Tangent approximation
advertisement

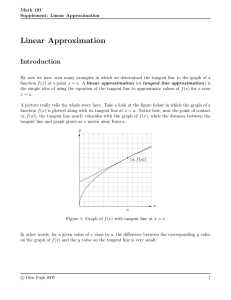
Tangent approximation 1. Find the equation of the tangent plane to the graph of z = xy 2 at the point (1,1,1). ∂z ∂z ∂z ∂z Answer: = y 2 and = 2xy ⇒ (1, 1) = 1 and (1, 1) = 1. ∂x ∂y ∂x ∂y The tangent plane at (1,1,1) is � � ∂z �� ∂z �� (z − 1) = (x − 1) + � (y − 1) = (x − 1) + 2(y − 1). ∂x � 0 ∂y 0 2. Give the linearization of f (x, y) = ex + x + y at (0,0). Answer: The tangent approximation formula at the point (x0 , y0 , z0 ) is f (x, y) − f (x0 , y0 ) ≈ fx (x0 , y0 )(x − x0 ) + fy (x0 , y0 )(y − y0 ). (We usually abbreviate this as Δz ≈ fx |0 Δx + fy |0 Δy.) Linearization is just the following form of the tangent approximation formula f (x, y) ≈ f (x0 , y0 ) + fx (x0 , y0 )(x − x0 ) + fy (x0 , y0 )(y − y0 ). In our case, fx (x, y) = ex + 1 and fy (x, y) = 1 ⇒ f (0, 0) = 1, fx (0, 0) = 2, fy (0, 0) = 1 Thus, for (x, y) ≈ (0, 0) we have f (x, y) ≈ 1 + 2x + y. MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02SC Multivariable Calculus Fall 2010 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.