2007 Extension Research Report Disease Management
advertisement

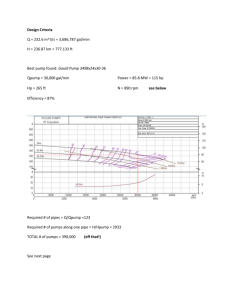
2007 Extension Research Report Disease Management THE EFFECT TIME OF CHEMIGATION AND RATE AND METHOD OF METAM SODIUM APPLICATION ON ROOT KNOT NEMATODE SOIL POPULATION AND PHYTOPHTHORA CAPSICI AND RHIZOCTONIA SOLANI SURVIVAL IN RAISED PLASTIC-MULCHED SOIL BEDS B. L. Candole and A. S. Csinos, Department of Plant Pathology, University of Georgia, Tifton Campus, D. Wang, Department of Soil, Water, and Climate, University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Campus 37.5 gal/A sprayed then rototilled, 3) 75 gal/A sprayed and rototilled, 4) 37.5 gal/A drip-applied for 8 h, 5) 37.5 gal/A drip-applied for 4 h, 6) 75 gal/A drip-applied for 8 h, 7) 75 gal/A dripapplied for 4 h, and 8) methyl bromide (67% methyl bromide + 33% chloropicrin). The treatments were applied three weeks prior to transplanting of BHN 640 tomato. Each bed measured 30 ft long and 30 in wide and preirrigated for eight hours a day prior to chemigation. Tape used was Aqua-Traxx® Premium drip tape. Emitters were spaced one inch apart and had a flow rate of 1.14 l/hr at 0.069 MPa. Each bed received about 250 l of water after each drip irrigation. The experiments were arranged in an RCBD with five replications. The effects of the treatments on the mortality of P. capsici, and R. solani were determined by preparing sets of two nylon mesh packets with one packet containing 50 R. solanicolonized beet seeds and another packet with 50 P. capsici-colonized beet seeds . Each set of packets were inserted before treatment application at the three preselected sites: 10 cm below the emitter, 20 cm laterally away from the emitter, and 30 cm laterally away from the emitter and retrieved 10 days after exposure to the treatments. After packet retrieval, respective colonized beet seeds were transferred onto plates containing Rhizoctonia- and Phytophthora- selective media. After 48 hrs of incubation under dark at room temperature, pathogen mortality was determined by counting the number of beet seeds that were negative for pathogen growth and expressed as a percentage of the total number of beet seeds tested for the pathogen. To determine the yield, tomato Introduction Methyl bromide alternatives such as metam sodium, the precursor of the biologically active compound methyl isothiocyanate (MITC) is a pre-plant fumigant that can be applied through drip irrigation in raised plastic-mulched beds. As with other water-based alternatives, metam sodium are distributed in the soil largely by the water in which it was applied with. MITC were detected at high concentrations within the 10 cm below the emitter and concentrations diminish beyond these locations even with increased rate of metam sodium application. Specifically, concentrations and residence time of MITC towards the bed shoulders were almost nondetectable and short, respectively. As a consequence, Phytophthora capsici and Rhizoctonia solani and yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus L.) survival were higher towards the bed shoulders. This study was conducted to determine if the rate of application, time of chemigation and method of metam sodium application can improve the efficacy of MITC against the soil populations of root knot nematode(Meloidogyne incognita) and the survival of P. capsici, and R. solani at preselected sites within the treated beds. Materials and Methods The experiment was conducted at the Black Shank Farm of the University of Georgia’s Coastal Plain Experiment Station, Tifton, GA on a Fuquay loamy sand (loamy, siliceous, thermic Arenic Plinthic Paleudults). Vapam (42% metam sodium EC) was applied according to the following treatments: 1) nontreated control, 2) 44 fruits were hand-harvested three times from 10 plants per plot. Marketable fruits were counted and weighed. Data on final plant stand count were also collected. Root gall indices were determined six weeks after transplanting and after the final harvest. from the emitter when applied at 75 gal/A. Mortality of R. solani with lateral distance from the emitter of drip applied Vapam were ranked as follows: 0 cm (59-100%) > 20 cm (10-34%) > 30 cm (3-28%) regardless of the rate and duration of application. Of all the fumigant treatments, Vapam drip-applied at 37.5 gal/A for 8 h and methyl bromide were the least effective in reducing R. solani survival at 0 cm. Sprayed and rototilled Vapam were the most effective at both rates of application in reducing R. solani at 20 cm away from the emitter but not at 30 cm away from the emitter where the most effective treatment was sprayed and rototilled Vapam at 37.5 gal/A. All treatments had no effect on plant stand (as a percentage of the base count) (Table 4). Tomato plants from plots sprayed and rototilled with Vapam at 75 gal/A had the highest total fruit yield but the differences in marketable fruit yield among the treatments were not significant. However, there was a trend toward highest marketable fruit yield from sprayed and rototilled Vapam (75 gal/A) treatment. The data indicated that any of the Vapam treatments were equally effective in reducing RKN soil populations and consequently root gall severity. However, drip-applied Vapam’s efficacy against P. capsici and R. solani diminished with lateral distance from the point of application. The data did indicate that sprayed and rototilled Vapam had the better chance of reducing pathogen survival at bed shoulders. Furthermore, there is a potential for a higher yield with sprayed and rototilled Vapam. Results and Conclusion Root knot nematode (RKN) soil populations were not significantly different among the three preselected sites 10 days after fumigation regardless of the method, rate and duration of application (Table 1). Within a preselected site, RKN populations were also not significantly different among the fumigated plots. The method, rate and duration of application also had no effect on root gall severity index of tomatoes six weeks after transplanting (6 WAT) (Table2). At harvest time root gall index was lowest in plots where Vapam was sprayed and rototilled at 75 gal/A . Root gall index was not significantly different among drip-applied Vapam plots regardless of the application duration. Sprayed and rototilled Vapam at both rates of application were effective against P. capsici at the three preselected sites (Table 3). Mortality of P. capsici with lateral distance from the emitter of drip applied Vapam were ranked as follows: 0 cm (86-100%) >20 cm (54-78%) >30 cm (1-43%) regardless of the rate and duration of application. All fumigation treatments were equally effective at 0 cm. Sprayed and rottotilled Vapam at both rates of application had the tendency to be more effective in reducing P. capsici survival than the other treatments at 20 cm away from the emitter. At 30 cm away from the emitter, Vapam sprayed and rototilled at 75 gal/A was the most effective in reducing P. capsici survival. Sprayed and rototilled Vapam at 37.5 gal/A was effective against R. solani at all preselected sites but ineffective at 30 cm away Acknowledgment The authors wish to thank Don Hickey, Unessee Hargett, Shad Law, Buddy Powell, Brad Russel, Clint Powell, Channing Paulk, Crystal Simataro and Zack Moye for technical assistance. 45 Table 1. The effect of rate and method of metam sodium application on the soil populations of root knot nematode before and after fumigation and preselected sites within the treated plastic-mulched beds. Root knot nematodes/150 cc soila Treatment and time of observation 0 cm 20 cm 30 cm Nontreated control 153 a (a) 80 a (a) 240 a (ab) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 185 a (a) 78 a (a) 195 a (ab) Vapam (75 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 228 a (a) 110 a (a) 128 a (b) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 150 a (a) 80 a (a) 130 a (b) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 108 a (a) 78 a (a) 35 a (b) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 88 a (a) 98 a (a) 55 a (b) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 113 b (a) 83 b (a) 443 a (a) 20 a (a) 3 a (a) 20 a (b) Nontreated control 135 a (a) 92 a (a) 225 a (a) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 35 a (a) 73 a (a) 25 a (b) Vapam (75 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 128 a (a) 80 a (a) 65 a (ab) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 23 a (a) 13 a (a) 23 a (b) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 35 a (a) 108 a (a) 48 a (b) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 58 a (a) 38 a (a) 30 a (b) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 48 a (a) 18 a (a) 23 a (b) Initial (Before Fumigation) Methyl bromide (67% MB + 33% chloropicrin) 10 days after fumigation Methyl bromide (67% MB + 33% chloropicrin) 8 a (a) 15 a (a) 23 a (b) In a row, treatment means from the three preselected sites (0 cm = 10 cm below the emitter, 20 cm away from the emitter, and 30 cm away from the emitter) followed by the same letters; or treatment means within a column within an observation time followed by the same letters in parentheses not significantly different by DMRT at P=0.05. a 46 Table 2. The effect of rate and method of metam sodium application on root gall index of BHN 640 tomato at 6 weeks after transplant (WAT) and at harvest. Root gall indexa Treatment 6 WATb Harvest Nontreated control 2.30 a 6.10 a Vapam (37.5 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 1.30 b 4.80 ab Vapam (75 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 0.65 b 2.45 c Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 0.90 b 3.52 bc Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 1.35 b 5.00 ab Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 1.25 b 4.55 ab Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 0.70 b 3.90 bc Methyl bromide (67% MB + 33% chloropicrin) 0.80 b 4.60 ab Root gall index: 0 = Complete and healthy root system, no infestation; 2 = Very few small galls can only be detected upon close examination; 3 = Small galls as in "1" but more numerous and easy to detect; 3 = Numerous small galls, some grown together, function of roots seriously affected; 4 = Numerous small galls, some big galls, majority of roots still functioning; 5 = 25% of root system severely galled and not functioning; 6 = 50% of root system severely galled and not functioning; 7 = 75% of root system severely galled and lost for production; 8 = No healthy roots, nourishment of plant interrupted, plant still green; 9 = The completely galled root system is rotting, plant is dying; 10 = Plant and roots are dead. b Within a time of observation, treatment means with the same letters are not significantly different by DMRT at P=0.05. a 47 Table 3. The effect of rate and method of metam sodium application on the mortality of Phytophthora capsici and Rhizoctonia solani after 10 days of exposure at three preselected sites within the treated plastic-mulched beds. Mortality (%)a Treatment and time of observation 0 cm 20 cm 30 cm Phytophthora capsici Nontreated control 24 a (b) 31 a (c) 29 a (cd) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 85 a (a) 91 a (a) 70 a (b) Vapam (75 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 83 a (a) 91 a (a) 99 a (a) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 100 a (a) 78 a (ab) 1 b (d) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 97 a (a) 54 b (bc) 13 c (d) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 86 a (a) 73 a (ab) 43 b (bc) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 100 a (a) 71 b (ab) 23 c (cd) 94 a (a) 82 a (ab) 51 b (bc) Methyl bromide (67% MB + 33% chloropicrin) Rhizoctonia solani Nontreated control 18 a (c) 3 a (c) 0 a (c) 100 a (a) 89 a (a) 99 a (a) Vapam (75 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 92 a (a) 72 a (a) 37 b (b) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 59 a (b) 10 b (bc) 3 b (c) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 100 a (a) 26 b (bc) 5 b (c) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 99 a (a) 28 b (bc) 5 b (c) Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 100 a (a) 34 b (b) 28 b (bc) Vapam (37.5 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled Methyl bromide (67% MB + 33% chloropicrin) 51 a (b) 1 b (c) 12 b (bc) In a row, treatment means from the three preselected sites (0 cm = 10 cm below the emitter, 20 cm away from the emitter, and 30 cm away from the emitter) followed by the same letters; or treatment means within a column and within a pathogen followed by the same letters in parentheses not significantly different by DMRT at P=0.05. a 48 Table 4. The effect of rate and method of metam sodium application on plant stand and fruit yield of BHN 640 tomato. Treatment Plant Total fruit Marketable stand (%) yield (t/ha) fruits (t/ha) Nontreated control 65 a 45.76 c 35.86 a Vapam (37.5 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 98 a 91.81 ab 75.85 a Vapam (75 gal/A) sprayed and rototilled 98 a 98.62 a 76.01 a Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 63 a 64.46 bc 45.77 a Vapam (37.5 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 85 a 87.42 ab 61.81 a Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 8 h 90 a 76.28 abc 51.31 a Vapam (75 gal/A) drip applied for 4 h 95 a 78.16 ab 53.35 a Methyl bromide (67% MB + 33% chloropicrin) 85 a 75.03 abc 54.79 a Within a column, treatment means with the same letters are not significantly different by DMRT at P=0.05. 49