Minimum Spanning Tree Introduction to Computers and Programming • Kruskal’s Algorithm
advertisement
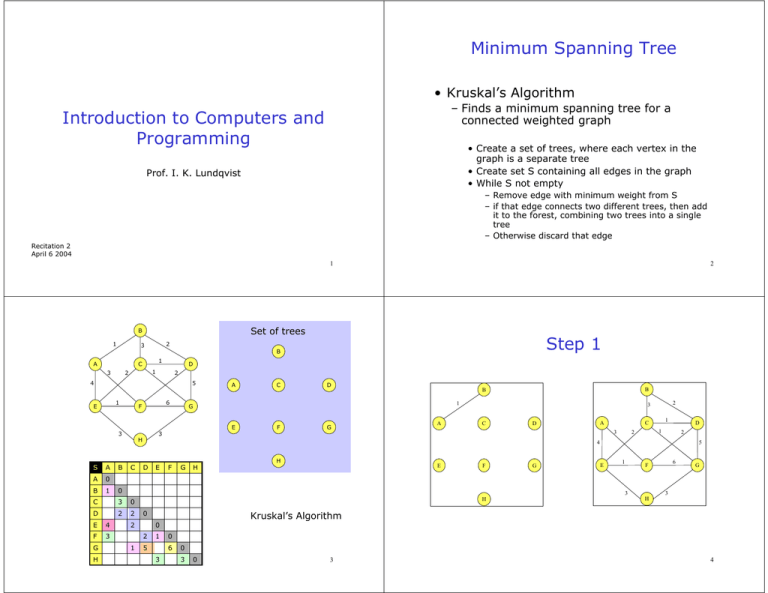
Minimum Spanning Tree
• Kruskal’s Algorithm
– Finds a minimum spanning tree for a
connected weighted graph
Introduction to Computers and
Programming
• Create a set of trees, where each vertex in the
graph is a separate tree
• Create set S containing all edges in the graph
• While S not empty
Prof. I. K. Lundqvist
– Remove edge with minimum weight from S
– if that edge connects two different trees, then add
it to the forest, combining two trees into a single
tree
– Otherwise discard that edge
Recitation 2
April 6 2004
1
Set of trees
B
1
B
1
C
3
D
1
2
2
4
5
1
E
S
A
A
0
B
1
C
D
E
4
F
3
G
H
B
6
F
3
C
A
C
D
B
B
1
G
E
3
H
Step 1
2
3
A
2
F
G
A
C
A
D
2
2
2
2
4
D
E
F
G
H
H
E
F
H
0
2
G
5
E
1
1
5
G
3
H
0
6
3
6
F
Kruskal’s Algorithm
0
2
1
D
1
3
0
1
C
3
0
3
2
3
0
3
0
3
4
Step 2
Step 3
B
B
B
B
1
1
A
C
A
D
A
1
C
3
C
A
D
1
D
1
2
2
3
2
3
C
3
2
D
1
2
2
5
4
5
4
1
1
E
F
E
G
E
6
F
F
E
G
6
F
3
3
G
G
3
H
H
3
H
H
5
6
Step 4
Step 5
B
B
B
1
2
3
A
1
C
D
A
1
1
F
G
E
6
F
3
H
C
1
D
A
2
C
D
2
3
1
5
4
5
4
E
A
D
2
2
2
3
1
C
3
B
E
G
3
1
F
H
H
7
G
E
6
F
3
G
3
H
8
Slide 6
Slide 7
B
B
1
3
1
2
3
2
A
C
1
A
D
C
D
1
2
1
F
4
G
1
C
E
6
F
A
D
1
2
C
D
2
3
5
3
H
A
2
3
E
B
B
4
G
E
3
1
F
G
5
E
H
H
9
Minimum Spanning Tree
10
Prim – Initialization
• Prim’s Algorithm
– Finds a subset of the edges (that form a tree)
including every vertex and the total weight of
all the edges in tree is minimized
• Choose starting vertex
Initialization
• Create the Fringe Set
• Loop until the MST contains all the vertices in the
graph
Body
G
3
3
H
6
F
– Remove edge with minimum weight from Fringe Set
– Add the edge to MST
– Update the Fringe Set
11
• Pick any vertex x as the starting vertex
• Place x in the Minimum Spanning Tree
(MST)
• For each vertex y in the graph that is
adjacent to x
– Add y to the Fringe Set
• For each vertex y in the Fringe Set
– Set weight of y to weight of the edge
connecting y to x
– Set x to be parent of y
12
Prim – Body
Prim’s Algorithm
B
While number of vertices in MST < vertices in
the graph
1
A
Find vertex y with minimum weight in the Fringe Set
Add vertex and the edge x,y to the MST
Remove y from the Fringe Set
For all vertices z adjacent to y that are not in MST
A
1
C
3
MST
2
3
D
1
2
2
5
4
E
1
6
F
Parent
G
A
If z is not in the Fringe Set
3
Add z to the Fringe Set
Set parent to y
Set weight of z to weight of the edge connecting z to y
3
H
4
1
B
Else
3
E
F
Fringe Set
If Weight(y,z) < Weight(z) then
Set parent to y
Set weight of z to weight of the edge connecting z to y
13
Prim’s Body
MST
Prim’s Body
B
1
2
3
A
1
C
3
A
14
D
1
2
2
MST
1
B
A
4
1
2
3
A
2
1
C
3
D
5
B
D
1
2
2
4
5
1
1
E
B
3
Parent
3
E
H
G
F
E
3
Parent
3
3
E
D
Fringe Set
6
F
H
G
3
B
A
4
2
C
1
3
B
A
4
6
F
F
3
C
Fringe Set
15
16
Prim’s Body
MST
B
1
A
D
1
2
1
6
F
3
E
F
B
1
5
1
E
4
1
E
Fringe Set
G
3
H
D
A
C
6
F
3
1
2
4
G
Parent
D
1
2
3
H
1
C
3
D
2
3
A
2
A
D
4
B
1
5
3
A
MST
2
4
E
Parent
1
C
3
D
2
3
A
2
Prim’s Body
B
1
2
C
5
F
G
Fringe Set
17
Prim’s Body
MST
B
1
A
1
1
2
3
1
C
3
D
Prim’s Body
B
A
2
18
D
1
2
2
MST
4
1
5
C
1
A
2
1
C
3
D
2
3
D
1
2
2
4
5
C
1
E
3
Parent
B
1
A
B
A
4
E
6
F
H
G
3
3
Parent
D
2
E
G
Fringe Set
6
F
H
G
3
D
C
2
5
F
1
E
2
1
G
F
Fringe Set
19
20
Prim’s Body
MST
B
1
A
1
1
C
3
D
2
3
A
2
Prim’s Body
B
1
D
1
2
MST
2
B
1
4
1
5
C
1
C
3
D
2
3
A
2
A
B
1
D
1
2
2
4
5
C
1
E
6
F
G
1
E
1
6
F
G
G
3
Parent
2
H
3
Parent
D
C
2
2
E
F
G
Fringe Set
3
H
D
C
2
1
E
3
F
Fringe Set
21
Prim’s Body
MST
B
1
1
2
3
1
C
3
D
1
Prim’s Body
B
A
2
A
22
D
1
2
MST
2
4
D
2
3
1
C
3
D
1
2
2
4
5
C
1
E
1
6
F
2
G
3
G
2
E
3
Parent
H
F
Fringe Set
G
H
3
D
G
3
2
6
F
G
3
D
C
3
H
1
E
1
E
G
H
1
A
2
1
5
C
Parent
B
1
A
B
2
F
Fringe Set
23
24
Prim’s Body
MST
B
1
A
D
1
2
3
A
2
Prim’s Body
B
1
1
C
3
D
1
2
MST
2
B
1
1
5
C
1
C
3
D
1
2
2
4
5
C
2
1
E
1
E
6
F
2
G
F
1
3
H
3
Parent
3
G
3
H
G
1
3
F
H
6
F
G
3
E
G
1
E
1
E
G
Parent
D
2
3
A
2
A
4
B
1
H
Fringe Set
Fringe Set
25
Prim’s Body
MST
B
1
D
1
Prim’s Body
B
1
2
3
A
2
A
26
1
C
3
D
1
2
MST
2
B
1
C
2
1
F
2
3
1
C
3
D
1
2
2
4
5
C
E
1
E
D
1
5
1
A
2
A
4
B
1
6
F
2
G
E
G
1
3
H
E
1
F
1
6
F
G
G
3
3
H
3
3
Parent
H
G
3
Parent
H
Fringe Set
Fringe Set
27
DONE!
DONE!
28
Inserting into a Binary node
Inserting into Ordered Binary Tree
-- insert procedure
procedure Insert (Root
: in out Nodeptr;
Element : in
Integer ) is
New_Node : Nodeptr;
begin
if Root = null then
New_Node:= new Node;
New_Node.Element := Element;
Root := New_Node;
else
if Root.Element < Element then
Insert(Root.Right_Child, Element);
else
Insert(Root.Left_Child, Element);
end if;
end if;
end Insert;
• Insert 10, 11, 9, 7, 8, 12
• Insert 10
10
• Insert 11
10
29
Inserting into Ordered Binary Tree
if Root.Element < Element then
Insert(Root.Right_Child, Element);
else
Insert(Root.Left_Child, Element);
end if;
30
Inserting into Ordered Binary Tree
• Insert 9
• Insert 7
10
9
11
10
9
11
11
7
if Root.Element < Element then
Insert(Root.Right_Child, Element);
else
Insert(Root.Left_Child, Element);
end if;
31
32
Inserting into Ordered Binary Tree
Inserting into Ordered Binary Tree
• Insert 8
• Insert 12
10
9
10
9
11
7
11
7
8
12
8
33
Shortest Path Problems
34
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
• Dijkstra’s algorithm
• Dijkstra(G,w,s)
– Finds shortest path for a directed and
connected graph G(V,E) which has nonnegative weights.
– Applications:
Init_Source(G,s)
S := empty set
Q := set of all vertices
• Internet routing
• Road generation within a geographic region
•…
while Q is not an empty set loop
u := Extract_Min(Q)
S := S union {u}
for each vertex v which is a neighbor of u loop
Relax(u,v,w)
35
36
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
a
• Init_Source(G,s)
∞
for each vertex v in V[G] loop
d[v] := infinite
previous[v] := 0
d[s] := 0
b
1
∞
10
s
0
2
9
3
5
• v = Extract_Min(Q) searches for the vertex v
in the vertex set Q that has the least d[v]
value. That vertex is removed from the set Q
and then returned.
4
6
7
∞
c
∞
2
d
• Relax(u,v,w)
V = {a, b, c, d, s}
E = {(s,c), (c,d), (d,b), (b,d),
(c,b), (a,c), (c,a), (a,b), (s,a)}
S = {∅}
Q = {s, a, b, c, d}
0
∞
d= ∞
∞
∞
prev =
0
0
0
0
0
if d[v] > d[u] + w(u,v) then
d[v] := d[u] + w(u,v)
previous[v] := u
37
38
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
a
10
∞
b
1
∞
10
s
0
2
9
3
5
4
6
7
∞5
c
2
Extract_Min (Q) Æ s
Neighbors of s = a, c
Relax (s,c,5)
Relax (s,a,10)
∞
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
a
S = {s}
Q = {a, b, c, d}
0
∞
d= ∞
∞
∞
Æ
10
8
0
10
∞
5
∞
s
0
2
Æ
9
3
5
5
0
s
0
s
0
4
2
Extract_Min (Q) Æ c
Neighbors of c = a, b, d
39
6
7
c
prev =
14
∞
10
d
0
0
0
0
0
b
1
Relax (c,a,3)
Relax (c,b,9)
Relax (c,d,2)
∞7
S = {s, c}
Q = {a, b, d}
0
10
d= ∞ Æ
5
∞
0
8
14
5
7
0
s
0
s
0
0
c
c
s
c
d
prev =
Æ
40
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
a
8
b
1
14
13
10
s
0
2
9
3
5
4
6
7
5
c
7
2
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
a
S = {s, c, d}
Q = {a, b}
0
8
d = 14 Æ
5
7
8
s
prev =
Æ
8
b
9
10
s
0
2
9
3
5
4
6
0
c
d
s
c
7
5
c
2
Extract_Min (Q) Æ b
Neighbors of b = d
Relax (b, d, 4)
7
Æ
0
8
9
5
7
Æ
0
c
a
s
c
d
prev =
0
c
a
s
c
4
43
6
7
2
Extract_Min (Q) Æ a
Neighbors of a = b, c
Relax (a,b,1)
Relax (a,c,3)
S = {s, c, d, a, b}
Q = {}
0
8
d= 9
5
7
9
3
5
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
1
2
5
41
a
0
c
Extract_Min (Q) Æ d
Neighbors of d = b
Relax (d,b,6)
13
9
10
0
8
13
5
7
d
0
c
c
s
c
b
1
7
S = {s, c, d, a}
Q = {b}
0
8
d = 13 Æ
5
7
0
8
9
5
7
0
c
d
s
c
0
c
a
s
c
d
prev =
Æ
42