Implementation of the Mid Term Guidelines (MTG) in the real network project 2002-12-11
advertisement

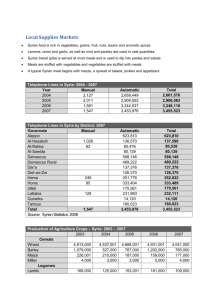
2002-12-11 Implementation of the Mid Term Guidelines (MTG) in the real network project Jakov Stojanović, MOBTEL ”Serbia”, Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro, Network Planning Centre, Radio Network Optimisation Group Manager Milan Gospic, ERICSSON d.o.o., Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro, Senior Support Engineer Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Agenda • Implementation of MTG in Serbia and Montenegro for Mobile Operator Mobtel • GSM/GPRS network as a first step in transition of existing 2G network towards IMT-2000: – GSM (Evolved) Core Network – GPRS protocols and coding schemes – EDGE/EGPRS implementation – some examples of Radio-Network statistics – definition and descriptions of major KPIs • Pre-commercial trial WCDMA/UMTS network Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 1 2002-12-11 Implementation of MTG • Transition towards IMT-2000 – A core network with links to the PSTN, ISDN, the Internet/Intranet and external mobile and data network – Radio Access Network based on the radio-interface IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread (WCDMA/UMTS) – Dual-mode and multi-mode terminals allowing subscribers to enjoy services on pre-IMT-2000 and IMT-2000 network Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 GSM (Evolved) Core Network • For the support of packet data services, GSM (Evolved) Core Networks have been complemented by IP-based GPRS-backbone networks providing a specific fast Mobile Management to the packet data services, capable of handling fast handovers for realtime packet data services (Mid Term Guidelines) Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 2 2002-12-11 GSM/GPRS network diagram Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 GPRS protocols Appl. Appl. TCP UDP TCP UDP IP IP SNDCP SNDCP GTP GTP IP IP L2 L2 L1 L1 LLC LLC Relay LLC RLC RLC BSSGP BSSGP MAC MAC FR FR PHY PHY L1 L1 MS BSS SGSN L2 L2 L1 L1 GGSN Host Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 3 2002-12-11 Network upgrades Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 EDGE – 8 PSK modulation Currently: GMSK Modulation EDGE: 8PSK Modulation Q (0,1,0) (0,0,0) “1” (0,1,1) I I (0,0,1) “0” Q (1,1,1) (1,0,1) (1,1,0) (1,0,0) “1 bit per symbol” “3 bits per symbol” Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 4 2002-12-11 GPRS/EGPRS coding schemes kbps 60 59.2 54.4 50 40 44.8 30 29.6 20.0 20 12.0 11.2 8. 0 14.8 17.6 GPRS MCS9 MCS8 MCS7 MCS6 MCS5 MCS4 MCS3 MCS2 MCS1 CS4 8.4 CS3 CS1 0 14.4 CS2 10 22.4 EGPRS 8PSK modulation GMSK modulation Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 EDGE/EGPRS implementation Internet GPRS MS GPRS Protocol EDGE BTS TRU EDGE MS EDGE Protocol SGSN GGSN GGSN PCU No changes Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 5 2002-12-11 Radio Network Performance (Circuit Switched) • • • • Accessibility – relates to blocked calls Retain ability – relates to dropped calls Integrity – relates to speech quality All of these can be measured and translated to into a user perception of service quality Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Network Performance (Packet Switched) • It is much more difficult to define counters and formulas and relate these to the user perception of service quality • There are two main reasons: – GPRS/EDGE (EGPRS) system has many layers of protocols – GPRS/EDGE (EGPRS) is a bearer for a number of different applications, so user perception of network performance can vary depending on application used in session Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 6 2002-12-11 Radio Network Performance (Packet Switched) • The Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) focus on the main task – transfer of IP packets and are grouped into following areas: – Level one performance indicators – directly related to the ability to transport IP packets (for example the IP throughput on cell level) – Level two performance indicators - indirectly related to the ability to transport IP packets. They should be used for trouble-shooting purposes to identify the specific factors that are causing the level one indicators to show poor performance Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Network Performance (Packet Switched) • The factors that can affect the user perception of the GPRS/EDGE (EGPRS) services: – Quality of the radio link – Circuit Switched (CS) traffic load – Packet Switched (PS) traffic load – Channel allocation and reservation – MS capability – Users mobility and QoS profile – Operator parameter setting – TCP/IP and other effects Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 7 2002-12-11 Radio Network Performance PS Level One - IP throughput • IP throughput (measured on LLC layer) - similar to "modem speed" concept for fixed internet • The factors that can affect: – Poor radio link quality (Level two) – Less PDCH reserved than requested by user (Level two – Multi slot utilisation) – PDCH reserved by other users (Level two – GPRS traffic load) – QoS scheduling prioritizing different users – Delays in setup of downlink Temporary Block Flow (TBF) Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Network Performance PS Level One - IP throughput • The factors that could affect the IP throughput but are not included in the measured IP throughput: – Discard of the contents of the IP buffer in the MS or in the PCU (Level one – IP buffer discard) – Cell reselection during transfer (Level one – discards due to flush) – Delays in setup of uplink Temporary Block Flow (TBF) Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 8 2002-12-11 Radio Network Performance PS Level One - IP throughput • Additional factors: – The total time to perform a data transfer – Effects of protocol layers above the LLC layer (for example TCP slow start) – Outside events that cause IP packets to be retransmitted by the TCP protocol Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Network Performance PS Level One - IP throughput • The Mobile Station capability is another factor that can impact the measured IP throughput. Factors are: – GPRS or EDGE (EGPRS) capable – Multi-slot capability (Level two – Multi slot utilisation) – Frequency band capability – 3GPP Release of the mobile station Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 9 2002-12-11 Radio Network Performance PS Level One - IP buffer discards • IP throughput measures the speed with witch the IP packets are shipped to and from user • IP packets can’t transfer to user – the entire contents of the IP buffer will be discarded (user experience is dependent on the application running) • The contents of the IP buffer may be discarded due to inter Routing Area or Inter Cell Reselection – “planned” IP buffer discard Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Network Performance PS Level One - IP buffer discards • Absolute number of IP buffer discards is a relevant performance indicator • It is suggested to calculate the number of IP buffer discards per data transfer session minutes Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 10 2002-12-11 Radio Network Performance PS Level Two – Radio Link Quality • The quality of each users radio link determines the maximum IP throughput they can achieve • The perfect radio link quality is represented by: – Close to 12 kbit/s for CS-1/2 transfers – Close to 20 kbit/s CS-1/2/3/4 transfers – Close to 59 kbit/s for EDGE (EGPRS) transfers Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Network Performance PS Level Two – Mobility • The mobility of the user will affect the IP throughput • If they remain in one cell for the duration of the data session than there will be no impact • If they move rapidly between cells there will be a large impact • User experiences due to cell reselection is very dependent on the application type Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 11 2002-12-11 GPRS/EGPRS radio network dimensioning • The objective is that GPRS/EGPRS users will experience an estimated throughput on application level • The throughput achieved is depended on the channel capabilities, amount of GPRS and EGPRS traffic, interference environment, Mobile Station multi slot class and the type of traffic generated by the users • It is based on Radio Network statistics Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Network Performance PS Level One - IP buffer discards 20.00 18.00 16.00 14.00 12.00 10.00 8.00 6.00 4.00 2.00 BSC TKC 1 BSC TKC 2 BSC ANEX BSC AERO BSC NOVI SAD 1 BSC NOVI SAD 2 BSC NIŠ 27-May-05 26-May-05 25-May-05 24-May-05 23-May-05 22-May-05 21-May-05 20-May-05 19-May-05 18-May-05 17-May-05 16-May-05 15-May-05 14-May-05 13-May-05 12-May-05 11-May-05 9-May-05 10-May-05 8-May-05 7-May-05 6-May-05 5-May-05 4-May-05 0.00 BSC KRAGUJEVAC Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 12 2002-12-11 Radio Network Performance PS Level Two – Radio Link Quality 14.00 12.00 10.00 8.00 6.00 4.00 2.00 BSC TKC 1 BSC T KC 2 BSC ANEX BSC AERO BSC NOVI SAD 1 BSC NOVI SAD 2 BSC NIŠ 27-May-05 26-May-05 25-May-05 24-May-05 23-May-05 22-May-05 21-May-05 20-May-05 19-May-05 18-May-05 17-May-05 16-May-05 15-May-05 14-May-05 13-May-05 12-May-05 11-May-05 9-May-05 10-May-05 8-May-05 7-May-05 6-May-05 5-May-05 4-May-05 0.00 BSC KRAGUJEVAC Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 GSM/UMTS - Common Core Network Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 13 2002-12-11 Core Network upgrades • Horizontally layered network architecture • Separation of control and connectivity layer • Network elements are evolving to adapt to new architecture (control and connectivity) Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Horizontally Layered Network Architecture MGW controlled by network servers, adapt and connect different access types to a common backbone network Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 14 2002-12-11 UMTS Layered Network Architecture Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Radio Access Network • IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread (WCDMA/UMTS): – A spread spectrum system based on direct sequence – It is spectrally efficient – high data rates – Flexibility to manage multiple traffic types (voice and data) – HSDPA (High Speed Downlink Packet Access) is an enhancement – achieves high speeds through the addition of higher order modulation such as 16 QAM Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 15 2002-12-11 Mobtel - Ericsson WCDMA/UMTS Network Diagram – Trial Configuration AEROINŽENJERING LEGEND: TSM -1 Fiber Optic E1 Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Mut Mut Mp, Gr /2 Mp, Gr /2 /1 /1 MSC Server 3.0 TKC Iub /1 Iu-C /2 RXI AERO RBS 1 Iub /2 /10 HLR MSC/STP 2 SMSC /2 /2 MGW 3.0 Iu-C, Iu-U /2 MSC/STP 1 O&M Interface /1 O&M Interface /1 Existing Mobtel GSM Network Mur /1 Mur /1 RXI TKC RNC P2.1 Iub /1 Iu-U Gom, Gn /2 /2 Iu-C, Gr Gom, Gn /2 /2 Iub SGSN W 5.5 /1 1 1 0 1 1 3 1 2 1 5 1 4 1 7 1 6 1 9 1 8 2 2 0 1 3 2 2 2 2 2 4 5 2 7 2 6 2 9 2 8 1 3 0 3 3 3 2 3 4 3 3 5 3 6 7 3 3 9 3 8 4 4 0 1 4 2 1 3 2 G 5 4 7 6 9 8 1 0 1 1 3 1 2 1 5 1 4 7 1 6 1 1 1 8 9 2 2 0 1 2 2 3 2 5 2 4 2 2 6 7 2 9 2 8 1 3 3 0 3 3 2 3 3 5 3 4 3 7 3 6 3 9 3 8 4 1 4 0 T M Summit 48i R Iub /1 PM O RBS 15 O C N S OE L 9 4 5 0 4 4 2 3 4 4 4 5 7 4 4 6 8 4 Summit 48i /1 O&M Interface Traffic Interface Mur,Mub ECDS 2.0 /2 1 1 0 1 RBS 16 1 3 1 2 1 5 1 4 1 1 6 7 1 9 1 8 2 1 2 0 2 3 2 2 2 5 2 4 2 7 2 6 2 9 2 8 1 3 3 0 3 3 2 3 3 5 3 4 3 7 3 6 3 8 3 9 4 0 4 1 4 2 Gn,Gom,Gi /2 Gn,Gom,Gi /2 Netgear switch RBS 20 OMINF RANOS P2.1 OSS RC1.1 GGSN R2 Existing equipment AXI 520 - 4 O&M Network Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Thank you for your attention ! Contacts : jakov.stojanovic@mobtel.co.yu milan.gospic@ericsson.com Damascus, Syria, 13 - 15 June 2005 Rev PA1 16