Document 13715600
advertisement

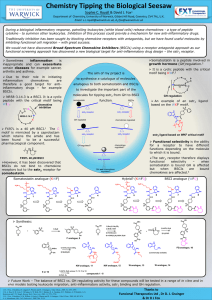
During a biological inflammatory response, patrolling leukocytes (white blood cells) release chemokines a type of peptide cytokine - to summon other leukocytes. Inhibition of this process could provide a mechanism for new anti-inflammatory drugs. Chemistry Tipping the Biological Seesaw Sophie C. Royall & David J. Fox* Chemistry, University of Warwick, Gibbet Hill Road, Coventry, CV4 7AL, U.K. Email: s.c.royall@warwick.ac.uk, d.j.fox@warwick.ac.uk Department of NR58-3.14.3 is a BSCI. It is a cyclic peptide with the critical motif being WIQ. Sometimes inflammation is inappropriate and can exacerbate certain diseases for example cancer, arthritis and asthma. Traditionally inhibition has been sought by blocking chemokine receptors with antagonists, but we have found useful molecules by inhibiting functional cell migration – with great success. Due to their role in initiating inflammation chemokines are therefore a good target for anti-inflammatory drugs – for example BSCIs. C S L C S FX97L is a 40 pM BSCI.1 The Q motif is mimicked by a caprolactam which retains the amide and has been found to be a successful pharmacological component. chemokine inhibition Q However, it has been discovered that BSCIs do not bind to chemokine receptors but to the sstr2 receptor for somatostatin. F N A HH O N D F C S WSomatostatin S C 14 K S T T F Q K NH O K Somatostatin is a peptide involved in growth hormone (GH) regulation.2 FX97L 40 pM BSCI G An example ligand based motif. of on O O S N H N H HN It is a cyclic peptide with the critical motif being KWF.3 K I NR58-3.14.3 W P We would not have discovered Broad-Spectrum Chemokine Inhibitors (BSCIs) using a receptor antagonist approach as our functional screening approach has discovered a new biological target for anti-inflammatory drug design – the sstr2 receptor. O O an sstr2 the KWF. O NH H O H2N sstr2 ligand based on WKF critical motif GH regulation The sstr2 receptor therefore displays functional selectivity – when somatostatin is bound GH is affected but when BSCIs are bound chemokines are affected.4 Functional selectivity is the ability for a receptor to have different functions depending on the molecule to which it is bound. somatostatin BSCIs sstr2 receptor sstr2 receptor sstr2 receptor sstr2 receptor sstr2 receptor GH regulated? GH regulated O H N O O O S O O 'anti-inflammatory' binding site Growth Hormone regulation binding site N S O O NH2 HN Growth Hormone regulation binding site 'anti-inflammatory' binding site O O N H N OO S O O HN N H 'anti-inflammatory' binding site BSCIs to investigate the important part of the molecules for tipping sstr2 from GH to BSCI function. O 1 HN 2 HN 3 HN O NH O NH 5 O NH 6 HN NH 7 HN 8 HN O O O NH F Somatostatin 14 F O S O N O S O O S O N O S O N O S O N OO O S O H N N O O OH + O O S Cl H N O O O S N 1) Et3N OH W N O S O 3) HCl/dioxane + ClH3N H O O O H N HN OH N O S O 1) HATU, Et3N NH 2) H2/Pd/C 4) 4-ClSO2C6H4COOH, Et3N F analogue, 9 HO HN O O O NH H N H N NHBoc O OH H N 1) HATU, Et3N, R-NH2 2) MeSO2OH H N NH2 O O NHH NH2 O NH FQ analogue, 10 H N NH2 O NH NH2 9 or 10 O CbzHN KW analogue, 11 CbzHN KW analogue, 12 W analogue, 13 1) HATU, Et3N, amines 11, 12, 13 or 14 (commerically available) W analogue, 14 2) Pd,C, H2 OO OO HN NH NH HN K 'anti-inflammatory' binding site Growth Hormone regulation binding site The smaller BSCIs such as FX97L or a benzoyl analogue are non-competitive in their binding with regards to somatostatin. A series of benzoyl amino lactams were synthesised with different length alkyl chains to determine the point at which they start becoming competitive with somatostatin. 'anti-inflammatory' binding site sstr2 sstr2 N O 1) Boc2O, Na2CO3 N H H N OBn 2) BnBr, KOH OH O O O S O BSCI analogue (WFQ) O N H N HN Hybrid? (KWFQ) O O O S O HN HN Somatostatin analogue (KWF) sstr2 T Growth Hormone regulation binding site N Growth Hormone regulation binding site S S S F O NH 'anti-inflammatory' binding site T NH HN 'anti-inflammatory' binding site C N O 4 HN O O O NH NH O NH O NH O K NH NH NH NH HN A G O O NH Binding: Competitive or non-competitive H2N O H2N H2N HN OO sstr2 C H2N S O O Growth Hormone regulation binding site sstr2 The aim of my project is to synthesise a catalogue of molecules analogous to both somatostatin and OO N H Growth Hormone regulation binding site sstr2 N NH N H NH3 sstr2 O OO N H NH3 H N R N H N H NH3 O H N R N chemokines regulated? chemokines regulated O N H GH and chemokines regulated? The larger BSCIs such as BN83250 are competitive in their binding with regards to somatostatin however. n n H N O H N O NH O NH O To determine the competitive nature of the ligands they will be subjected to an sstr2 binding assay measuring the percentage displacement of somatostatin and a GH regulation assay. To determine their abilities as BSCIs they will be subjected to an in vitro leukocyte migration assay and an in vivo anti-inflammatory activity assay. compounds 1 - 8 1. D. J. Fox, J. Reckless, H. Lingard, S. Warren and D. J. Grainger, J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52, 3591-35 2. B. A. Hay, B. M. Cole, F. DiCapua, G. W. Kirk, M. C. Murray, R. A. Nardone, D. J. Pelletier, A. P. Ricketts, A. S. Robertson and T. W. Siegel, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2001, 11, 2731-2734. 3. D. J. Fox, J. Reckless, S. M. Wilbert, I. Greig, S. Warren and D. J. Grainger, J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48, 867874. 4. A. Schonbrunn, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 2008, 286, 35-39.