7.014 Lecture 29 & 30: Population Growth Lecture Slides
advertisement

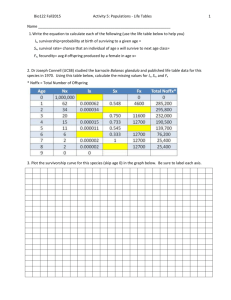
MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 7.014 Lecture 29 & 30: Population Growth Lecture Slides April 25 & 27, 2005 2005 Population Age Distribution MORE DEVELOPED COUNTRIES 80-90 AGE INTERVAL 70-80 60-70 50-60 40-50 30-40 20-30 10-20 0-10 MALES NUMBER OF PEOPLE (MILLIONS) FEMALES Figure by MIT OCW. 1 Population Summary for the US 2000 2025 2050 http://blue.census.gov/ Population Age Distribution LESS DEVELOPED COUNTRIES AGE 300 MALES 300 NUMBER OF PEOPLE (MILLIONS) FEMALES Figure by MIT OCW. 2 Population Summary for Uganda 2000 2025 2050 http://blue.census.gov/ Life Tables x = age or interval (defined) N0 = number of individuals in original cohort (defined) dx = number of original cohort dying during interval Nx = number of individuals surviving to age x (measured) lx = proportion of individuals surviving to age x l x = Nx / N0 mx = per capita births during age interval x to x+1 (measured) “age specific fecundity” = female offspring produced per female 3 A COHORT LIFE TABLE (for Unicorns) N0 = 100 Age Number Surviving Proportion Surviving X 0 1 2 3 4 Nx 100 50 40 30 0 lx 1.0 .5 .4 .3 0 SURVIVORSHIP CURVES High Probability of Survival Log (Number Surviving) Type I Steady Survival Type II Low Probability of Survival Low Probability of Survival Type III High Probability of Survival Age 4 Log (Number Surviving) SURVIVORSHIP CURVES HOMO SAPIENS SPERGULA VERNALIS (GRASS) Log (Number Surviving) Log (Number Surviving) AGE AGE COMMON BIRD SPECIES AGE Figure by MIT OCW. A COHORT LIFE TABLE (for Unicorns) N0 = 100 Age Number Surviving Proportion Surviving Average Offspring per female of age x X 0 1 2 3 4 Nx 100 50 40 30 0 lx 1.0 .5 .4 .3 0 mx 0 4 2.5 0 0 5 A COHORT LIFE TABLE (for Unicorns) N0 = 100 Age Number Surviving Proportion Surviving Average Offspring per female of age x X 0 1 2 3 4 Nx 100 50 40 30 0 lx 1.0 .5 .4 .3 0 mx 0 4 2.5 0 0 Realized Fecundity Values lxmx 0 2 1 0 0 R0 = Σ lxmx = 3 R0 = Net Replacement A STATIC LIFE TABLE (for Unicorns) Sample of 100 unicorns N0 = 100 Age Interval Number Surviving at Beginning of X Number Dying Proportion Surviving by Age X X Nx dx lx 0 1 2 3 4 100 50 40 30 0 50 10 10 30 0 1.0 .5 .4 .3 0 6 A COHORT LIFE TABLE (for Unicorns) N0 = 100 Age Number Surviving Proportion Surviving Average Offspring per female of age x X 0 1 2 3 4 Nx 100 50 40 30 0 lx 1.0 .5 .4 .3 0 mx 0 4 2.5 0 0 Realized Fecundity Values lxmx 0 2 1 0 0 lxmxX 0 2 2 0 0 R0 = Net Replacement = ∑ lxmx = 3 G ~ (∑ lxmxx) / (∑ lxmx) = (∑ lxmxx) / R0 = 4/3 years Intrinsic Rate of Increase r ≈ (ln R0) / G ≈ (ln 3)/1.33 ≈ 0.82 yr -1 Density-Dependant Factors Regulate Population Size Density-dependent death rate - d Density-dependent birth rate 1 dN N dt 1 dN N dt Density-independent birth rate - b Density-independent death rate Population Density (N) Population Density (N) Equilibrium Density r = b-d Density-dependent death rate 1 dN N dt Density-dependent birth rate as N r stabilizing Population Density (N) 7 Human Population Growth 6,432,150,287 (4/22/05) 6,363,174,549 (4/28/2004) Now projected to reach 9 Billion and level off 6,289,870,258* (4/30/2003) 6 Population (Billions) 5 3 2 Hunter Gatherers 1 4 million 10,000 BC 6 Billion (1999) Modern Medicine (reduced mortality) (1900) 4 Agriculture & domestification of animals Fossil Fuel Industrial Revolution (1800) Bubonic Plague (1400) 7 million 8,000 BC 4,000 BC 0 2,000 AD Year Adapted from: Cohen, “How Many People Can the Earth Support” http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html Four “Evolutions” in Human Population Growth Evolution Driver Midpoint Population (billions) Doubling Time (years) before after 40,000 - 300,000 1,400 – 3,000 750 – 1,800 100 – 130 2.5 87 36 3.7 34 (peak) >40 (since 1990) Local Agriculture 8000 B.C. 0.005 Global Agriculture 1750 A.D. 0.75 Public Health 1950 Fertility Control 1970 F Adapted from: Cohen, “How Many People Can the Earth Support” 8 and recall from lecture 20…… 6 380 CO2 1800 2 0 N2O (310 x CO2) 340 Population size 1400 300 CH4 ppbV Population size (billions) 4 CO2 and N2O ppmV CH4 (21x CO2) 1000 260 600 0 500 1000 1500 Time, Calendar years (A.D.) 2000 Falkowski and Tchernov 2004 http://www.census.gov/ipc/prod/wp02/wp02-1.pdf 9 DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION BIRTH RATE D TH EA TO TA L PO PU LA TI O N TE RA Time STAGE 1 High birth rate High, but fluctuating death rate STAGE 2 Declining death rates Continuing high birth rates STAGE 3 Declining birth and death rates STAGE 4 Low death rate Low, but fluctuating birth rate Figure by MIT OCW. 10