About Candida fungal infections
advertisement

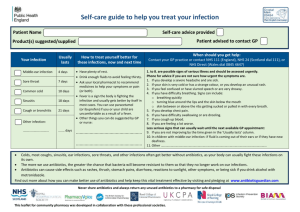
About Candida fungal infections Candida is a type of fungus that is common in the body of normal healthy people. Most babies acquire Candida soon after birth and may develop a mild infection in the mouth called “thrush.” Patients with low blood counts are at risk for a Candida infection. Their low blood counts can be the result of their disease or its treatments, such as stem cell transplants and chemotherapy (cancer-fighting drugs). Use of antibiotics may also increase the risk of a Candida infection. By killing both good and bad bacteria, antibiotics can disrupt the body’s natural balance of good bacteria so that Candida grows more easily. The best way to prevent infection is frequent hand washing, especially before caring for central venous catheters (IV lines that have been surgically placed in the chest area). It is important to keep the skin, mouth tissues and diaper areas clean. Rashes and mouth sores may increase your child’s risk for Candida infections. An infection can develop in almost any part of the body. The first sign of a serious fungal infection is usually a fever that does not go away when the patient takes antibiotics. Your child’s doctor will start therapy with an antifungal drug, if needed. If you have more questions about fungal infections, please talk to your child’s doctor or nurse. Adapted with permission from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. Revised 5/03 UC Davis Cancer Center 12/06 w w w. u c d m c . u c d a v i s . e d u / c a n c e r Page 1 of 1