Configuring the 615M-1 serial client and serial server
Technical Application Note
Purpose
This application note demonstrates how to configure
the ELPRO 615M-1 Wireless Modem as a serial client
and serial server for a point‑to‑point RS‑232 connection.
The 615M-1 supports an RS‑232 serial client and serial
server for point‑to‑point communication, and allows for
point‑to‑multipoint serial communication for up to 50 devices
when used with the ELPRO 605M-R1 Cellular Serial Router.
NNote: This application note covers point‑to‑point connection
without the use of a 605M‑R1 router. It does
not describe how to provision the cellular PPP
connection. For instructions on configuring that
connection, see the 615M-1 quick start guide.
Network example overview
615M-1 Cellular
Modem and Router
RS-232 cable
Configuring the 615M-1 serial server
Use the following procedure to configure the
centrally located 615M-1 as the serial server.
1. Log onto the Web interface of the 615M-1 to be
configured as the serial server.
2. On the menu, click Serial.
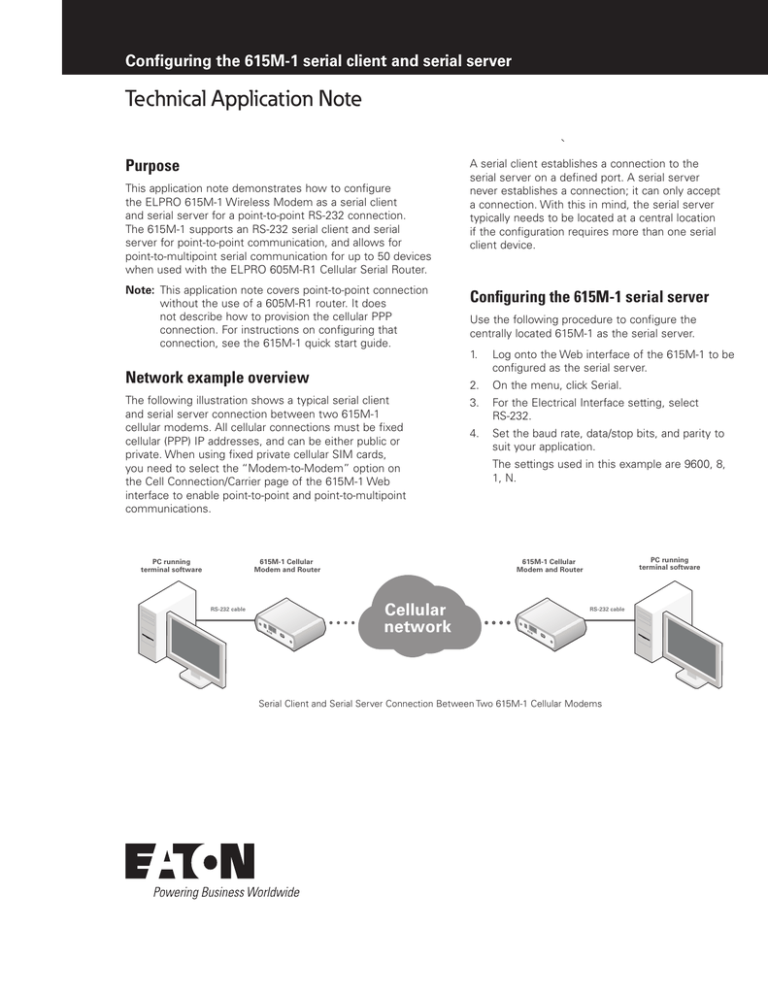
The following illustration shows a typical serial client
and serial server connection between two 615M-1
cellular modems. All cellular connections must be fixed
cellular (PPP) IP addresses, and can be either public or
private. When using fixed private cellular SIM cards,
you need to select the “Modem-to-Modem” option on
the Cell Connection/Carrier page of the 615M-1 Web
interface to enable point‑to‑point and point‑to‑multipoint
communications.
PC running
terminal software
A serial client establishes a connection to the
serial server on a defined port. A serial server
never establishes a connection; it can only accept
a connection. With this in mind, the serial server
typically needs to be located at a central location
if the configuration requires more than one serial
client device.
3. For the Electrical Interface setting, select
RS‑232.
4. Set the baud rate, data/stop bits, and parity to
suit your application.
The settings used in this example are 9600, 8,
1, N.
PC running
terminal software
615M-1 Cellular
Modem and Router
Cellular
network
RS-232 cable
Serial Client and Serial Server Connection Between Two 615M-1 Cellular Modems
5. Leave the DTR setting at the default, AT&D0.
This setting ignores the DTR. The DTR control is used
by the client to establish a connection to the server.
Because this modem is selected as a server, DTR can
be left at the default setting, which ignores the DTR.
4. Set the baud rate, data/stop bits, and parity to suit your
application.
The settings used in this example are 9600, 8, 1, N.
5. Set the DTE as follows:
6. Under the External PAD Settings, select Server as the
PAD Mode, and select TCP as the PAD Protocol.
This application example demonstrates two PCs
connecting their terminal sessions together. There are
two types of serial communication devices, DTE and
DCE. PCs are DTE devices, which means by default the
DTR line (pin 4) is ON.
7. In the Incoming Friendly IP Address field, enter the
cellular IP address of the remote modem (the serial
client).
You can find the cellular IP address of the remote
modem by logging onto its Web interface and
displaying the Unit Status page.
•
For DTE devices, select AT&D9 from the DTR
drop‑down menu. The modem connects to the
server when DTR is ON. When DTR is OFF, the
modem does not connect or the connection will
close if in session.
•
For DCE devices, such as other modems or ELPRO
115S modules, DTR is OFF by default. For these
devices, select AT&D8 from the DTR drop‑down
menu. The modem connects when DTR is OFF and
disconnects when DTR is ON.
8. In the Incoming Port field, enter the TCP port to be
used.
Both the serial server and serial client must use the
same TCP port. Port 5002 is used in this example.
9. Click Save.
For more information, see the Help link on the Serial
Web page.
6. Under External PAD Settings, select Client as the PAD
Mode, and select TCP as the PAD Protocol.
7. In the Outgoing Port field, set the outgoing port to
match the incoming port of the serial server.
Both the serial server and serial client must use the
same TCP port. Port 5002 is used in this example.
8. In the Remote Host IP Address field, enter the cellular
IP address of the serial server.
You can find cellular IP address of the serial server by
logging on to its Web interface and displaying the Unit
Status page.
9. For TCP Client Keep Alive, select the Enabled option.
When this option is enabled, an “alive” packet is
periodically sent from the client to the server in order to
detect a broken connection. The modem automatically
tries to re-establish the connection if necessary.
Serial Server Configuration
10. Click Save.
Configuring the 615M-1 serial client
Use this procedure to configure the remote 615M-1 modem
as the serial client that will establish the connection to the
serial server.
1. Log onto the Web interface of the remote 615M-1
modem.
2. On the menu, click Serial.
3. For the Electrical Interface setting, select RS‑232.
2
Technical Application Note
September 2014 www.eaton.com
Pin 4 is the DTR line that is required by the client
modem to establish a connection.
b. After connecting the serial cables, open a terminal
session on both PCs and connect to the modems.
You should be able to pass serial data from one end
to the other (see the following examples).
Serial Client Modem Sending Data
Serial Client Configuration
Testing serial communication
After configuring the modems, follow these steps to test
serial communication.
Serial Server Receiving Data
1. Verify serial communication by displaying the Unit
Status page on the Web interface of each modem and
confirming that the PPP status is UP.
This confirms that there is a cellular connection. The
PPP IP Address field shows the cellular IP address
provided from the carrier. This is the IP address used
on the Serial page for the Incoming Friendly IP Address
and the Remote Host IP Address.
PPP Information on the Unit Status Page
2. Verify that serial data can be passed between the
modems:
a. Use a straight-through serial cable (with minimum
pins 2, 3, 4, and 5 connected) to connect the serial
server and serial client modems to separate PCs
running terminal software.
Technical Application Note
September 2014 www.eaton.com
3
Eaton’s wireless business
www.eaton.com/wireless
North America & Latin America
5735 W. Las Positas Suite 100
Pleasanton, CA 94588
United States
Telephone: +1 925 924 8500
Australia, New Zealand
9/12 Billabong Street
Stafford Queensland 4053
Australia
Telephone: +61 7 3352 8600
Southeast Asia
2 Serangoon North Avenue 5
# 06-01 Fu Yu Building, 554911
Singapore
Telephone: +65 6645 9888
Europe
Hein-Moeller-Straße 7-11
53115 Bonn, Germany
Telephone: +49 228 602 5573
China
955 Shengli Road
East Area of Zhangjiang High-Tech Park
Shanghai, 201201
China
Telephone: +86 21 2899 3600
Eaton
1000 Eaton Boulevard
Cleveland, OH 44122
United States
Eaton.com
© 2014 Eaton
All Rights Reserved
Printed in USA
September 2014
Eaton is a registered trademark.
All other trademarks are property
of their respective owners.