Document 13341146
advertisement

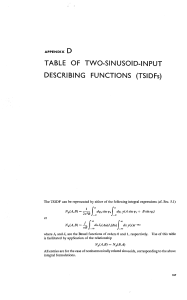
APPENDIX E TABLE OF RANDOM-INPUT DESCRIBING FUNCTIONS (RIDFs) In this table we employ the probability function (cf. Sec. 7.2) denoted by and its integral, the probability integral, denoted by 1 1" exp PZ(X) = = 4 2 -a ~ (- g) dv These functions are plotted in Fig. E.2-1. This table is given in three sections: E. 1 Gaussian-input RIDFs E.2 Gaussian-plus-bias-input RIDFs E.3 Gaussian-plus-bias-plus-sinusoid-inputRIDFs E.1 GAUSSIAN-INPUT RlDFs x(t) = r(t) an unbiased Gaussian process TABLE O F R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S (RIDFs) (Continued) -- Nonlinearity 16. Linear gain Comments TABLE O F RAN DOM-INPUT DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S (RIDFs) (Continued) - Nonlinearity - Comments See Sec. 7.2 n=2,4,6, ... See Sec. 7.2 y - = 4 x (x 2 0) = -4-x (x < 0) 26. Odd square root y =~ See Fig. E.l-3 1 1 % 27. Cube root characteristic r ( x ) is gamma function 574 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.1-2 RIDFs for litniter and tlrr.esholrlcharacteristics. R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.1-3 RZDFfor the simple polynonlial nonlinearityy o r y = c,xn-' 1x1 (n even). = c,xn (n odd) 575 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.1-4 Harmonic nonlinearity RIDF. E.2 GAUSSIAN-PLUS-BIAS-INPUT RlDFs x(t) = r(t) +B The gain to the gaussian input component is given by: and the corresponding gain to the bias input component is: 1 N,(a,B) = jm - ~ Z O By@+ B)exp This section uses the additional function G ( x ) = xPI(x) (- $) + PF(x). The functions PF(x), PI(x), and G(x) are plotted in Fig. E.2-1. dr TABLE O F RANDOM-INPUT DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S (RIDFs) (Continued) Nonlinearity 7. Sharp saturation or limiter 8. Dead zone or threshold 9. Gain-changing nonlinearity Comments TABLE OF R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S (RIDFs) (Continued) Nonlinearity y=x 16. Linear gain Comments TABLE O F R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S (RIDFs) (Continued) Nonlinearity 56. Biased ideal relay Comments R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.2-I Graphs of PF(x), PZ(x), and G(x). 587 E.3 GAUSSIAN-PLUS-BIAS-PLUS-SIN U S O I D - I N P U T RlDFs x(t) = r(t) + B + A sin ( o t + 8) The gain to the gaussian input component is given by the gain to the bias input component is dry(r + B + A sin 0 ) exp (- and the corresponding gain to the sinusoid input component is 2) TABLE O F RANDOM-INPUT DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S (RIDFs) (Continued) Nonlinearity Comments y = xS 18. Cubic characteristic y = Msinmx J, and J, are the Bessel functions of orders 0 and 1 , respectively. NR = Mm cos mB exp M NB = - sin mB exp B ?)J,,(mA) (- (- 2M Nd = A con mB exp 29. Harmonic nonlinearity (- my)~o(m~) mSuz i)l,(mA) 590 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-I Three-input RZDFs for the ideal-relay nonlinearity. In 3 parts Figure E.3-Ia Gain to the gaussian input component. (ideal relay) R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S 591 1.o 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.09 0.08 I Figure E.3-lb 2 3 4 5 6 7 4 0 Gain to the bias input component. (ideal relay) 1.o 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 I I I I I 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 A u Figure E.3-lc Gain to the sinusoid input cotnponent. (ideal relay) 592 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-2 Three-input RIDFs for the limiter nonlinearity. In 1 1 parts Figure E.3-2a Gain to the gaussian and bias input components. (limiter, IB1/6 = 0) 0 Figure E.3-26 Figure E.3-2c 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gain to the sinusoid input component. (limiter, IB)/6 = 0) Gain to thegaussian input component. (limiter, IBI/S = 0.5) 6 Figure E.3-2d Gain to the bias input component. (limiter, IBI/S = 0.5) 6 596 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-2h Gain to the sinusoid input component. (limiter, 1B1/6 = I) R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-2i Gain to theguussiun input component. (limiter, IBI/S = 2) 597 6 598 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-2j Gain to the bias input component. (limiter, lB1/6 = 2 ) 6 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-2k Gain to the siriusoid input conlponent. (limiter, 1Bj/6 = 2 ) 599 600 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-3 Three-input RZDFs for the relay with dead zone nonlinearity. In 1 1 parts 6 0 NB 1 0.8 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.008 0.006 0.005 0.004 0.003 0.002 o.OO11 0 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 4 6 Figure E.3-3a I W = 0) Gain to the gaussian and bias input compotlents. (relay with dead zofie, R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-36 Gain to the sinusoid input component. 601 (relay with dead zone, [BI/S = 0 ) 601 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S 6 Figure E.3-3c Gain to the gaussian input component. (relay with dead zone, IB)/6 = 0.5) R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-3d Gain to the bias input component. (relay with dead zone, IB1/6 = 0.5) 603 604 RANDOM-INPUT DESCRIBING FUNCTIONS Figure E.3-3e Gain to the sinusoid input component. (relay with dead zone, ( B ( / 6= 0.5) 605 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.09 0.08 0.07 0 Figure E.3-3f I 2 3 4 Gain to thegaussian input component. 5 6 (relay with dead zone, lBl/6 ' = A 6 I) 606 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-3g Gain fo the bias input component. (relay with dead zone, IB1/6 = I ) R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-3h Gain to the sinusoid input component. (relay with dead zone, IB1/6 607 = I) 608 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-3i Gaitr to the gaussian input component. (relay with dead zone, 1B1/6 = 2 ) R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-3j Gain to the bias input component. (relay with dead zone, IB1/6 =2) 609 610 R A N D O M - I N P U T DESCRIBING F U N C T I O N S Figure E.3-3k Gain to the sinusoid input component. (relay with dead zone, IB1/6 = 2)