Document 13479006
advertisement

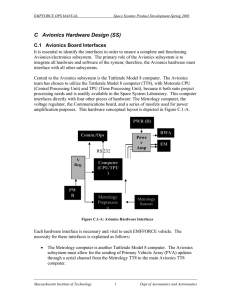
CDIO EMFF Test Bed Design Concept CDIO Space Systems Product Development Databasing Team 21 February 2002 1 Mission Objective z Demonstrate the feasibility of electromagnetic control for formation-flying satellites. z 2-D Flat floor test bed z 3 independent devices z 3 DOF per device Æ Simplifies problem while achieving objective Æ Proves feasibility of planar control Æ Simplifies dynamics Planar control vs. linear control… it takes 3 points to make a plane. Plus, if we can prove controllability for 3 devices, adding more should be… trivial… 2 Requirements Flowdown Mission objective Power Simulated Solar Cells ACDS Actuation EM Shielding Structure Communication Avionics Carriage Ground Comm Power Amp Frictionless mount Inter-device Comm On-board Computer Reaction De-spin Inertial Metrology Omnidirectional Software Signal Conditioning Operations Controller Interface Ground computer Human Flat floor facility 20' x 30' Relative Metrology Separation distance Separation distance: O(10cm)-O(1m) 3 Design Trades z z z z z Mass Cost ($) Time Control accuracy Control precision z z z Electrical power (current, voltage, resistivity) Feasibility B-field 4 Design Concept: Part I z External power source Ç È z Air bearing Ç Ç È È z Bumpers Ç Ç Simplifies problem while achieving objective Not configuration used in space Provides near-frictionless test environment Effective representation of dynamics Cost Requires air supply Safety consideration Low cost Power: Also, can take more data at various power levels. 5 Design Concept: Part II z One electromagnet, reaction wheel assembly per device Ç Ç Ç È z z All circuitry oriented to move with EM package (aligned with field) Ç Shielding using highpermeability materials Ç Ç Permits full range of motion Simplified dynamics Less mass Need more for control of more DOF Reduces magnetic interference with circuits Reduces need for shielding Prevents magnetic interference È Mass vs. cost tradeoff 6 Design Concept: Inter-device Positioning Relative Metrology Infrared Sensors Sonar pseudo-GPS Highly directional Directional Omnidirectional Computer capacity Not functional in space Computer capacity 7 Design Concept Cylindrical Housing Avionics and Communication Rate Gyro Torque Wheel Electromagnet Air Bearing 8 Operations Concept z Human interface via laptop computer Ç Ç Ç È z z Ground/device communication via RF wireless modem Disturbance rejection autonomous; no input required Ç Ç Ç È Familiar to users Portable Supports adequate software packages Not used in actual space mission Applicable to actual operational situation Fast Simulates actual operational situation More complicated avionics 9 Questions? 10