Document 13612091
advertisement

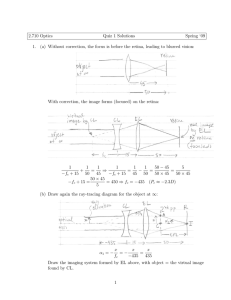
2.71 Optics Quiz 1 Solutions Spring ‘09 1. (a) Solution: Without correction, the focus is before the retina, leading to blurred vision: With correction, the image forms (focused) on the retina: 1 1 1 1 1 1 50 − 45 5 + = ⇒ = − = = −fc + 15 50 45 −fc + 15 45 50 50 × 45 50 × 45 50 × 45 −fc + 15 = = 450 ⇒ fc = −435 (Pc ≈ −2.3D) 5 (b) Solution: Draw again the ray-tracing diagram for the object at ∞: x x x =− = fc −435 435 Draw the imaging system formed by EL above, with object = the virtual image found by CL. α1 = − 1 Angular magnification MA = − 450 = −9 50 ⇒ α2 = −9 · α1 = − 9x x = − 1 435 48 3 From �ICA (see diagram on previous page), x = tan α2 = α2 (paraxial approximation) EFL x 1 = 1 ⇒ EFL = 48 3 48 3 (c) 1st method: Using the 2nd PP and EFL 1 xi = α · (EFL) = 48 α 3 2nd method: Using the imaging condition 2 x0 = αfc = −435α The lateral magnification of EL’s imaging system (with the virtual image formed by CL as the object and real image formed on the retina) is given by: 50 1 1 = − ⇒ xi = ML x0 = − · (−435α) 9 9 450 435 1 = α = 48 α ⇒ Image is erect. 9 3 ML = − (d) Solution: Use the eye’s pupil as the object and flip the optical system for proper ray-tracing. 1 1 1 15 × 435 + = ⇒z=− 15 z −435 450 ∴ virtual image created as shown x�p z 435 87 = ML = − = = xp 15 450 90 The myopic person’s eyes appear smaller and erect. 2. (a) Solution: First consider an on-axis point at the object plane. NA = a f1 Clearly, S1 limits the angle of acceptance, so S1 is the Aperture Stop. Now consider the chief ray from an off-axis point object. 3 FOV = a2 ff12 f1 = a2 f2 Clearly, S2 limits the chief ray if the point object elevation off-axis becomes suf­ ficiently large, so S2 is the Field Stop. (b) Solution: Entrance Pupil: image S1 through L1 ⇒ ∞ to the left Exit Pupil: image S1 through L2 ⇒ ∞ to the right Entrance Window: image S2 through L2, L1 ⇒ object plane Exit Window: ⇒ collocated with S2 So the completely annotated system is: (c) Solution: Numerical Aperture & Field of View a1 f1 From Figure 2, S2 is imaged through L2, L1 onto the object plane. The lateral magnification is found as follows: From Figure 1, the angle of acceptance is NA = � �� a2 f � a2 � a2 f 1 � � FOV = � � = 2 = f1 f1 f2 ���� limiting angle of the chief ray 4 (half-field) MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.71 / 2.710 Optics Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.