P E
advertisement

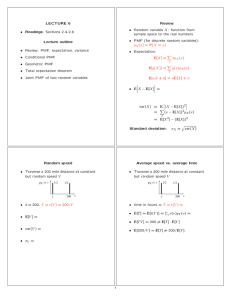
LECTURE 6
Review
• Random variable X: function from
sample space to the real numbers
• Readings: Sections 2.4-2.6
• PMF (for discrete random variables):
pX (x) = P(X = x)
Lecture outline
• Review: PMF, expectation, variance
• Expectation:
• Conditional PMF
E[X] =
• Geometric PMF
E[g(X)] =
• Total expectation theorem
!
x
!
x
• Joint PMF of two random variables
xpX (x)
g(x)pX (x)
E[αX + β] = αE[X] + β
"
#
• E X − E[X] =
$
var(X) = E (X − E[X])2
=
!
x
%
(x − E[X])2pX (x)
= E[X 2] − (E[X])2
Standard deviation:
σX =
&
var(X)
Random speed
Average speed vs. average time
• Traverse a 200 mile distance at constant
but random speed V
• Traverse a 200 mile distance at constant
but random speed V
1/2
pV (v )
1
200
1/2
pV (v )
1/2
v
1
• d = 200, T = t(V ) = 200/V
1/2
200
v
• time in hours = T = t(V ) =
• E[T ] = E[t(V )] =
• E[V ] =
'
v t(v)pV (v) =
• E[T V ] = 200 =
" E[T ] · E[V ]
• var(V ) =
• E[200/V ] = E[T ] "= 200/E[V ].
• σV =
1
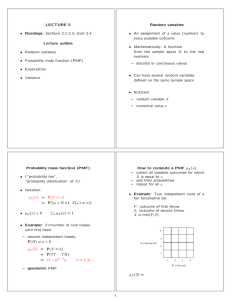
Conditional PMF and expectation
Geometric PMF
• X: number of independent coin tosses
until first head
• pX|A(x) = P(X = x | A)
• E[X | A] =
!
x
xpX |A(x)
pX (k) = (1 − p)k−1p,
pX (x )
∞
!
E[X] =
k = 1, 2, . . .
∞
!
kpX (k) =
k=1
k=1
k(1 − p)k−1p
• Memoryless property: Given that X > 2,
the r.v. X − 2 has same geometric PMF
1/4
p
pX (k)
pX |X>2(k)
p(1-p)2
1
2
3
4
p
x
...
• Let A = {X ≥ 2}
...
k
1
k
3
pX- 2|X>2(k)
pX|A(x) =
p
E[X | A] =
...
k
1
Total Expectation theorem
Joint PMFs
• Partition of sample space
into disjoint events A1, A2, . . . , An
• pX,Y (x, y) = P(X = x and Y = y)
y
A1
4
1/20 2/20 2/20
3
2/20 4/20 1/20 2/20
2
1/20 3/20 1/20
1
1/20
B
A2
A3
1
P(B) = P(A1)P(B | A1)+· · ·+P(An)P(B | An)
•
pX (x) = P(A1)pX |A1 (x)+· · ·+P(An)pX |An (x)
!!
x
y
2
3
4
x
pX,Y (x, y) =
!
E[X] = P(A1)E[X | A1]+· · ·+P(An)E[X | An]
• pX (x) =
• Geometric example:
A1 : {X = 1}, A2 : {X > 1}
• pX |Y (x | y) = P(X = x | Y = y) =
E[X] =
P(X = 1)E[X | X = 1]
+P(X > 1)E[X | X > 1]
•
• Solve to get E[X] = 1/p
2
!
x
y
pX,Y (x, y)
pX |Y (x | y) =
pX,Y (x, y)
pY (y)
MIT OpenCourseWare
http://ocw.mit.edu
6.041 / 6.431 Probabilistic Systems Analysis and Applied Probability
Fall 2010
For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.