Design of an ESD Core Methodology Subject February 7, 2007
advertisement

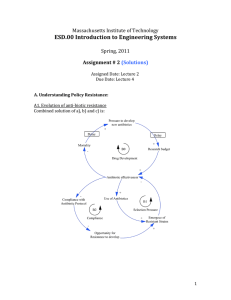
Design of an ESD Core Methodology Subject February 7, 2007 Dick Larson, Dan Frey, with Roy Welsch Engineering Systems: At the intersection of Engineering, Management & Social Sciences Social Sciences Management ESD Engineering 2 For the new Methods subject We want to educate doctoral students to conduct research on these types of large scale engineering projects, which fall at the intersection of traditional engineering, management and social sciences ESD.86 Models, Data, Inference for Socio-Technical Systems (New) Prereq: ESD.83, 6.041 G (Spring) 3-0-9 Use data and systems knowledge to build models of complex sociotechnical systems for improved system design and decision-making. Enhance model-building skills, including: review and extension of functions of random variables, Poisson processes, and Markov processes. Move from applied probability to statistics via Chi-squared t and f tests, derived as functions of random variables. Review classical statistics, hypothesis tests, regression, correlation and causation, simple data mining techniques, and Bayesian vs. classical statistics. Class project. Enrollment limited to 25 students. Preference given to ESD Ph.D. Students. Richard C. Larson, Daniel D. Frey Overview > A new QUANTITATIVE methods subject, with aspects of each of three disciplinary areas: Engineering, Management and Social Science. > To be required of 1st year ESD Ph.D. students, spring semester > There will be another new subject on QUALITATIVE methods. 5 More Overview > In ESD tradition, the ‘math part’ would be augmented with reading assignments and discussions tracing the history and application of each of the major concepts discussed and developed. > There would be a term project for each student. > There would be computer-based as well as paper-based homework assignments. The subject would be rigorous. > While a byproduct would be continued ‘class bonding’ of the first year doctoral students, the primary focus is on intellectual content. 6 This is a Knowledge Requirement > For students whose academic plan is to take MIT subjects that go much deeper than this subject (in statistics, probability, quantitative research methods), the requirement for taking this subject can be waived. > This subject represents a 'knowledge requirement' that will be assumed on doctoral general exams. 7 Building from… > Subject will have an enforceable prerequisite: 6.041 or equivalent. > It will leverage all the fine work that Dan Frey has done with SOE curriculum development grant support -- funded in response to the oft-cited ‘Odoni report’ on the lack of a good solid engineering-focused statistics subject in the SOE. > But, this is NOT a statistics subject! 8 An ESD Service Subject > If we are successful, we should attract students from elsewhere in the SOE who are not associated with ESD. > This should be ESD's first 'service subject.’ > Tentatively, the 2007 spring semester new subject will be teamtaught by Dan Frey and yours truly, with a cameo by Roy Welsch. 9 Subject Operates Along Parallel Tracks Lectures, Problem Sets, Tutorials Readings: Historical Context, including Cases Computer-Based Exercises Media Project Term Project 10 Fundamentals, via Sample Space Approach > Start with constructing probabilistic models using functions of random variables with a sample space approach. > Then we slide into statistics via experimental design with threats to validity, saying in essence that all designs are compromised by one or more of these. > Then, the statistical part should be a continuum of the sample space applied probability treatment so everything is fundamental -- no memorization of weird stat formulas, just for the sake of memorization. > We will do more with less in the stats area. > We cover Bayesian as well as classical statistics, highlighting the philosophy, strengths and weaknesses of each. > If they want a true stats course, that would follow this course. 11 Want students to be able to work with ‘blank sheets of paper.’ They know fundamentals and can derive results. They are not just users of computer routines. 12 Go Deep, Use all Available Subjects > We cannot think that ESD is so unique that no other MIT subjects can contribute to ESD students' knowledge of 'methods.' In the course of an ESD doctoral student's studies, she/he will rely most often on existing subjects at MIT or perhaps Harvard to go deep in the required methods. 13 Model Building > Model building, based on empirical evidence and axiomatic conjectures, should be the emphasis for the new subject. > We are not creating a new subject in applied probability nor are we creating one in statistics. But we use both to obtain our objective. > The focus is more on model synthesis, not data analysis per se. > It is an active model creating focus, not a passive critical social science focus. > Axiomatic models would be emphasized more than data inferred models, inferred from curve fitting -- where causation and correlation can become confused. 14 Introduce New Ideas in Homework > Stochastic Dynamic Programming, Real Options, via Sequential Decision Trees > Shannon measure of information, Entropy (the element of ‘surprise’) $67,200 Mold .4 $34,080 > Derivation of certain $41,280 Storm statistical tests No Mold $12,000 .6 .5 or $24,000 (F, T, Chi-Squared) $35,640 $42,000 $35,640 $39,240 $39,240 Wait .5 No Storm $37,200 25% .4 .4 .2 20% $36,000 <19% $30,000 Harvest $34,200 $34,200 Figure by MIT OCW. After example by Akinc. 15 Linkages to ‘ilities…” > Reliability – Measures of.. – Systems designs with redundancy > Robustness > Predictability 0,n+1 1 0,1 1,0 2 0,2 0 1n+1 2,0 0,3 n+1 3 3,0 0,n : 3,n+1 4,n+1 n,0 > Stability 2n+1 n n+1,0 Figure by MIT OCW. 16 http://www.mathpages.com/home/kmath336/kmath336_files/image001.gif A Real Null Hypothesis: A Sports ‘.500’ Team > Each game is essentially decided by an independent flip of a fair coin > Track the media coverage as certain expected ‘streaks’ during the year. – Wide use of derived distributions of Max and Min random variables. – Random incidence, potential fallacies in sampling 17 E RT Y L L IB IB Y 19 9 4 IB E RT Y L L 19 9 4 E RT IB E RT Y 19 9 4 E RT Y IB E RT Y L IB L L 19 9 4 IB E RT Y A 4-Game Winning Streak! E RT Y IB E RT 19 9 4 Y 19 9 4 L IB L L 19 9 4 IB E RT Y Streak 19 9 4 19 9 4 19 9 4 Figure by MIT OCW. 18 In a 162 game season, we should not be surprised to see > At least one 7 game loosing streak. :( > At least one 7 game winning streak. :) > All within the null hypothesis that each game is an independent fair coin flip. > But imagine the press coverage of these two events. > Generalize to more important topics. 19 On-Going Student Project > Track media weekly to find media mis-interpretation or misuse of data. – Statistical significance of the media phrase, “If it bleeds, it leads.” – Making inferences based solely on sampling from extremes. 20 http://news.csumb.edu/site/Images/news/headlines.jpg Class Projects The End!