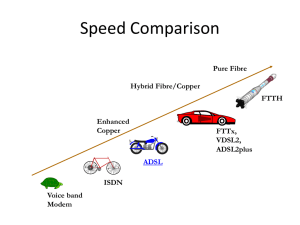
Multiple Play: Market and Policy Trends in OECD Countries Dimitri Ypsilanti
advertisement

Multiple Play: Market and Policy Trends in OECD Countries Dimitri Ypsilanti OECD www.oecd.org/sti/telecom ITU-T IPTV Global Technical Workshop 12-13 October 2006 1 D e N nm et he a rk rl a nd Ic s el an d Sw Ko i tz rea er la n Fi d nl a N nd or w Sw ay ed en U C ni a na te d Ki da ng do U Bel m ni te giu m d St at es Lu J a x e pa m n bo u Au rg st ri Fr a an Au ce st r G ali a er m an y Sp ai n Ita l N Por y ew tu g C ze Zea a l ch l a R nd ep ub l Ire i c la H nd un ga ry Po la n Sl ov Tu d a k rk R ey ep ub M lic ex ic G o re ec e OECD Broadband (June 2006) OECD Broadband subscribers per 100 inhabitants, by technology, June 2006 35 DSL Cable Other OECD average 30 25 20 15 OECD average 10 5 0 Source: OECD 2 Convergence (Step 1): Multiple play Network Services Voice (Fixed) Telecom Television Cable TV Internet Mobile Network Voice (mobile) Other 3 Convergence (Step 2): Next generation networks Network Services Fixed Copper Fibre Wireless 3G Wi-Fi WiMAX Satellite UWB IP platform with QoS Voice (FMC) Video Internet Other 4 Development of multiple play (88 firms in 30 OECD countries) Triple play Double play ADSL Cable Fibre 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 5 Average broadband speeds OECD average broadband speeds, by technology, Mbit/s, September 2005 56.38 53.27 Download Upload 7.49 6.90 0.70 ADSL 0.65 Cable Fibre 6 Need for speed… (10000 feet = 3.12km) Source: http://www.farina1.com/bookmark/000004/2005/02/27/00020260.HTM 7 Broadband pricing per Mbit/s, by technology Broadband costs per Mbit/s, by technology, Septem ber 2005, USD/PPP Yahoo! BB (Japan) NTT West (Japan) KT (Korea) Bredbandsbolaget (Sw eden) Glocalnet (Sw eden) Mstar (USA) Lyse (Norw ay) Smart Telecom (Ireland) Fibre J:COM (Japan) Noos (France) UPC Norw ay (Norw ay) UPC Chello extreme Kabel Deutschland (Germany) Com Hem (Sw eden) UPC (Austria) Cogeco (Canada) Telenet (Belgium) C&M (Korea) Welho (Finland) Casema (Netherlands) Telstraclear (New Zealand) TV Cabo (Portugal) Comcast (USA) Cable Hanaro (Korea) Free Telecom (France) TeliaSonera (Sw eden) Versatel (Netherlands) Sonera (Finland) Internode (Australia) France Telecom (France) Homechoice (UK) Hive (Iceland) Elisa (Finland) Arcor (Germany) T-Com (Germany) Cabovisao (Portugal) Simmin (Iceland) KPN (Netherlands) ADSL $0 $4 $8 $12 $16 8 Percentage of operators offering unlimited nationwide calling to fixed lines, by technology 35% 32% 29% ADSL Cable Fibre 9 Average number of video channels available, by technology Average num ber of video channels available, by technology, Sept 2005 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 ADSL Cable Fibre Satellite 10 Top offers (unlimited fixed calling) Company Free Telecom Casema Versatel Kabel Deutschland Cablecom TeliaSonera France Telecom Lyse Mstar Smart Telecom Noos Telenor TDC Telewest Belgacom SBC Type ADSL Cable ADSL Cable Cable ADSL ADSL Fibre Fibre Fibre Cable ADSL ADSL Cable ADSL ADSL Country France Netherlands Netherlands Germany Switzerland Sweden France Norway USA Ireland France Norway Denmark UK Belgium USA Price USD (PPP) 32.50 48.43 60.62 68.77 71.83 75.00 78.98 80.86 90.26 91.38 91.89 98.54 100.68 106.50 113.54 124.97 Price USD 36.72 53.75 67.28 78.40 102.72 92.25 89.25 120.48 90.26 122.44 103.83 146.83 143.97 119.28 124.89 124.97 Down (kbit/s) 20 000 10 000 20 000 6 200 2 000 24 000 8 000 4 000 15 000 2 000 10 000 4 000 4 096 1 000 4 000 3 000 Bit Cap (MB) TV Chan 93 42 1 38 87 23 34 23 24 70 100 25 18 100 42 60 30 000 11 Top offers (timed/charged fixed calls) Company Yahoo! BB NTT West Welho Elisa Auna KT J:COM Com Hem Simmin Sonera Aliant Bell Canada Bigpond AON TCNZ Telefonica Type Fibre Fibre Cable ADSL Cable Fibre Cable Cable ADSL ADSL ADSL ADSL ADSL ADSL ADSL ADSL Country Price USD (PPP) Japan 29.27 Japan 44.93 Finland 48.59 Finland 50.62 Spain 54.40 Korea 62.81 Japan 73.28 Sweden 73.49 Iceland 78.29 Finland 87.54 Canada 90.14 Canada 92.17 Australia 92.54 Austria 93.78 New Zealand 95.50 Spain 95.84 Price USD Down (kbit/s) 39.22 60.20 61.71 64.28 51.13 54.01 98.20 90.39 126.05 111.18 94.65 96.77 99.01 105.03 101.23 90.09 100 000 100 000 6 000 8 000 2 048 100 000 30 000 8 000 6 000 24 000 5 000 5 000 1 500 2 048 2 000 1 000 Bit Cap (MB) TV Chan 10 000 15 000 10 000 12 24 21 12 12 50 44 100 35 10 12 70 53 33 13 36 48 Bit caps and limitations on service Com pany Country Bit Cap MB Belgium Versatel Iceland Video Voice call Podcasts DIVX Video 2064 kbps 64 kbps 30 m in 1.5 hours Minutes Minutes Dow nloads Dow nloads 500 32 1 042 17 1 Og Vodafone 2 000 129 4 167 67 3 Portugal AR Telecom 6 000 388 12 500 200 9 Portugal Portugal Telecom 8 000 517 16 667 267 11 Portugal TV Cabo 8 000 517 16 667 267 11 Australia Bigpond 10 000 646 20 833 333 14 New Zealand TCNZ 10 000 646 20 833 333 14 New Zealand Telstraclear 10 000 646 20 833 333 14 Australia Optus 12 000 775 25 000 400 17 Austria AON 15 000 969 31 250 500 21 UK BT 15 000 969 31 250 500 21 Ireland Eircom 16 000 1 034 33 333 533 23 Luxembourg Coditel 20 000 1 292 41 667 667 29 Austria inode 20 000 1 292 41 667 667 29 13 Mobile multiple play (France) Prices Web access TV EUR 0.20 per minute EUR 0.98 per megabyte EUR 0-0.25 per minute for the video + EUR 0.10 per minute for the connection Charged on traffic as above, but roughly EUR 0.40 per minute of video. TV free on weekends for one year 30 minute sitcom EUR 10.50 1.5 hour movie EUR 31.50 EUR 12.00 EUR 36.00 14 Slingbox Television without borders US FR 15 Multiple Play and Convergence Q Merging of two different traditions: – – Q Q Q Q Broadcasting: High public impact, high relevance for democracy and society; Distribution via scarce resources; Policy focus on plurality of voices, and neutrality of news, quality of information and public decency; Active government interference, especially on content layer Telecommunications: No scarcity: access to networks for anyone; Policy focus on liberalisation, competition and innovation; No government interference with what’s transmitted Restrictive broadcasting licensing declines, competition increases – less scarcity Development of multiplatform environment Lowering of access barriers: active consumers on different layers. Enables interactivity, consumers produced content and multimedia 16 Key policy issues Q Q The evolution of video regulation: How and if existing regulations should apply to linear (traditional broadcast) and non-linear (streamed, time shifted) video delivery How to maintain social and cultural objectives (universal access – telephony, broadcasting; plurality of voices, cultural diversity, consumer protection); Q Q Q Q Q Q Must be vigilant against anti-competitive behaviour from firms using bundled services to leverage market power Consumers should retain the ability to access competitive services from outside service providers in a network-neutral manner – Avoid walled gardens Balancing equal access to services with QoS demands Limited access to content (such as exclusive contracts) could hinder alternative multiple play providers Current ADSL technologies limited in bandwidth so need to invest in fibre The future role of “must carry" regulations in a converged environment Retransmission rights & access to content; 17