Humid Air Water vapor in air Trace Glasses 1%
advertisement
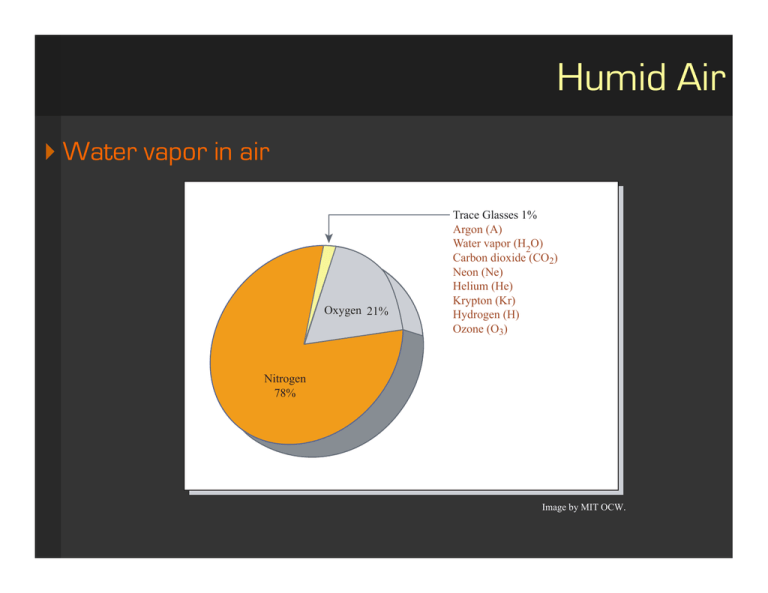
Humid Air Water vapor in air Oxygen 21% Trace Glasses 1% Argon (A) Water vapor (H2O) Carbon dioxide (CO2) Neon (Ne) Helium (He) Krypton (Kr) Hydrogen (H) Ozone (O3) Nitrogen 78% Image by MIT OCW. Humid Air Water vapor in air saturation humidity (SH) (= max AH) moisture content (absolute humidity AH) = kgvapor / kgdry air (partial) vapor pressure [Pa] relative humidity (RH) GAZE wet-and-dry bulb psychrometer ETHER Image by MIT OCW. Humid Air Water vapor in air saturation humidity (SH) (= max AH) moisture content (absolute humidity AH) = kgvapor / kgdry air (partial) vapor pressure [Pa] relative humidity (RH) in [%] wet-and-dry bulb psychrometer enthalpy (H) in [kJ/kg] ­ Sensible heat vs. Latent heat specific volume Humid Air Psychrometric chart absolute humidity AH and saturation line relative humidity RH wet bulb temperature enthalpy specific volume e lin n tio tu ra 16 12 4 0 10 20 40 30 0 bu l b te g) J/k (k m pe ra tu re ( C) 30 80 10 20 30 40 75 0 50 50 00 30 20 40 Dry bulb temperature ( oC) 25 60 50 0.8 70 25 90 0.8 10 0.9 100 P 00 W et 110 0.8 10 20 60 120 0.9 40 15 50 130 0.8 10 20 70 130 50 0.93 /kg) (m 25 120 110 100 90 80 0 0 50 0% 10 % 80 % 60 40% 20% Dry bulb temperature ( o C) o 5 20 8 30 0 24 Absolute humidity (g/kg) 28 Sa (kJ/kg) Image by MIT OCW. Humid Air 50 of nd ou 35 .018 .016 More Latent No Change Heat in Total Heat 25 Less Sensible Heat 20 15 .014 More Sensible Heat % 20 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 o Temperature F 85 90 95 .010 .006 .004 0% 40 .012 .008 No Change in Total Heat Less Latent Heat 35 .020 100 105 110 .002 Pounds of Moisture Per Pound of Dry Air 40 % .022 Absolute Humidity (Humidity Ratio) 10 0% 60 % ir .024 Dr yA .026 40 30 De .028 Pe rP U BT To t al He at ( En th alp y) 45 Cooling P Heating on ati c i if id m u h P Dew Point Temperature Temperature Increase (Vapor to Liquid) or Decrease (Liquid Humidity Increase Relative Humidity Dew Point Amount of condensation heating and cooling dew-point then condensation (de)humidification (adiabatic) enthalpy increase Moisture removed by sorbent or added by evaporation Latent Heat Content Increase Psychrometric processes Vapor) Image by MIT OCW. Feeling comfortable Bruits Noise Couleur Color Eclairage Lighting Pureté l'air Airde purity Humidité de l'air Air humidity Rayonnement solaire Solar radiation Drafts Courants d'air mpérature des surfaces Surfaces temperature Température de l'air Air temperature 0 1 2 3 Factors of thermal comfort Air temperature (sensitive to ΔT > 1°C) 180 160 Heat flux (W) 140 120 100 80 Radiation 60 Conduction 40 Convection Evaporation 20 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 o Temperature ( C) Image by MIT OCW. Factors of thermal comfort Air temperature ΔT between air and building surfaces (MRT) (keep < 3°C) Direct Sunlight Thermal Discomfort Radiant Energy Exchange Direct Sunlight Glare Cold Drafts Image by MIT OCW. Factors of thermal comfort Air temperature ΔT between air and building surfaces (MRT) Air movement (keep < 1.5 m/s unless overheated) Image by MIT OCW. Factors of thermal comfort Air temperature ΔT between air and building surfaces (MRT) Air movement Relative humidity (30% to 65%) Comfort zone Standard Effective Temperature (SET) SET isotherms on psychrometric chart neutral temperature Tn = 17.6 + 0.31 x Tmonth (±2.5°C for comfort) 10 0% 85 AH 80 30 25 75 70 35 40 DBT ( o C) 5 45 50 55 60 15 HOT AND HUMID 65 COLD AND HUMID COLD AND DRY 10 20 20 15 10 COMFORT ZONE HOT AND DRY 5 DRY 25 30 35 40 45 50 Image by MIT OCW. Comfort zone Standard Effective Temperature (SET) SET isotherms on psychrometric chart neutral temperature Tn = 17.6 + 0.31 x Tmonth (±2.5°C for comfort) comfort zone depends on climate 30 40 % Darwin o 0C 10 20 30 40 50 30 15 0% 2 · 0 SET 30 Budapest 10 20 30 40 50 g/kg 20 · 30 22.3 24.8 27.3°C 40 11.5 10 8.5 g/kg 5 · ET 25 o 0C ET 20 -10 0 · 0 SET 3 20 % 10 35 · 10 ET 40 -10 g/kg 10 % 20 50 0 Images by MIT OCW. Comfort zone Standard Effective Temperature (SET) SET isotherms on psychrometric chart neutral temperature Tn = 17.6 + 0.31 x Tmonth (±2.5°C for comfort) comfort zone depends on climate 40 % .022 .020 75 .018 70 .016 65 35 ET 64 o FW SUMMER 55 WINTER 40 45 50 .014 68 o FW 60 ET BU LB % 20 BU LB .010 .008 .006 .004 0% 35 40 45 50 .012 55 60 65 70 75 .002 Pounds of Moisture Per Pound of Dry Air % .024 Absolute Humidity (Humidity Ratio) .026 60 80 .028 85 80% 10 0% Relative Humidity 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 o Temperature F Image by MIT OCW. Comfort zone Standard Effective Temperature (SET) SET isotherms on psychrometric chart neutral temperature Tn = 17.6 + 0.31 x Tmonth (±2.5°C for comfort) comfort zone depends on climate shift with MRT and air movement .018 70 .016 65 .014 Original Location 60 55 35 40 45 % 20 50 .012 .010 .008 .006 .004 o 95 100 105 110 % % .018 .016 65 .014 60 % 20 55 35 40 45 35 40 45 .022 .020 70 Original Location 50 .012 .010 .008 .006 .004 10% Temperature F .024 60 80% 0% 10 75 .002 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 .026 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 o Temperature F 85 90 Absolute Humidity (Humidity Ratio) .020 80 .028 85 40 % 40 75 .022 Pounds of Moisture Per Pound of Dry Air % .024 Absolute Humidity (Humidity Ratio) .026 60 80 Relative Humidity .028 85 80% 0% Relative Humidity 10 .002 10% 95 100 105 110 Image by MIT OCW. Humid Air, Thermal Comfort Reading assignment from Textbook: “Introduction to Architectural Science” by Szokolay: § 1.1.3 + § 1.2 Additional readings relevant to lecture topics: "How Buildings Work" by Allen: Chap 7 + pp. 58 - 60 in Chap 8 "Heating Cooling Lighting" by Lechner: Chap 4


