OF DARWIN’S
THEORY
•
•
•
•
•
Organisms have enormous repro. potential
Their full potential isn’t being met
All populations contain variants
Some variants outperform others
If variation is heritable, they leave more
offspring and become more common
• Given enough time, new species can arise
evol_3
42
DARWIN’S ALGORITHM
• Substrate neutrality
• Underlying mindlessness • Guaranteed results. evol_3
43
ALWAYS REMEMBER:
• Can’t have evolution by Natural Selection
without variation
• Can’t have evolution by Natural Selection
without variation being heritable
• Natural Selection works on existing
variation i.e. it is not progressive
evol_3
44
THOUGHT EXPERIMENT 1:
SELECT FOR SIZE
NO VARIATION - NO EVOLUTION!!
45
THOUGHT EXPERIMENT 2:
SELECT FOR SIZE
HIGH
MEDIUM
10
LOW 3
0
NO HERITABILITY - NO EVOLUTION!!
46
THOUGHT EXPERIMENT 3:
SELECT FOR SIZE
HIGH
MEDIUM
10
LOW 3
0
NO CONSISTANCY - NO EVOLUTION!!
47
THOUGHT EXPERIMENT 4:
SELECT DE NOVO FOR PATTERN CURRENT STOCK
GOAL
NO PROGRESSIVE EVOLUTION!!
48








