Document 13657385
advertisement

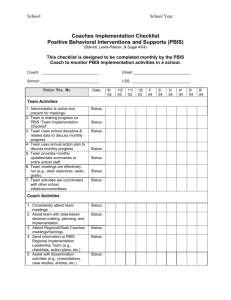
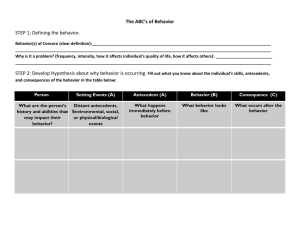
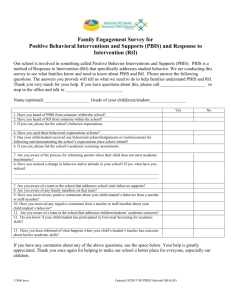
s, Roots, PBIS: Myth o n s, & Misconcepti ls Fundamenta www.pbis.org George Sugai OSEP Center on PBIS Center for Behavioral Educa9on & Research University of Connec9cut August 19 2014 www.cber.org www.pbis.org www.cber.org 9:00-9:45 PU R P OSE is to tation n e s e r BIS his p n of P se of t Purpo nce precisio iewing key enha text by rev tation PBIS in con n e m imple res of lture e featu limate & cu r o c r o ool c of sch SWPBS is about establishing capacity for…. te? hool clima c s e v i9 s o What is p !! you see it id d r o t i l e Did you fe Improving classroom & school climate Integra9ng academic & behavior ini9a9ves Improving support for students w/ EBD Decreasing reac9ve management Maximizing academic achievement 1 Coercive Cycle Effec9ve Organiza9ons Common Language SCHOOL: Nega9ve School Climate Nega9ve School Climate • Non-­‐compliance & non-­‐ coopera9on • Disrespect • Teasing, harassment, & in9mida9on • Disengagement & withdrawal • NonaZendance, tardy, & truancy • Violent/aggressive behavior • LiZering, graffi9, & vandalism • Substance use School Climate Common Experience KID: Common Vision/Values • Reac9ve management • Exclusionary disciplinary prac9ces • Informal social skills instruc9on • Poor implementa9on fidelity of effec9ve prac9ces • Inefficient organiza9on support • Poor leadership prepara9on • Non-­‐data-­‐based decision making • Inefficient, ineffec9ve instruc9on • Nega9ve adult role models Quality Leadership Posi9ve Reinforcement Cycle SCHOOL: KID: Posi9ve School Climate Posi9ve School Climate • Posi9ve > nega9ve contacts • Predictable, consistent, & equitable treatment • Challenging academic success • Adults modeling expected behavior • Recogni9on & acknowledgement • Opportunity to learn • Safe learning environment • Academic & social engagement • Compliance & coopera9on • Respect & responsibility • Posi9ve peer & adult interac9ons • Engagement & par9cipa9on • AZendance & punctuality • Anger & conflict management • Safe & clean environment • Healthy food & substance use • Self-­‐management behavior How to jumpstart change? (-­‐) S.C. ?????? (-­‐) student behavior Coercive Cycle (-­‐) S.C. ?????? ?????? (+) (+) student behavior S.C. ?????? (+) S.C. Positive Reinforcement Cycle What’s What’s it itgonna gonna take taketotoshift shiftfrom….. to….. Positive School Climate Investment in best evidence-­‐based prac9ces Data-­‐based decisions Cultural & contextual considera9on Sound theory Teaching behavior explicitly , o& ol l xplicitoo ise, Prec 9v veee SScct hh NPeogsai9 efficien ? e t 9on aate lilim ta men implCCem capacity Mul9-­‐9ered approach Ac9ve, par9cipatory leadership ory Sound the kit Basic tool Strategic long term implementa9on investment 2 are much How illing to you w your n bet o n? io decis THEORY OF ACTION “Roadmap of Causal Pathway” are much How illing to you w your n bet o n? io decis “Addressing X with Y has high probability of producing Z” X Data-­‐based Ques9on Z Desired Outcomes “To achieve X, we should do Y” THEORY OF ACTION “Behavior Example” Behavior is learned Z “Posi9ve School Climate” Se6ng Condi8ons Antecedents . . . . . . . Suspension & expulsions NOT Equal STUDENT BEHAVIOR Disability Consequences ADULT BEHAVIOR OUTCOMES • Bullying behavior • In school deten9on • Dropping out • Non-­‐compliance • Out of school suspension • School failure • Social w/drawal • Substance use • Weapon possession Bullying Consequences • Dispropor8onality • Law/norm viola9ons Restraint & seclusion Behaviors • Office referral • Truancy Dispropor9onality & Equity Enhance environment to influence & teach behavior • Aggression • Insubordina9on orm School Ref ntext Co Problem Delinquency School comple9on & dropping out Antecedents Behaviors Under-­‐ achievement Behavior is lawful, therefore understandable & influence-­‐able Behavior Analysis Biology is important Y “Teach & acknowledge 3-­‐5 Behavioral Expecta9ons” School violence Behavior & environment are func9onal related George’s (PBIS) Theory of Action “Addressing X with Y has high probability of producing Z” “To achieve X, we should do Y” Substance use Z “Improved phonemic awareness” “To achieve X, we should do Y” Y “Explicitly teach & acknowledge leZer-­‐ sound associa9on” X “Reduce use of reac9ve management” School Climate “Addressing X with Y has high probability of producing Z” X “Enhance early reading” Y Evidence-­‐based Strategy are much How illing to you w your n bet o n? io decis THEORY OF ACTION “Literacy Example” • Harassment • Self-­‐injury • • Proba9on & parole • Arrests & incarcera9on • Restraint & seclusion • Mental health referral • Mental illness • School-­‐to-­‐prison pipeline • Achievement gap • Unemployment • Delinquency • • Apply Behavior Analytic Logic 3 ! CONTEXT CONDITIONS RISK • • • • • • • • • • • Se6ng Antecedents Condi8ons Se6ng Condi8ons PREVENTIVE-PROTECTIVES Hunger Chronic illness Disability Race Gender Violence & trauma exposure Unemployment Gangs Substance use Mental illness • • • • • • • • Employment Physical health Recreation Healthy diet Preschool Literacy exposure Safe neighborhoods Positive role models STUDENT BEHAVIOR • • • • • • • • • • • • • Antecedents Student Behaviors • • • • • • • • • Aggression Bullying behavior Non-compliance Insubordination Social w/drawal Truancy Law/norm violations Substance use Weapon possession Harassment Self-injury Problem solving Conflict & anger management Asking for assistance Communicating feelings Literacy Self-management skills Managing bullying behavior • • ADULT BEHAVIOR • • • Office referral In school detention Out of school suspension Probation & parole Arrests & incarceration Restraint & seclusion Mental health referral • • • • • • STUDENT OUTCOME • • • • • Disproportionality Dropping out School failure Mental illness School-to-prison pipeline Achievement gap Unemployment Delinquency • • • • • Consequences Adult Behaviors Teach, supervise, reinforce Active supervision Check in check out Function-based support Positive reinforcement Precorrection Opportunity to respond Generalization training Data-based decision making • • • • • • • • • Consequences • • • • • • • • • Postsecondary education Employment Family Recreation & leisure activities Physical & mental health Positive peer group Safe neighborhood A bit o f review port? ms of Sup e t s y S d e r Mul9-­‐9e ents for all stud s s e c c u s Planning • • ! IMPLEMENTATION W/ FIDELITY CONTINUUM OF CONTINUOUS EVIDENCE-BASED PROGRESS INTERVENTIONS MONITORING UNIVERSAL SCREENING CORE FEATURES MTSS/PBIS DATA-BASED DECISION MAKING & PROBLEM SOLVING CONTINUUM OF SCHOOL-WIDE INSTRUCTIONAL & POSITIVE BEHAVIOR SUPPORT CONTENT EXPERTISE & FLUENCY PBIS (aka SWPBS, MTBF) Framework for enhancing adop9on & implementa9on of of evidence-­‐based Continuum interven9ons to achieve & behaviorally Academically important outcomes for TEAM-BASED IMPLEMENTATION FEW ~5% ~15% SOME Primary Prevention: School-/ClassroomWide Systems for All Students, Staff, & Settings ALL Tertiary Prevention: Specialized Individualized Systems for Students with High-Risk Behavior Secondary Prevention: Specialized Group Systems for Students with At-Risk Behavior students All Intensive Targeted Universal Few Some Con9nuum of Support for All All ~80% of Students Dec 7, 2007 4 Be ha vio rS up po rt Continuum of Support for ALL: “Molcom” Anger man. Intensive Prob Sol. Targeted Technology Intensive __________ Targeted __________ _________ Ind. play Adult rel. Self-assess ________ _______ Universal Homework Coop play _________ ________ Attend. Universal Con9nuum of Support for ALL: “________” __________ ___________ Peer interac _________ Dec 7, 2007 Label behavior…..not kids _________ Dec 7, 2007 Prac9ce Feedback Engagement Precision TERTIARY PREVENTION • Multi-disciplinary team w/ behavior expertise • Function-based behavior support • Wraparound, culture-driven, person-centered supports & planning • School mental health • Continuous monitoring of progress & implementation fidelity • Increased precorrection, supervision, reinforcement SECONDARY PREVENTION • Team-led implementation w/ behavior expertise • Increased social skills instruction, practice • Increased supervision & precorrection • Increased opportunities for reinforcement • Continuous progress monitoring • PRIMARY PREVENTION • Team-led implementation • Behavior priority • Social behavior expectations • SW & CW teaching & encouraging of expectations • Consistency in responding to problem behavior • Data-based decision making Teamwork SWPBS: Core Practice Features ecision Data for d making? ac:ons le b a d n e f De 1. Specify/define need Data-­‐based Decision Making 2. Select right evidence-­‐ based solu9on Data used to….. 3. Monitor implementa9on fidelity 4. Monitor progress y or Capacit f n o 9 a t n Impleme Building rivers hases & d p n o : a t n Impleme 5. Improve implementa9on 5 Effec9ve Organiza9ons Effec9ve Organiza9ons Common Language Common Experience “Organiza9ons are groups of individuals whose collec9ve behaviors are directed toward a common goal & maintained by a common outcome” MTSS & School Climate (Skinner, 1953, Science of Human Behavior) Common Vision/Values Common vision & objec9ves Common language Common experiences & rou9nes Quality leadership & coaching Quality Leadership Implementa9on Drivers State Team District School Funding* General Implementa9on Process Visibility*&* Dissemina4on* Policy*&* Systems* Alignment* Poli4cal* Support* Students Agreements Staff Principal, Superintendent Data-based Action Plan “Plan” = Coaching Evaluation “Check” Personnel* Selec4on* LEADERSHIP*TEAM* Coordina4on,*Readiness,*Priority* Professional* Development* Implementation “Do” Coaching*&* Technical* Assistance* Evalua4on*&* Performance* Feedback* Content* Exper4se* Local*Implementa4on*Demonstra4ons* All Staff, Students, Administrators Stages of Implementa9on Basic MTBF Implementa9on Framework Regional/State Leadership • SWPBS prac9ces, data, systems • Policy, funding, leadership, priority, agreement District Behavior Team Internal Coaching Support School Behavior Team • 2 yr. ac9on plan • Data plan • Leadership • Team mee9ng schedule External Coaching Support • SWPBS • CWPBS • Small group • Individual student School Staff Student Benefit • Academic • Expecta9ons & rou9nes • Social skills • Self-­‐management • • • • • • Explora9on Installa9on Ini9al Implementa9on Full Implementa9on Innova9on Sustainability 2–4 Years Team Support Fixsen, Naoom, Blase, Friedman, & Wallace, 2005 6 ALL STAFF engage in…. General Phases, Activities, & Outcomes of Implementation • Teaching, promp9ng, acknowledgement of posi9ve behavior • Precorrec9ve ac9ve supervision • Consistent & predictable processing of rule viola9ons • Greater posi9ve than nega9ve contacts & interac9ons Phase 1 Explora9on & Adop9on Phase 2 Ini9al Implementa9on * Document SC DISTRICT priority Phase 3 Full Implementa9on * Establish school * Document SC PRINCIPAL behavior leadership priority * Develop/implement team ac9on plan for SW * Document SC STAFF * Establish school implementa9on priority behavior coach * M onitor implementa9on * Secure staff agreement fidelity & student See Readiness Checklist progress * Par9cipate training for SW & CW * Develop/implement ac9on plan for * Develop/implement specialized behavior ac9on plan, including support data system SC = School Climate SW = School-Wide CW = Classroom-Wide Expected Outcomes STUDENTS…. STAFF Expected Outcomes • Learn SW & CW behavioral expecta9ons • Increase posi9ve social & self-­‐management skills • Increase posi9ve peer-­‐peer & peer-­‐adult contacts • Increase academic engagement & aZendance • Decrease problem behavior discipline referrals, & suspensions STUDENTS PHYSICAL & SOCIAL CLIMATE PHYSICAL & SOCIAL CLIMATE perceived as…. • Safer • More predictable • More posi9ve • More responsive Readiness avior h e b l ia c o s Teaching explicitly? behavior ic m e d a c Like a Teaching calcula9ng hypotenuse of triangle “Work w/ another for4 partner & ADJUST do these Efficiency examples….” “C2 = A2 + B2 where DEFINE C is side opposite rightSimply angle….” “I noticed that everyone gotMONITOR #1 & #3 & “Watch me,…If A = 3 correct. #2ACKNOWLEDGE was tricky & B = 4,MODEL then C2 = Continuously because no right 25, & C = 5….” angle….” “Work w/ your partner & calculate hypotenuse PRACTICE of triangle for these 3 In Setting examples……” Teaching social behaviors like academic skills “You got it. Tomorrow let’s for figure out howADJUST to handle Efficiency cyber-teasing.” “If someone won’t stop teasing your friend, you DEFINE should look cool & walk Simply away w/ your friend…” “That was great. What would that look like if MONITOR you were stuck on the& “Watch. This is how I ACKNOWLEDGE MODEL bus? In the would do it at a Continuously classroom?” concert.” “Tell me how you would do it if you were in PRACTICE hallway.”In“At school Setting dance.” 7 Culture = Culture & g in r e id s Co n Context? istory h g in n r a e L Group of individuals Overt/verbal behavior Flexible, dynamic, & changed/shaped over 9me & across genera9ons & setng. Collec9on of learned behaviors, maintained by Shared learning history similar social & environmental con9ngencies Differen9ates 1 group from others Predic9ng future behavior Sugai, O’Keeffe, & Fallon 2012 Poten9al for cultural exchange & conflict 1. School establishes policy for norm viola9ng behavior 2. Kid caught engaging in norm-­‐ viola9ng behavior Student Teacher Community Family Administrator 3. Educator opts to complete discipline referral 4. Administrator opts to formalize incident ODR Data Point Se6ng Condi8ons Antecedents Policy makers Behaviors 4 a9ons! e consid r Consequences Antecedent Administrator Antecedent Behavior Behavior Consequence Educator Antecedent Behavior Antecedent Consequence Student CONCLUS ION Educator Consequence Behavior Antecedent Consequence Behavior Administrator Consequence 8 Supporting Important Culturally Equitable Academic & Social Behavior Competence Cultural/Context Considera8ons Supporting Culturally Valid Decision Making Start w/ effec9ve, efficient, & relevant, doable ST EM S S ST EM SY TA DA Supporting Culturally Knowledgeable Staff Behavior PRACTICES Implementation Fidelity PRACTICES Vincent, Randall, Cartledge, Tobin, & Swain-Bradway 2011; Sugai, O’Keeffe, & Fallon, 2012ab BASIC PBIS LOGIC TA DA OUTCOMES SY SWPBS emphasis Supporting Culturally Relevant Evidence-based Interventions Prepare & support implementa9on Training + Coaching + Evaluation Maximum Student Outcomes Improve “Fit” 9