Computer lab 9: One-way ANalysis Of VAriance (ANOVA)
advertisement

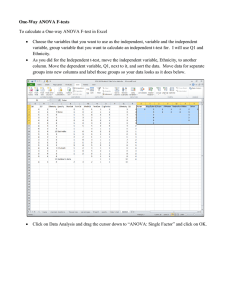
Computer lab 9: One-way ANalysis Of VAriance (ANOVA) In linear regression we study the relationship between a response variable and one or more explanatory variables. If one explanatory variable is a qualitative variable, then we have to form dummies for it instead and we are the able to fit a regression model. Now the analysis of the regression coefficients is equivalent to comparison of the mean values for each value of the qualitative variable. Analyzing a analysis of variance model (ANOVA model) is more intuitive then a regression model. In ANOVA, the explanatory variables are called factors and there values factor levels. The explanatory variables can be quantitative but in pure ANOVA there are only factors. Learning objectives After reading the recommended test and performed the computer lab the student shall have knowledge in: Formulate a one-way ANOVA model in two ways and explain how the model parameters can be interpreted. Use a data set and make statistical inference about the parameters in the model by using SAS. Understand the relationship between a regression model and a ANOVA model. Recommended reading Chapter 16.1-16.8 i Kutner et al Exercise Consider the dataset in exercise 16.7 in the textbook. a) Perform descriptive statistics on the data set. b) Use One-way ANOVA in Minitab and perform dotplots and boxplots for each level by using the Graph menu. Study the plots. Are there any notable differences between the levels? Does the variances appear to be equal? c) Calculate all Tukey-intervals. Which factor level means are significantly different? d) Run proc glm in SAS and save fitted values and residuals. Plot them. Are you satisfied? To hand in Nothing of the exercise above 1. Solutions to exercises 16.5 and 16.16. To create the graph in 16.5a, use Minitab: Graph → Probability Distribution Plot. 2. Solution to exercise 16.12 b, c, d, e and f. Hand in no later than Wednesday 30th October to tommy.schyman@liu.se.