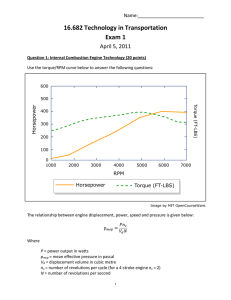
Document 13352571
advertisement

16.06 Principles of Automatic Control
Lecture 3
Modeling principles:
1. Identify the states of the system:
• positions
• velocities
• inductor currents
• capacitor voltages
• etc
2. Use physics to find dx1 {dt, dx2 {dt,...
3. Organize as:
dx
“ f px, uq
dt
y “ gpx, uq
where
x´state vector
u´control input
y´output of measurement
4. Linearize if necessary.
1
Modeling a DC Motor
Physical layout:
N
S
S
N
Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
Model:
e= Keθ
Image by MIT OpenCourseWare.
The states are:
x1 “ Θ - motor angle
9 - motor angular velocity
x2 “ Θ
x3 “ ia - armature current
Find equations of motion:
dΘ
9 “ x2
“Θ
dt
91
dΘ
:
“Θ
x9 2 “
dt
x9 1 “
2
(Kinematicsq
From free body diagram:
: “ ´ bΘ
9 `T
JΘ
9 “ viscous drag on rotor
´bΘ
T “ torque due to current
“Kt ia , where Kt is a motor torque constant
So
: “´ bΘ
9 ` Kt ia
Θ
J
J
b
Kt
x9 2 “ ´ x2 `
x3
J
J
Now model the circuit. Start with motor part itself. The power supplied to the motor is
P “ eia
This must equal (by 1st law) the torque power:
9 “ Kt ia Θ
9
P “ TΘ
Equating the previous two equations:
9
e “ Kt Θ
Therefore,
Ke “ Kt
So now we can find dia {dt:
dia 1
“ pva ´ ia Ra ´ eq
dt L
1
9
“ pva ´ ia Ra ´ Kt Θq
L
Therefore,
3
x9 3 “ ´ KLt x2 ´
Ra
x
L 3
` L1 va
In state-space form:
¨
˛
¨ ˛
0
1
0
0
Kt {J ‚x ` ˝ 0 ‚va
x9 “ ˝0 ´b{J
1
0 ´Kt {L ´Ra {L
L
`
˘
θ“ 1 0 0 x
This is in the form
x9 “Ax ` Bu
y “Cx ` Du
Note: FPE uses
x9 “F x ` Gu
y “Hx
4
MIT OpenCourseWare
http://ocw.mit.edu
16.06 Principles of Automatic Control
Fall 2012
For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.