BCIS 5520 IT Service Management Service Operations (Part 1)
advertisement

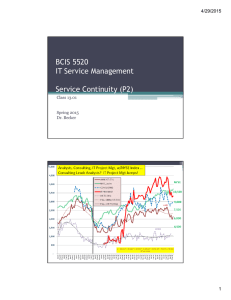
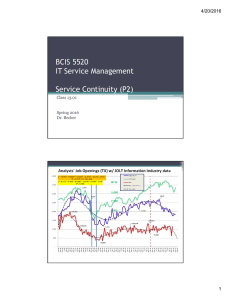
3/30/2016 BCIS 5520 IT Service Management Service Operations (Part 1) Class 10.01 Spring 2016 Dr. Becker Class 11: Service Operations: NEXT • Class #11 –(4/6; click here) • Readings: ▫ Foundations of ITSM based on ITIL v3, Jan von Bon (JVB) Chapter: 6 Service Operations Foundations in ITSM (ITIL v3 Foundations Course in a Book), Orand & Villarreal (O&V) Chapters: 8-9 Service Operations Overview & Processes Other Materials Class Handouts & Readings • Homework 7A (100 pts): Pre-Final Project DRAFT (in lieu of a Paper Reviews) MUST COMPLETE! 1 3/30/2016 2016 Project Topics DRAFT 1. Curran, Kevin: “ITSM/ITIL Risk related to Security” 2. Gill, Manrajdeep, “ITSM/ITIL Service Transition Issues: Service Catalogs & CMDBs” 2 3/30/2016 Term Paper & Presentation Project (400 pts.) The subject of the paper should be relevant to the management of information assets and can be based on one of the topics covered in class, mentioned in your textbook, or any other topic relevant to IT Service Management. I. Introduction to topic. Title and statement of the topic (100 to 250 words). The topic statement should be in paragraph rather, rather than outline, form. Answer the question: Why should we care about your topic? Use outline form for rest of the paper when appropriate. II. Key Issues (KIs) for management of topic. Answer the question: To what things (i.e., nouns) must you pay attention in order to be successful at managing topic? You cannot have more than 10 or fewer than 5 KIs, preferably 6 to 8. NOTE: These MUST lead to the definition of CSFs in V. below III. Model/framework/theory/taxonomies. Answer the question: What concepts, paradigms, approaches, etc. are there to help us understand and/or organize the subject matter? IV. Primary content -- Cover the subject matter – Provide management with the “how to do it” details. Ideally the content of section III and/or II provides you with a way to organize this section into several sub-headings. Case examples could go here too. Put longer cases, and supporting materials which cannot be easily cited in the References section into the Appendix. V. Critical success factors (CSFs) for successful management of this area. Answer the question: What things must be done right in order to be successful at managing this? Ideally this section links back to section II’s KIs. Section V's CSFs should serve as your conclusions and summary section; but, if necessary, include a separate section before this one to deal with additional conclusions. You cannot have more than 10 or fewer than 5 CSFs, preferably 6 to 8. VI. References. [Not included in word counts] VII.Appendix. [Not included in word counts] Include PowerPoint Presentation Slides here. Copies of important references; website materials; and figures and tables not included in main body of report. • • Proposal (25 pts.. 400-750 words) due: Feb 19th Paper (325 pts.; 3000-5000 words) & Presentation (50 pts.; slides) due: April 30th Class 10: Service Operations (Part 1) • Class #10 –(3/30; click here) • Readings: ▫ Foundations of ITSM based on ITIL v3, Jan von Bon (JVB) Chapter: 6 Service Operations Foundations in ITSM (ITIL v3 Foundations Course in a Book), Orand & Villarreal (O&V) Chapters: 8-9 Service Operations Overview & Processes Other Materials Class Handouts & Readings Homework #6A: Service Management Operations or Service Desk Operations 3 3/30/2016 ITIL ITSM Lifecycle: Operations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Service Strategy Service Design Service Transition Service Operation Continual Service Improvement Service Operations -- Miscellaneous • McLean CIO Leadership Model • Alternative Service Operations Frameworks for Help Desks (2012 Student Projects): ▫ Case-based Reasoning Models (CBR); Nintzel ▫ Help Desk Metrics – 3 dimensional model (level, silo, where/how displayed); Garrison ▫ Help Desk Costs and Benefits. Strategic automated approach.; Z. Mohammed 4 3/30/2016 Service Operations – DICE Mode • Assessing Likelihood of Success of an ITIL implementation or Improvement Effort ▫ Model developed by: Harold L. Sirkin, Perry Keenan and Alan Jackson (study of 225 companies) ▫ Determined common denominators of successful organizational behavior change ▫ DICE: Duration – length of time between project reviews (months) Integrity – Extent to which organization can depend on team Commitment – Senior Mgt & Stakeholder Commitment Effort – Estimate of additional time & effort above normal jobs to make the change (%) Service Operations Overview • Service Operations Purpose ▫ Deliver Value to the Customer ▫ Coordinate and perform activities and prcesses required to deliver and manage services in accordance with SLAs • Service TransitionPackage main input to Service Operations • Key Concepts ▫ Communication is key ▫ Operations Balance 5 3/30/2016 Service Operation Main Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Service Desk Technical Management Application Management IT Operations Management Service Operations Key Concepts • Balance ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Internal and External Views Stability vs. Responsiveness Cost vs. Quality Reactive vs. Proactive • Key to Effectiveness – Manage SLAs ▫ Customer Expectations through carefully crafted SLAs 6 3/30/2016 9.0. Service Operations: The Basic Processes • Objective: Deliver value to the customer through effective management of all service operations. • BIG 5 Processes: 1. Event Management 2. Incident Management 3. Request Fulfillment 4. Problem Management 5. Access Management 9.1 Event Management Process • Definition: ▫ A change of state which has significance for the management of a CI or IT Service: • Notifications of Regular Operations activities; Unusual events; and Exceptions Activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Event Detection Event Filtering Significance Event Correction Review Close Event Response Selection 7 3/30/2016 9.2 Incident Management • Definition: ▫ An unplanned interruption (error!) to an IT service or a reduction in the quality of service • Purpose ▫ To ensure that the service is restored as quickly as possible • Levels of Support (Operational Level Agreements) 1. Tier-1: First-level support (80% of all incidents) 2. Tier-2: Second-level; higher technical skills 3. Tier-3: Third-level; specialized expert-level skills 9.3 Request Fulfillment • Definition: ▫ A “personal” request from a user for information or advice or for a Standard Change or access to an IT Service • Purpose ▫ Manage requests from users to ensure they are addressed in a timely manner in accordance with SLAs and OLAs • Key Point ▫ Request Models are established to automate common user requests 8 3/30/2016 9.4 Problem Management Process • Definition ▫ Responsible for eliminating errors from the environment and reducing the incident volumes experienced by the users • Purpose ▫ Prevent Incidents from occurring, as well as minimizing the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented • Key Points ▫ Establish Known Error Databases (KEDB) Problem Mgt: Tools and Techniques • Workarounds ▫ Chronological Analysis Follow the sequence of events that got us here! ▫ Pain Value Analysis What is the overall “pain” of this problem ▫ Kepner and Tregoe ▫ Brainstorming ▫ Ishikawa (Fishbone) Diagrams Root cause analysis ▫ Pareto Analysis (80-20 rules) 9 3/30/2016 Problem Management Activities • • • • • • • • • Detection Logging Categorization Prioritization Investigation & Diagnosis Deploying Workarounds Raising and Known Error Record Problem Resolutions Closure 9.5 Access Management • Definition ▫ The level and extent of a service’s functionality or data that a user is entitled to • Purpose ▫ To provide access for services that users are authorized to use, while preventing access to services to those, who are not so authorized. 10 3/30/2016 Access Management: Key Activities • Activities (includes DBA; DBMA activities) ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Access Requests Verification Providing Rights (via Directory Services) Monitoring Identity Status Logging and Tracking Access Removing or Restricting Rights Cherwell Dashboard – Webinar? 11 3/30/2016 THE END… Class 10 • PMBOK Webinar Online ▫ V4 vs. V5 12