Search Strategies Chemistry and Intellectual Property - Catalysing Innovation Dr. Peter Burkhardt
advertisement

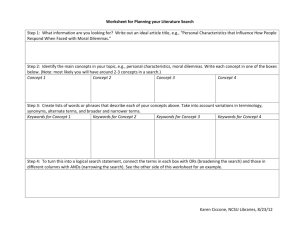
Search Strategies Chemistry and Intellectual Property - Catalysing Innovation Dr. Peter Burkhardt Malta 15.02.2011 What's inside the Mind of an Examiner? clarity patentability novelty Added Subject-matter Structure of the presentation • Understanding the invention • Search strategy Understanding the invention Description Drawings Claims Claims Description • Specific embodiments? • Acknowledged prior art? `Feature reservoir´ The full picture "Patent searching is an art... ... which is practiced by applying common sense, a working knowledge of patent laws, familiarity with the technology and familiarity with the databases and classification of document sources. The order of these elements shifts depending on the search subject" © Prior Art searches Inc., Arlington VA, USA Model search strategy Intuitive and iterative process Analyze application End of search Quick search Analyze results: - keywords, classes - scope/focus search Complete the search - select databases - formulate query - retrieve results Written opinion analyze results: - fields covered, - relevance of documents Formulate opinion Analyze the application • Determine what needs to be searched – read the claims – identify the technical features of the solution(s) – try to identify the "invention" (use the description when necessary) • Classify the claimed subject matter – ECLA, IPC. • Collect keywords, synonyms, etc. • Identify applicant and inventors Quick search The Aim of the quick search is to get an quick overview of the field. • Keyword search in e.g. Google, Scirus, PubMed. • Search for publications from the inventors and applicant. – scientific literature. – patent literature. – applicant web-site. • Search for a recent review on the subject. • Collect more keywords. Complete the search • • Sequence/Structure searches, – large proteins/polynucleotides EBI – small peptides/polynucleotides Chem. Abstr., Registry – structure CA, Registry, Beilstein Search patent and non-patent literature (full-text and bibliographic databases), – classification – keywords, synonyms, etc. – inventors/applicant • Chemical Abstracts – keywords – thesaurus Written opinion. • Analyze the documents. – new keywords? – additional players in the field? – citing/cited documents. – select the closest prior art. • Determine the objective technical problem to be solved. – inventive effect? – which feature(s) is/are responsible? • Everything covered? • Formulate opinion. – any missing links? PROCEDURAL EFFICIENCY clarity SERVICE patentability STRATEGY novelty QUALITY Added Subject-matter Questions? www.epo.org