HECToR User Group Meeting 23 September 2008 rd
advertisement

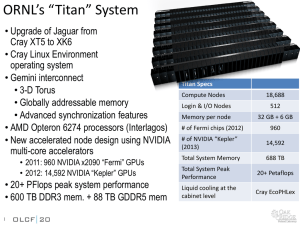
HECToR User Group Meeting 23rd September 2008 Agenda Recent Cray Announcements Cray XT4 Cray XT5 HECToR Phase II 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 2 Cray Processor Technologies. Cray and AMD have worked together in HPC since 2002. Cray currently delivering petascale XT5 systems. Cray “Baker” systems driving to multi-petaflops in 2010-2011 Cray advancing interconnect technologies. Cray and Intel formed a strategic partnership in HPC in 2008 Intel-Cray partnership blends complementary skills Intel has world’s best IC process, and very strong IC design capabilities Cray has brings excellence in system architecture, networking and software expertise in HPC 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 3 The Cray CX1 We Take Supercomputing Personally “Ease of Everything” HPC Experience Ease of Acquisition Online configuration and ordering Configurations designed for specific HPC workloads Ease of Installation Complete system delivery Clear, easy to follow installation instructions Pre-installed software Wizards/GUI for cluster deployment Ease of Use No requirement for computer room and dedicated infrastructure Strong ISV library and available HPC tools to get the job done The Cray High Efficiency Cabinet with ECOphlex Technology (PHase change Liquid EXchange(PHLEX)) Departmental Cray Supercomputing Cray XT5m Affordable Supercomputing Smaller and more limited configurations Maximum of 4 cabinets (possible extension to 6) 2D Torus High Speed Interconnect Standard Cray XT Compute Blades Customer assist “P1” Service Plan 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 8 Single Cabinet XT5m SPECIFICATIONS Compute cabinets: 1 (3 chassis) Compute Sockets: 168 Peak: Memory: 6.1 Tflops .7 – 2.6 TBytes Topology: 12 x 8 Floor space: 2 Tiles 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 9 Four Cabinet XT5m SPECIFICATIONS Compute cabinets: 4 (12 chassis) Processors: Peak: Memory: Topology: Floor space: 23rd September 2008 736 27.1 Tflops 2.9 – 11.5 TBytes 16 x 24 8 Tiles Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 10 Cray XT4 Cray XT4 Node 6.4 GB/sec direct connect HyperTransport Cray XT4 Node Characteristics Number of Cores 4 Peak Performance > 35 Gflops/s Memory Size 2-8GB per node Memory Bandwidth 12.8 GB/sec Cray SeaStar2+ Interconnect 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary 12.8 GB/sec direct connect memory (DDR 800) Slide 12 ORNL Currently have 84 cabinets of quad-core Cray XT4 installed 68 Upgraded Cray XT4 Cabinets 16 Cray XT3 Cabinets upgraded to Cray XT4 Quad Core ~263Teraflops In full production for true capability computing 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 13 From the Cray Center of Excellence – LSMS Performance on Jaguar The Challenge: Potential to develop revolutionary new magnetic storage media Need realistic thermodynamic description of the magnetic behavior of FePt nanoparticles The Science Solution: Use LSMS code to model magnetic properties In addition, model changes in temperature Need system that handles calculation for thousands of atoms The HPC Challenge & Solution: Code must scale to run on thousands of processors Currently running at 192 Teraflops sustained on 31,400 cores on Jaguar (73% of peak) 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 14 9 Cabinet Cray XT4 740 Quad-core Opterons 2.2 GHz 26 Tflops Astrophysics Research Install Date: March, 2008 Shipped as Quad Core Tokyo Mitaka City 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 15 Recent Cray Activity in Europe Contracted over 400 TF in last 18 months Europe now ~30% of Cray worldwide revenue Cray User Group conf. in Lugano (‘06), Helsinki (‘08), Edinburgh (‘10) 5th Cray Technical Workshop Europe, September 2008 in Edinburgh 23 TF 41 TF 35 TF → 100 TF 50 TF → 200 TF September 08 Cray Inc. Confidental Slide 16 Bergen The University of Bergen has installed a Cray XT4 at the Bergen Center for Computational Science (BCCS). The supercomputer is being used for advanced research in fields including: Marine molecular biology Large scale simulation of ocean processes Climate research Geosciences Computational chemistry Computational physics Computational biology Initial install with dual core processors Upgraded to Quad Core and accepted in August 2008 9/23/2008 Cray Propietary Information Provided Under NDA Slide 17 CSC Finland “After an extensive selection process we chose the Cray XT4 supercomputer to replace a cluster system that could no long keep up with the computing demands of our research groups. We determined that the Cray XT4 system matched our needs by delivering the best combination of performance and value.” Kimmo Koski Managing Director CSC Finland 9/23/2008 Cray Propietary Information Provided Under NDA Slide 18 CSC Finland – the Finnish IT Center for Science Cray XT4 Contract awarded in October 2006 Phase 1 (12 cabinets, dual-core ) shipped and accepted in Q1 2007 Quad-core upgrade in Q2 2008 Will grow to over 70 TF Cray XT4 / Cray XT5 quad-core – installation is under way CSC Finland hosted Cray Technical Workshop 2007 and CUG2008 9/23/2008 Cray Propietary Information Provided Under NDA Slide 19 Danish Meteorological Institute (DMI) Cray contract award in December 2007 Two identical Cray XT5 systems with shared Lustre file system Cray XT5 installation summer 2008 The system will run the operational weather forecast for Denmark and Greenland 35 TF within 200 KW envelope 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 20 CSC Finland – the Finnish IT Center for Science Cray XT4 Contract awarded in October 2006 Phase 1 (12 cabinets, dual-core ) shipped and accepted in Q1 2007 Quad-core upgrade in March 2008 Will grow to over 70 TF Cray XT4 quad-core in stages through 2008 CSC hosted Cray Technical Workshop 2007 and CUG2008 in Helsinki 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 21 Cray XT5 Cray XT4 Node 6.4 GB/sec direct connect HyperTransport Cray XT4 Node Characteristics Number of Cores 4 Peak Performance > 35 Gflops/s Memory Size 2-8GB per node Memory Bandwidth 12.8 GB/sec Cray SeaStar2+ Interconnect 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary 12.8 GB/sec direct connect memory (DDR 800) Slide 23 Cray XT5 Node 6.4 GB/sec direct connect HyperTransport Cray XT5 Node Characteristics Number of Cores 8 Peak Performance > 70 Gflops/s Memory Size 8-32 GB per node Memory Bandwidth 25.6 GB/sec 25.6 GB/sec direct connect memory Cray SeaStar2+ Interconnect 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 24 The Importance of Link Level Reliability Error detected and corrected at the offending link Link with Error IB IB 23rd September 2008 IB IB IB IB IB IB IB IB IB IB Source Node must Error detected at the retain copies of all destination. Packet potential in-flight is discarded. messages – an Resent after O(n2) problem… timeout Cray Inc. Proprietary IB IB IB IB Slide 25 Measurement of ORNL PDU (drives 12 XT4 quad-core cabinets) Linpack Running ~18.5 kW / cabinet Normal Workoad ~15 kW / cabinet 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 26 Example: 6 Cabinet Cray XT5 System SPECIFICATIONS Compute cabinets: 6 (18 chassis) Processors: 1112 Peak: 43 Tflops Memory: 8.5-17 TBytes Topology: 6 x 12 x 8 Floor space: 7 Sq Meters System power: ~250 kW Power and floor space do not include IO & storage units = 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary ! Slide 27 30 Cabinet Cray XT5 System SPECIFICATIONS Compute cabinets: 30 (90 chassis) Processors: 5600 Peak: 206 Tflops Memory: 11-88 TBytes Topology: 15 x 12 x 16 Floor space: 45 Sq Meters System power: ~1300 kW Power and floor space do not include IO & storage units 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 28 Example: 108 Cabinet Cray XT5 System SPECIFICATIONS Compute cabinets: 108 (324 chassis) Processors: 20424 Peak: 780 Tflops Memory: 319 TBytes Topology: 17 x 24 x 24 Floor space: 150 Sq Meters System power: ~4500 kW Power and floor space do not include IO & storage units 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 29 Example 144 Cabinet XT5 SPECIFICATIONS Compute cabinets: 144 (432 chassis) Processors: 27336 Peak: 1006 Tflops Memory: 427 TBytes Topology: 24 x 24 x 24 Floor space: 180 Sq Meters System power: ~6000 kW Power and floor space do not include IO & storage units 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 30 Cray XT5 Customers DoD MSRC Program Cray XT5 won most of the TI08 procurement NAVO – 18 Cabinet system plus TDS ARL – 18 Cabinet system plus TDS ARL – 3 Cabinet system ARSC – 5 Cabinet system plus TDS 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 32 In Europe DMI Operational Weather forecasting 35Tflop/s Cray XT5 CSC Finland Over 70Tflop/s Cray XT3/4 Growing to over 100Tflop/s PRACE prototype CSC and CSCS collaboration) 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 33 University of Tennessee (NSF) 48 Cabinet Cray XT4 Quad-Core ~170 Tflops ~60 Cabinet XT5 Processor upgrade in 2009 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 34 ORNL Currently installing a very large Cray XT5 Using liquid cooled cabinets 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 35 The Cray High Efficiency Cabinet with ECOphlex Technology (PHase change Liquid EXchange(PHLEX)) What has changed today? In the past, liquid cooling was used primarily to increase performance The game was to pack circuitry as tightly as possible Or to run at higher clock cycles Or to cool very high power parts The move to distributed programming and commodity components has reduced the need to pack things tightly Today, the motivations are largely based on cost of ownership Although the high frequency signaling rate of copper (still the most cost effective) interconnects is a factor And floor space of existing facilities is becoming more of an issue 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 37 What does “Green” mean in HPC? Green in HPC means more computing in a fixed power envelope. Green in HPC means higher density Customers want more computer in less space Green is in the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Customers want fewer dollars diverted away from computing infrastructure. Green should be manageable No issues of condensation or leakage Easy Serviceability Green should be upgradeable Less landfill or recycling of components Green needs to be innovative Cray High Efficiency Cabinet with ECOphlex Technology (PHase change Liquid EXchange(PHLEX)) 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 38 R134A Phase Change Evaporative Cooling Gas Exiting air stream phase R134a out R134a Liquid Entering air stream phase R134a in Over 10 x more effective than a water coil of similar size (phase change much more effective method to remove heat) Corollary: Weight of coils, fluid, etc. is 10X less than water cooling 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 39 ECOphlex Technology in the Cray High Efficiency Cabinet R134a piping Exit Evaporators Inlet Evaporator 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 40 Cray HE Cabinet (cont) Introduced with Cray XT5 Signal Integrity Improvements Future Proof Cabinets will accommodate future blades and processors through at least 2012 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 41 Petaflop+ XT5 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 42 HECToR Phase II HECToR Phase II Currently discussing multiple possibilities Technology Timing Power and cooling Aiming to exceed original goals 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 44 HECToR Phase II Possibilities Upgrade existing Cray XT4 to Quad Core processors All 60 cabinets, as soon as possible, leads to ~208 TF Evaluate Cray X2 vector needs Install either Cray XT5 or the next generation Cray MPP system Multi-Core Liquid Cooled cabinets Next generation Cray custom interconnect Rich Programming Environment 23rd September 2008 Cray Inc. Proprietary Slide 45 End