Query Processing for Distributed RDF Databases Using a Three-dimensional Hash Index Akiyoshi MATONO

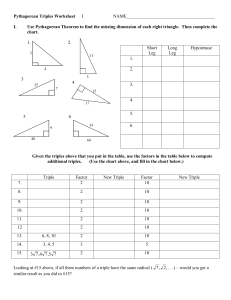
Query Processing for Distributed RDF Databases
Using a Three-dimensional Hash Index
Akiyoshi MATONO a.matono@aist.go.jp
Grid Technology Research Center,
AIST
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
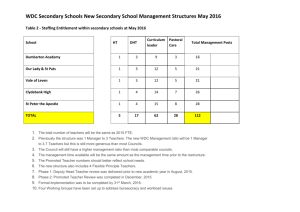
Agenda
Motivation & Aims
Background
Distributed Hash Table (DHT)
Our approach
Performance evaluation
Summary
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Motivation
It is essential to describe resources using RDF to provide semantic tasks (e.g., resource discovery).
Today, RDF data is widely used in many fields (e.g., bioinformatics and grid).
Thus, RDF data is scattered everywhere and the total data size is rapidly increasing.
Providing efficient and scalable RDF query processing in a distributed environment is an important issue.
We proposed a P2P -based RDF query processing.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Aims
RDF data is scattered everywhere.
Provide an efficient join operation in a distributed environment.
The amount of data is rapidly increasing.
Reduce the amount of data transferred among nodes.
Achieve scalability, availability, and reliability.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Distributed Hash Table (DHT)
A structured P2P network.
Achieve scalability, availability, reliability.
Support only exact-match lookup s.
Lookups for key-value pairs.
put (key, value) , get (key)
Routing is performed in O (log n ) .
Some protocols.
Chord, Tapestry, Pastry, CAN, Kademlia
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Chord [Stoica01]
…
The distance to the nodes
… increases exponentially.
…
N56
…
N50
N48 finger table distance
N42
+0 succ.
N42 keys
42
N42
+1
N42
+2
N48
N48
43
44-45
N42
+4
N42
N42
+8
+16
N42
+32
N48
N50
N63
N11
46-49
50-57
58-9
10-41
N42
…
N63
put ( 28,
N33
A )
Key 28
N33 is the target node
N2 on N42
N27
…
N6
…
N11 finger table distance
N11
+0
N11
+1
N11
+2
N11
+4
N11
+8
N11
+16
N11
+32 succ.
N11
N17
…
N17
N27
N27
N48 keys
11
12
13-14
15-18
19-26
27-42
43-10
N17 … finger table distance
N27
+0
N27
+1
N27
+2
N27
+4
N27
+8
N27
+16
N27
+32 succ.
N27
N33
N42
N48
N63 keys
27
28
29-30
31-34
35-42
43-58
59-26
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Our Approach
Threedimensional hash space called “ RDFCube ”
Each axis represents hash space for one of subject, predicate, and object.
Consist of a set of cubes of the same size called “ cells ”
Bit information of RDFCube called “ existence flag ”
Each cell contains a bit that indicates the present or absent of triples mapped into the cell.
Run on the top of two DHTs.
RDFPeers DHT is used to store triples.
RDFCube DHT is used to store bit information.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
RDFCube: three-dimensional hash space
Each axis represents hash space for one of triple’s elements (subject, predicate, and object).
RDFCube is composed of a set of cubes of the same size called “ cells ”.
A triple is mapped into RDFCube based on the hash values of elements.
Triple (13, 54, 39) s p o
Cell [0, 3, 2]
54
(13, 54, 39)
This triple is mapped into the point (13, 54, 39).
The point is contained in the cell [0,3,2].
object 39
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Existence Flag
Each of cells contains a bit that indicates the present or absence of triples mapped into the cell.
Cell [0, 3, 2] s p o
Existence Flag
1
0 1 1 0
Cell Sequence
[0, 1, *]
Bit Sequence object
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0
0 0 0 0
Cell Matrix
[0, *, *]
Bit Matrix
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Two DHTs: RDFCube & RDFPeers
RDFPeers DHT is used to store RDF triples.
RDFPeers is an RDF repository utilizing a DHT.
Proposed by [Min Cai and Martin Frank, 2004]
RDFCube DHT is used to store bit information.
Used as an index for RDFPeers.
1.
2.
Storing triples.
Store the triples to RDFPeers DHT.
Store the bit information of the triples into RDFCube DHT.
1.
2.
3.
Query processing with join operation.
Get the bit information from RDFCube DHT.
Perform AND operations of the bits.
Get triples from RDFPeers DHT based on the bit information.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
RDFPeers [Cai04]
An RDF repository utilizing a DHT.
We call the DHT for RDFPeers as RDFPeers DHT.
Key : Each of subject, predicate and object
Value : Triple
value:
The triple is stored 3 times into 3 nodes by 3 lookups using triple’s elements as keys.
key value
N63
N4
N55 N8 s p o value:
RDFPeers DHT
N41 N25
N21 s p o value: s p
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology o
RDFPeers [Cai04]
An RDF repository utilizing a DHT.
We call the DHT for RDFPeers as RDFPeers DHT.
Key : Each of subject, predicate and object
Value : Triple
Given a query triple
s p ?
Perform a lookup using one of the constants as a key.
key
N63
N4
N8 or value: s p o
RDFPeers DHT value: s p o
N41 N25 value: s p
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology o
Two DHTs: RDFCube & RDFPeers
RDFPeers DHT is used to store RDF triples.
RDFPeers is an RDF repository utilizing a DHT.
Proposed by [Min Cai and Martin Frank, 2004]
RDFCube DHT is used to store bit information.
Used as an index for RDFPeers.
1.
2.
Storing triples.
Store the triples to RDFPeers DHT.
Store the bit information of the triples into RDFCube DHT.
1.
2.
3.
Query processing with join operation.
Get the bit information from RDFCube DHT.
Perform AND operations of the bits.
Get triples from RDFPeers DHT based on the bit information.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
RDFCube DHT
Key : ID of cell matrix
Value : Bit matrix
Perform 3 lookups using 3 cell matrixes containing key value
[1, *, *] [*, 2, *] [*, *, 1] key: [*, *, 1] key: value:
[1, *, *]
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
N51
N57
N1
N15 key: value: value: 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
RDFCube DHT
N28
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
N36
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
[*, 2, *]
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0
RDFCube DHT
Key : ID of cell matrix
Value : Bit matrix
a key.
key key: [*, *, 1] value: 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 key: value: 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
N1
N51
N15
RDFCube DHT
N28
N36 key: [*, 2, *] value: 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Two DHTs: RDFCube & RDFPeers
RDFPeers DHT is used to store RDF triples.
RDFPeers is an RDF repository utilizing a DHT.
Proposed by [Min Cai and Martin Frank, 2004]
RDFCube DHT is use to store bit information.
Used as an index for RDFPeers.
1.
2.
Storing triples.
Store the triples into RDFPeers DHT.
Store the bit information of the triples into RDFCube DHT.
1.
2.
3.
Query processing with join operation.
Get the bit information from RDFCube DHT.
Perform AND operations of the bits.
Get triples from RDFPeers DHT based on the bit information.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Storing Triples
Given the triple
s p o
Update RDFPeers DHT
Store the triple into RDFPeers DHT by 3 lookups.
N55
N63
N4
N8 key value value: s p o
RDFPeers DHT
N41 N25
N21 value: s p o
Update RDFCube DHT
Get the cell where the triple is mapped into.
s p o hash (21, 45, 17) cell [1, 2, 1]
Set each bit in the 3 bit matrixes to 1 by 3 lookups.
value:
N1 key value
[1, *, *]
N57
[*, *, 1]
0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
N51
N15
RDFCube DHT
N28
N36
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology s p o
[*, 2, *]
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0
Two DHTs: RDFCube & RDFPeers
RDFPeers DHT is used to store RDF triples.
RDFPeers is an RDF repository utilizing a DHT.
Proposed by [Min Cai and Martin Frank, 2004]
RDFCube DHT is used to store bit information.
Used as an index for RDFPeers.
1.
2.
String triples.
Store the triples to RDFPeers DHT.
Store the bit information of the triples into RDFCube DHT.
1.
2.
3.
Query processing with join operation.
Get the bit information from RDFCube DHT.
Perform AND operations of the bits.
Get triples from RDFPeers DHT based on the bit information.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Query Processing (1/2)
Given the query
?x
?x
?x
p1 p1 p2 p2 o2
[*, 3, 2]
[*, 1, 1]
1.
Get bit information of the cells where the query triples are mapped into.
2.
Perform AND operation between the bits.
1 1 1 0
0 0 1 1
AND Operation
0 0 1 0
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Query Processing (2/2)
3.
Get triples from RDFPeers DHT based on the bit information
1.
2.
Access to a remote node where candidate answer triples are stored into.
For each triple, we check whether the bit of the cell where the triple is mapped into is equal to 1.
?x
p1 A1
Candidate answers value: s0 p1 A0 s1 p1 A1 s2 p1 A1 s3 p1 A2
N55
N63
N4
N8
N41
N21
N25
RDFPeersDHT
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Query Processing (2/2)
3.
Get triples from RDFPeers DHT based on the bit information
1.
2.
Access to a remote node where candidate answer triples are stored into.
For each triple, we check whether the bit of the cell where the triple is mapped into is equal to 1.
Filtering based on the bit information
?x
p1 A1 s0 p1 A0 s1 p1 A1 s2 p1 A1 s3 p1 A2
3.
Return the candidate answer triples that satisfy the condition from the remote node.
the candidate answers
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Performance Evaluation
?x
Compare RDFPeers with RDFPeers+RDFCube
Data Set PEERS CUBE
Transform XML documents of DBLP into RDF data.
Create 4 RDFs of different triples (12500, 25000, 50000, 100000).
Environments
Emulate 100-node Chord network.
#divisions of RDFCube is 32-256.
Queries
Query 1 Query 2 Query 3
Article type author year journal
“Jim Gray”
“1998”
“CoRR”
?x
series
?y
title
“LNCS”
?y
crossref ?x
title ?z
title
“VLDB2004”
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Storing Performance
1.6
1.4
1.2
2
1.8
• PEERS is the network costs for storing triples
• CUBE is the network costs for storing triples and index construction.
• If the ratio = 2, the cost for storing triples = index construction.
• If the ratio = 1, the cost for index construction is nothing.
2
#hops
Transfer size
#hops
Transfer size
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1
13761 (0.57%) 26413 (1.01%) 52926 (1.81%) 103076 (3.00%)
N um ber of triples (1-bit ratio)
1
32 (26.73%) 64 (6.36%) 128 (10.1%)
D ivision num ber (1-bit ratio)
256 (0.14%)
• The ratio of #hops is smaller than 2,
The cost for index construction is smaller than that for storing triples.
• The ratio of transfer data size is very close to 1,
The amount of data transferred for index construction is very small.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Retrieval Performance
2.5
• PEERS is the network costs to get triples from RDFPeers DHT.
• CUBE is the network costs to get bits and triples from two DHTs.
2.5
Q uery1(#hops) Q uery2(#hops) Q uery3(#hops)
Q uery1(transfer) Q uery2(transfer) Q uery3(transfer)
Q uery1(#hops) Q uery2(#hops) Q uery3(#hops)
Q uery1(transfer) Q uery2(transfer) Q uery3(transfer)
2 2
1.5
1
13761 (0.57%) 26413 (1.01%) 52926 (1.81%) 103076 (3.00%)
0.5
1
0.5
32 (26.73%)
0
1.5
64 (6.36%) 128 (10.1%) 256 (0.14%)
0
N um ber of triples (1-bit ratio) D ivision num ber (1-bit ratio)
• #hops on CUBE is twice as many as that on PEERS.
#hops to get triples is equal to #hops to get bit information.
• The transfer data size is reduced to at most 1/50 in query 1.
Our approach makes it possible to reduce transfer size.
In particular, when the query has lots of the same variables.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Scalability
1
0.5
Q uery1
Q uery2
Q uery3
0
13761& 64 26413 & 128 52926 & 256
#Triples & #D ivisions
103076 & 512
• The ratio of CUBE to PEERS stays constant in all queries.
Our approach achieves the scalability with respect to the number of triples.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Summary
What we have achieved.
Scalability with respect to #triples.
Reduce the amount of data transferred among nodes.
What are our major current challenges.
Provide efficient RDF query processing with join operations in a distributed environment.
What we will achieve in the near future.
Eliminate redistribution of triples.
Utilize the schema information.
Dynamic division mechanism of RDFCube.
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
Thank You
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology