Harnessing the power of digital technology to develop and test Susan Michie
advertisement

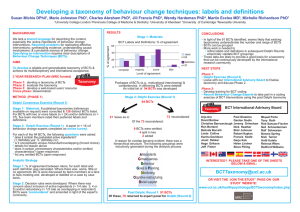
Harnessing the power of digital technology to develop and test behaviour change theory Susan Michie Professor of Health Psychology Director of Centre for Behaviour Change @SusanMichie Main messages • Digital interventions have huge potential to support behaviour change • However, this potential will only be realised if 1. informed by the science of behaviour change • Empirical evidence about what works, for whom, in what circumstances • Theoretical principles of motivation, self-regulation and engagement 2. Knowledge is accumulated using sophisticated experimental designs and cross-disciplinary collaboration, informed by theory Could revolutionise development and testing of behaviour change theory • Generate large amounts of data – continuous and rapid cycles of testing and adaptation • Allow interventions that are – in “real” time and context – tailored to the individual, setting and the moment – interactive and adaptive • Deliver interventions with perfect fidelity and specification But requires … • Strategic thinking about – what data need to be collected – how they should be structured and analysed • For example, how to deal with variation in amount of engagement with different parts of site – what collaborations need to be forged • Linking theoretical constructs and mechanisms of action to behaviour change techniques What do we mean by behaviour change techniques (BCTs) • “Active ingredients” within the intervention designed to change behaviour • They are – observable, – replicable and – irreducible components of an intervention • Can be used alone or in combination with other BCTs BCT Taxonomy v1: 93 items in 16 groupings The BCTTv1 smartphone app • Fully searchable version of BCTTv1 • Search by BCT label, BCT grouping or alphabetically • Increases familiarity with the taxonomy • Increases speed and recall of BCT labels and definitions Search for: BCTs bcts.23.co.uk* Search for: BCTs* bcts.23.co.uk* * You’ll need an internet connection to use the app www.bct-taxonomy.com Which behaviour change techniques? • Start with a model of behaviour change • Link to a comprehensive framework of behaviour change interventions • 9 intervention functions – each of these linked to behaviour change techniques Michie et al (2011), Implementation Science. [OPEN ACCESS] OR www.behaviourchangewheel.com The COM-B model Behaviour occurs as an interaction between three necessary conditions Michie et al (2011) Implementation Science Example of BCTs according to these drivers e.g. self-regulatory skills such as goal setting, self-monitoring, action planning, distraction e.g. messages to boost self-confidence, make long-term rewards more immediate and vivid, show progress e.g. stimulate social support, changing one’s environment, provide cues and alerts, information about locality Example: effective intervention for smoking cessation • Offers ongoing behavioural support – an automated advisor to help smokers stop using structured quit plan and a ready source of information – delivers up to 33 evidence- or theory-based BCTs (Michie et al, 2012) – One example …….. Principle / BCT Intervention content Website design Construct personal rule to Introduction of motto: ‘Not generate strong resolve a puff, no matter what’ & /Strengthen ex-smoker image to support identity Image attractive; simple motto; interactive – use site, emails & texts to deliver