Document 13477874
advertisement

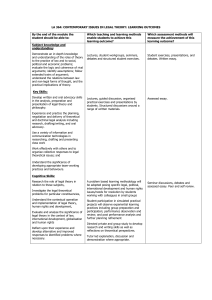
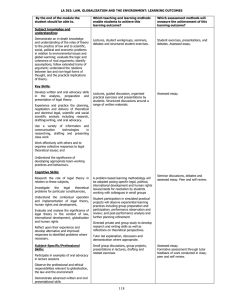
LA 116: INTRODUCTION TO LEGAL THEORY: LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of the module the student should be able to: Which teaching and learning methods enable students to achieve this learning outcome? Which assessment methods will measure the achievement of this learning outcome? Lectures, student workgroups, seminars, debates and structured student exercises. Student exercises, presentations, and debates. Written essay. Lectures, guided discussion, organised practical exercises and presentations by students. Structured discussions around a range of written materials. Assessed essay. Subject knowledge and understanding: Demonstrate an in-depth knowledge and understanding of the roles of theory to the practice of law and to social, political and economic problems; evaluate the logic and coherence of rival arguments; identify assumptions; follow extended trains of argument; understand the relations between law and non-legal forms of thought, and the practical implications of theory. Key Skills: Develop written and oral advocacy skills in the analysis, preparation and presentation of legal theory and philosophy. Experience and practice the planning, negotiation and delivery of theoretical and doctrinal legal analysis including research, drafting/writing, and oral advocacy. Use a variety of information and communication technologies in researching, drafting and presenting class work. Work effectively with others and to organise collective responses to legal theoretical issues; and Understand the significance of developing appropriate team-working practices and behaviours. Cognitive Skills: Research the role of legal theory in relation to these subjects, Investigate the legal theoretical problems for particular constituencies, Understand the contextual operation and implementation of legal theory, human rights and development, Evaluate and analyse the significance of legal theory in the context of law, international development, globalisation and human rights Reflect upon their experience and develop alternative and improved responses to identified problems where necessary. Subject-Specific/Professional Skills: Participate in examples of oral advocacy in lecture sessions Observe the professional and ethical responsibilities relevant to globalisation, the law and the environment A problem based learning methodology will be adopted posing specific legal, political, international development and human rights issues/needs for resolution by students working with colleagues in small groups Seminar discussions, debates and assessed essay. Peer and self review. Student participation in simulated practical projects will observe experiential learning practices including group preparation and participation; performance observation and review; and post performance analysis and further planning refinement Directed private and group study to develop research and writing skills as well as reflections on theoretical perspectives. Tutor led explanation, discussion and demonstration where appropriate. Small group discussions, group projects, presentations in lectures, drafting and related exercises Demonstrate advanced written and oral presentational skills 96 Assessed essay. Formative assessment through tutor feedback of work conducted in class; peer and self review.