Summary Lecture 3 Image by MIT OCW.

Summary Lecture 3
Image by MIT OCW.
L4: Cooperativity & introduction
λ phage model
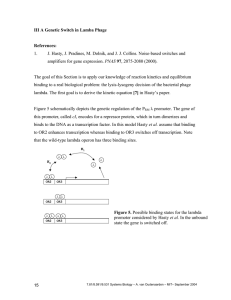
λ phage model (Hasty et al.) as example for applying mass action law.
K
2
λ λ
λ λ
OR2 OR3
λ λ
OR2 OR3
λ λ λ λ
OR2 OR3 biology
K
1
λ
λ
2X ←
K
1
X
2 most important step in modeling !!
D + X
2
←
K
2
D + X
2
←
K
3
DX
2
DX
*
2 most important
DX
2
+
DX
2
X
+
⎯ k d
P
X
2
←
K
4
DX
2
DX
2
⎯ k t
DX
2
+ P + nX
A step in modeling !!
math fast slow
2X ←
K
1
D + X
2
←
K
2
X
2
DX
2
D + X
2
←
K
3
DX
*
2
DX
2
+
DX
2
X
+
⎯ k d
P
X
2
←
K
4
DX
2
DX
2
⎯ k t
DX
2
+ P + nX
A mass action dx dt
σ
σ
1
2
=
=
=
1 + (1 + σ
1
)x
2
K
3
K
2
K
4
K
2
α x
2
+ σ
2 x
4 constants
− γ x + 1 relative binding
α
γ
=
= nk t p r
0 d
T r k d
K
1
K
2
~ synthesis/basal rate
~ degradation/basal rate choose elegant (dimensionless, relative) variables !
graphical stability analysis
How to experimentally verify these ideas ?
Synthetic Biology
Build your own designed network ‘from scratch’ and test your model
Examples for synthetic genetic switches:
Isaacs et al.
Prediction and measurement of an autoregulatory genetic module. PNAS 100 , 7714 (2003)
Gardner et al.
Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature 403 , 399 (2000)
First a short intro on ‘Genetic Engineering’
Toolbox of the genetic engineer:
1. Restriction enzymes
2. Plasmids
3. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
4. Fluorescent proteins