Development of the Pain-Related Beliefs and APtudes about Sleep (PBAS) scale for the assessment and treatment of insomnia comorbid with chronic pain
advertisement

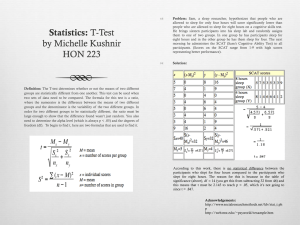
DevelopmentofthePain-RelatedBeliefsandAPtudes aboutSleep(PBAS)scalefortheassessmentand treatmentofinsomniacomorbidwithchronicpain EstherF.Afolalu1,CorranMoore1,FatanahRamlee1,ClaireE.Goodchild2,&NicoleK.Y.Tang1 1DepartmentofPsychology,UniversityofWarwick,UK.2DepartmentofPsychology,InsLtuteofPsychiatry,UK. INTRODUCTION Table2SAMPLECHARACTERISTICS Maladap&ve beliefs about the sleep-pain interac&on are possible factors underlying perpetua&on of sleep disturbances in chronic pain-related insomnia. However, there is currently no validated instrumentthatspecificallyassessesthesebeliefs. We evaluated the psychometric and func&onal proper&es of a 10item Pain-Related Beliefs and AEtudes about Sleep (PBAS) scale (Table 1), designed to assess pain-related dysfunc&onal beliefs and aEtudesaboutsleepamongpeoplewithchronicpain. METHODS ThePBASscalewasadministeredtofourclinicalsamplesofchronic pain pa&ents with comorbid insomnia (Table 2); to examine the scale’spsychometricproper&es(n=137),test-retestreliability(n=26), sensi&vity to treatment (n=20), and generalizability in a separate groupofchronicpainpa&entswithorwithoutinsomnia(n=62). Par&cipantsalsocompletedtheBriefPainInventory(BPI),Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), Dysfunc&onal Beliefs and AEtudes about Sleep Scale (DBAS-16) & Anxiety and Preoccupa&on about Sleep Ques&onnaire(APSQ). RESULTS Table1FACTORSTRUCTURE&INTERNALCONSISTENCY FACTOR1 FACTOR2 PAIN NEGATIVE StronglyDisagreeStronglyAgree M INTERFERING RECIPROCAL 012345678910 SLEEP LINKBETWEEN SLEEPANDPAIN 0.17 Myinsomniaislargelyaresultofthe 6.47 0.79 painandthereisnothingIcandoabout it. Withthepain,Icannevergetmyself comfortableinbed. Thepainisalwaystherewhenyoutryto haveagoodnight’ssleep. WhenIaminpain,Isimplycan’tgetto sleepnomaXerhowhardItry. IknowIcan’tsleepthroughthenight becausethepainwillwakemeup. 7.50 0.82 0.12 7.31 0.78 0.05 6.94 0.64 0.31 6.42 0.64 0.32 Igetveryannoyedwhenthepainwakes meup. 6.39 0.18 0.64 Notsleepingwellisgoingtomakemy painworsethenextday. Iwon’tbeabletocopewiththepainifI 5.01 0.06 0.83 4.68 0.11 0.88 UnlessIgetridofthepain,Iwon’tsleep well. 5.98 0.26 0.65 Theinsomniaistakingawayoneofmy fewrespitesfrompain. 5.56 0.24 0.65 58.81 Internalconsistency(α)ofitemsinbold 0.84 29.15 0.82 29.66 0.81 Meanscore(SD)ofitemsinbold 6.93 (2.14) 5.53 (2.51) don’tsleepwell. Varianceaccountedfor(R2) 6.23 (2.00) CONCURRENTVALIDITY In Sample 1, PBAS scores significantly correlated moderately withDBAS-16(r=.65),APSQ(r=.57)andISI(r=.37) Sample 4 PBAS scores also showed significant moderate correla&onswithDBAS-16(r=.57),APSQ(r=.45)andISI(r=.64) Age(yrs) Sex(Female%) Ethnicity (Caucasian%) PainduraLon (yrs) Painseverity (0-10NRS) InsomniaduraLon (yrs) Insomniaseverity (ISI) Sample1 (n=137) Sample2 (n=26) Sample3 (n=20) Sample4 (n=62) 46.0(11.3) 75.9 72.3 50.1(10.5) 53.8 80.8 48.5(8.9) 90.0 65.0 52.3(11.1) 67.7 100 8 4.3 6.1 8 5.7(2.6) 6.1(2.3) 6.1(1.8) 5.1(2.3) 5 4 6 4.5 20.4(3.9) 20.4(3.6) 20.3(3.3) 14.4(8.0) Figure1TEMPORALSTABILITY SignificantcorrelaLon(r=0.91)&nosignificantchangebetween PBASmeanscoresoneweekapart(t(25)=0.44,p=0.66) 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Figure2TREATMENTSENSITVITY Significant reducLons in mean PBAS scores from pre to post- treatment following hybrid cogniLve behavioural therapy for sleep&painmanagement(t(19)=6.94,p<0.0001,r=.85) 10 8 6 4 2 0 Pre-Treatment Post-Treatment PREDICTIVEVALIDITY Using a stepwise mul&ple regression model, PBAS scores significantly predicted ISI scores individually accoun&ng for 14% and 40% of the variance respec&vely in Sample 1 and Sample 4. PBAS also jointly predicted ISI scores with DBAS-16 in Sample 1 accoun&ngfor17%ofthevariance&withAPSQscoresinSample 4accoun&ngfor47%ofthevariance. Only PBAS scores emerged as a significant predictor of BPI pain interference scores in Sample 1, accoun&ng for 14% of the variance. CONCLUSIONS Pain-relatedsleepbeliefsappeartobeanintegralpartofchronic painpa&ents’insomniaexperience. These ini&al findings suggest that the PBAS can be used as a reliable, valid, and easily administered tool to quan&fy these perceivedbeliefs. Contact:e.f.afolalu@warwick.ac.uk