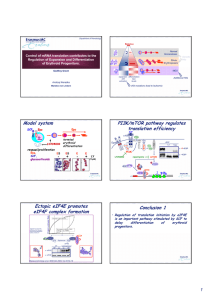
Model system
advertisement

Department of Hematology Model system SCF Epo Epo GR Identification of translationally controlled genes critical for the balance between expansion and differentiation of erythroid progenitors terminal LY294002 erythroid differentiation renewal/proliferation Epo, SCF, glucocorticoids Godfrey Grech Marieke von Lindern Bob Lowenberg Gene expression profiling using polysome bound mRNA Epo ES E E - + - + LY (15μM) Gene expression profiling using polysome bound mRNA SCF cell lysate cell lysate sucrose gradient sucrose gradient free mRNA ES polysomal mRNA free mRNA NF Epo SCF SCF Epo polysomal mRNA Nm23-M2 Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) NDPK-B mRNA expression is regulated at the level of translation initiation Total mRNA Polysomal mRNA free - E S E/S PI3K pathway regulates eIF4E availability SCF Epo bound c-Kit PTEN NF PIP2 p110 Pim-1 SCF C-Jun C-MYB 5 p8 -Y-P PIP3 PH E S ES P-4E-BPT37/T46 4E-BP PI3K E/S eIF4E 4EBP PIP3 PH PKB Epo P-Y- PDK1/2 EpoR Nm23-M2 mTOR Pi Pi 4EBP Pi Pi eIF4E Pi Pi 4EBP Pi Pi 1 PTEN PIP2 EpoR P-Y- PIP3 PH 5 p8 PI3K LY294002 rapamycine eIF4E 4EBP mTOR SCF presents active eIF4E for translation initiation +SCF 1. SCF, but not Epo, transduce the final phosphorylation of 4EBP at Ser64 needed to release eIF4E. P-4E-BPT37/T46 PKB PDK1/2 p110 -Y-P PIP3 PH U0126 c-Kit LY294002 SCF Epo rapamycine PI3K pathway regulates eIF4E availability 4E-BP Pi Pi 4EBP Pi Pi 2. Cap-pulldowns show increased levels of eIF4G to form eIF4F complex by SCF. eIF4E Pi Pi 4EBP Pi Pi Objectives • Identify the role of eIF4E in expansion and eIF4E overexpression results in delay in differentiation differentiation of erythroid progenitors. PTEN PIP2 EpoR P-Y- PIP3 PH PIP3 PH PKB p110 -Y-P 5 p8 have a role in SCF dependent expansion of erythroid progenitors. c-Kit PDK1/2 • Identify translationally controlled genes that Epo 4 days under Epo conditions PI3K eIF4E eIF4E eIF4E eIF4E eIF4E 4EBP eIF4E 4EBP eIF4E 4EBP Cell Numbers Cell Size Hemoglobin 800 Cell Numbers Cell morphology 600 0 0 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 24 48 72 96 120 144 10 1 600 400 200 0 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 hours 200 0 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 hours 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 hours 200 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 24 48 72 96 120 144 hours hours 600 1000 400 400 0 0 600 hemoglobin (Ab units) Mean Cell Volume Epo ESD ES 100 24 48 72 96 120 144 hours 800 1000 10 1 0 hours hours eIF4E overexpression 0 Epo ESD ES cell number 1 200 100 Hemoglobin (Ab units) 200 Epo ESD ES hemoglobin (Ab units) 400 400 cell number 600 Vector control Hemoglobin (Ab units) 10 Mean Cell Volume 100 cell number Vector control Hemoglobin 1000 Epo ESD ES cell number eIF4E overexpression eIF4E 600 1000 eIF4E overexpression empty vector 100 10 1 400 200 0 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 hours 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 hours 2 Translation efficiency Ectopic eIF4E promotes eIF4F complex formation NF eIF4E overexpressor ss ss NF Protein Synthesis Rate eV α -eIF4G α -4E-BP α -eIF4E α-myc Competitive mRNAs (β-actin, Fli1) Non-Competitive mRNAs (VEGF, Cyclin D1, c-myc, MMP-9) limiting increased eIF4E level Figure adapted fromJR Clinical & Experimental Adapted from Graff & Zimmer SG, ClinicalMetastasis & Experimental (2003) 20: 265-273, Graff JR & Zimmer SG Metastasis (2003) 20:265-273 Conclusion 1 Gene expression profiling polysome bound vs Total mRNA • Regulation of translation initiation by eIF4E is an important pathway stimulated by SCF to delay differentiation of erythroid progenitors. NF NF NF NF ES ES ES ES cell lysate What are the translationally controlled genes that have a role in the delay of Epo-induced differentiation? polysomal sucrose gradient free polysomal ES NF NF NF ES NF NF NF ES ES ES ES ANOVA comparison of individual replicates Cluster analysis Total mRNA Gene expression profiling Identification of translational targets Selection Criteria cluster analysis 394 genes – ANOVA signature A (249) B (89) C D 1 ANOVA signatures 2 Translationally upregulated polysome bound RNA 3 down regulated in differentiation early differentiation 4 Classified based on function/s late differentiation 5 Polysome recruitment dependent on eIF4E availability (signaling and/or overexpression) total RNA 3 Classification based on function Translation upreg genes [fc >1.5] Translation downreg genes [fc <0.75] 12% Unknown function 15% Signal transduction Cell cycle regulation Apoptosis 1% 15% Classification based on function 2% 18% chaperon proteins Enzyme 3% 5% 4% Cytoskeleton 3% 39% 3% 1% Proteolysis 7% 4% Metabolism 10% Ribosomal proteins 6% Translational factors 3% 4% mRNA processing DNA binding 17% 6% 15% 4% 1% 15% Membrane Cytoskeleton 1% Membrane 4% Translational factors 6% Unknown function Unknown function 15% 25 Targets with fold change >1,5 : 9 Cell cycle regulation 1% Apoptosis 2% Ribosomal proteins 15% Enzyme Metabolism 7% 17% chaperone proteins 5% Chromatin modeling Transcription complexes % of Group A : 10% No. of genes/EST : 23 Targets with fold change >1,5 : 10 • Is the recruitment to polysomes by SCF, PI3K dependent? DNA binding 10% Membrane 4% • Does eIF4E overexpression alone result in polysome recruitment of the selected transcripts. Cell cycle regulation 1% Apoptosis 2% mRNA processing 3% Translational factors 6% 12% No. of genes/EST : Polysome recruitment DNA binding Signal transduction 12% Cytoskeleton 3% % of Group A : DNA binding 10% mRNA processing 3% 4% Classification based on function Signal Signal transduction transduction 12% 12% Signal Transduction Enzyme Metabolism 7% 17% Ribosomal proteins 15% chaperone proteins 5% Polysome recruitment of selected transcripts is PI3K dependent Non-competitive mRNA Competitive mRNA alpha-4 Polysome association Fli-1 Polysome association 100 Percent polysome association Empty vector eIF4E overexpression 40 30 hnrpa1 rnf138 rbms1 Cnih 20 10 Empty vector S NF S+LY E+LY 0 E+rap S NF S+LY E+LY E+rap S+rap S S+LY E ES NF 0 50 S+rap 10 60 S 20 70 S+LY 30 80 E 40 90 ES 50 NF 60 ss 70 ss Percent polysome association 80 eIF4E overexpression PI3K dependent polysome recruitment of 13 transcripts shown by RT-PCR. Confocal microscopy by Bart Aarts 4 I11 cell line a4 #2_myc a4 #7_myc Empty vector mycAb DAPI overlay acp1 acp1 800 100 700 600 5730466P16Rik αα4 Stable overexpression of target genes in I11 cells. The proteins are myc tagged – western using myc antibody. The sizes of the tagged protein are expected as follows: 1. 5730466P16Rik - 27kD 2. acp1 - 23kD 3. a4 - 43kD Cell number p16Rik 4 500 400 10 300 200 ev acp1 eV eV eV a4 mEd2 acp1 a4 0 24 48 19 transcripts involved in signal transduction and DNA binding – regulated at translation level T24 Translation regulation of 13 / 17 transcripts are PI3K dependent and eIF4E level dependent T72 6 proteins successfully overexpressed 3 proteins not ectopically expressed: 2 show phenotype 96 RT-PCR of 2 transcripts not successful 3 proteins awaited: 4 do not show phenotype Translationally controlled genes Identify UTR sequencies - databases - RACE Future plans and ongoing experiments 72 Phenotypic Analysis of Target genes – conclusion 5730466P16Rik Department of Hematology 100 p16rIK 1 0 Phenotypic Analysis of Target genes Mean Cell Volume Empty vector acp1#1 _myc acp1#2 _myc Empty vector p16Rik #9 _myc kD 75 50 37 25 20 Phenotypic Analysis of Target genes Identify regulatory elements within UTRs contributing to translation control. Overexpression of targets 9 delay in differentiation in I/11 cells Mechanism of differentiation block by α4: 9 cap-pull downs 9 siRNA of a4 in eIF4E overexpressors. • Luciferase constructs to identify regulatory elements in 5’ UTR • REMSA to show that proteins bind to the 5’UTR RNA probe. • Cross-linking assays to extract proteins binding to specific UTRs • Mass spec. to identify proteins. • Y3H assay to confirm specific binding. 5