Document 13600719
advertisement

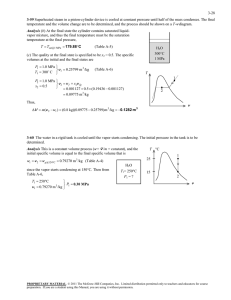
22.31411.5612.084113.14Fall 2006 Problem Set VI Due 10126106 his problem i l l u s t r a t e s a mechanism by which c l a d stresses can be reduced during up-power ramps by approaching f u l l power a t a slower rate. 1. Geometry (20°C) The c l a d outside diameter i s 11.2 nun; and t h e c l a d thickness i s 0.7 mm. 2. Clad Material Properties (assumed constant) Young's Modulus Poisson's Ratio C o e f f i c i e n t o f Thermal Expansion ;9 = c l a d creep r a t e (sl.) . where a has the u n i t s MPa. 9 3. Operating Conditions . = 76 GPa; = 0.25; = 6.7 m1m.K; and = (1 x 10-9)ag; - A t h o t zero power, the c l a d i s a t 280°C. t h e coolant pressure i s 15.5 MPa, t h e gas pressure i n s i d e the rod i s 5.4 MPa, and the clad i s touching t h e f u e l w i t h zero contact pressure. A t h o t f u l l power the coolant and gas pressures are unchanged, the average c l a d temperature i s 375'C, and t h e r a d i a l displacement o f t h e o u t e r surface o f the f u e l has increased by 35 run. Consider two cases: - An up-power - An up-power 4. ramp from zero t o f u l l power i n 30 minutes; r i i p from zero t o f u l l power i n 30 hours. Calculational Basis - Use a s i n g l e r i n g t o represent t h e c l a d - Consider t h a t t h e r a d i a l d e f l e c t i o n a t the f u e l outer surface and the c l a d average temperature vary l i n e a r l y w i t h time during each up-power ramp. - Use only e l a s t i c , thermal, and creep s t r a i n s . s t r a i n s equal zero a t h o t zero power. - Use zero a x i a l f o r c e from f u e l - c l a d contact. L e t the creep 5. Questions Obtain t h e following quantities upon reaching f u l l power i n each uppower ramp: ., - c l a d stress; - clad strain; - radial and displacement a t the c l a d o u t e r surface.