Document 13541390
advertisement

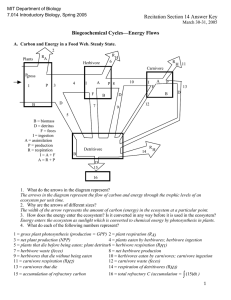
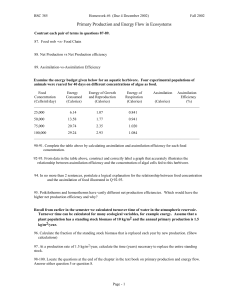
MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 Recitation Section 14 March 30-31, 2005 Biogeochemical Cycles—Energy Flows A. Carbon and Energy in a Food Web. Steady State. 2 Plants R R A H 6 Herbivore R H 11 Carnivore Pgross P 1 4 3 A I F B D 10 P 8 A I 13 B D B 7 P F 9 D 12 5 B = biomass D = detritus F = feces I = ingestion A = assimilation P = production R = respiration I=A+F A=R+P Detritivore 14 B R H D 15 16 1. What do the arrows in the diagram represent? 2. Why are the arrows of different sizes? 3. How does the energy enter the ecosystem? Is it converted in any way before it is used in the ecosystem? 4. What do each of the following numbers represent? 1= 3= 5= 7= 9= 11 = 13 = 15 = 2= 4= 6= 8= 10 = 12 = 14 = 16 = 1 5. Starting with 106 kcal/yr of GPP and given the following values, estimate the values of each of the flows from part 4 assuming steady-state conditions. NPP = 50% For plants : net production efficiency = GPP ingestion production from previous trophic level assimilation = 25% assimilation efficiency = ingestion production = 20% production efficiency = assimilation For the herbivores: exploitation efficiency = = 20% For the carnivores: exploitation efficiency = 90% (no reference) assimilation efficiency = 75% production efficiency = 5% Plants R RA H R Herbivore H Carnivore light Pgross A I P F B B A I P P F B D D D Detritvore R H B D 6. The carbon in respiration (R) flows can be used by other organisms, but the energy in the respiration (R) flows cannot. Both the carbon and energy of all other flows can be used by other organisms. What is different about the R flows? 2 B. Non-Steady State. Now consider the non-steady-state. Suppose you remove 50% of the herbivores at time = A. You then measure the plant-associated flows and find the following: 5 10 kcal/yr 15 (15) 11 (gross plant (gross plant production) production) (12) 10 (7.5) 2 (plant respiration) (6) (5.5) 5 (plant detritus) 5 (2) (1) (2) 4 (herbivore injestion) 0 A B C 1. What is going on? Consider the state of the ecosystem at times B and C. 3