Akira Hashimoto Chairman , ITU-R Working Party 9B
advertisement

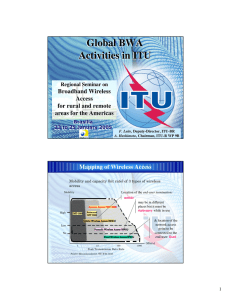
10 September , 2004 Akira Hashimoto Chairman , ITU-R Working Party 9B 1 This presentation focuses on; ? What is “ Wireless Access ” ? ? ITU-R standardization activity on BWA ? Recent topics including liaison with SDOs ( *) (* ) Standardization Development Organization 2 1 Definitions of Wireless Access in the ITUITU-R Recommendation F.1399 (Vocabulary of terms for wireless access) FWA: Fixed Wireless Access wireless access application in which the location of the end-user termination and the network access point to be connected to the end-user are fixed. MWA: Mobile Wireless Access wireless access application in which the location of the end-user termination is mobile. NWA: Nomadic Wireless Access wireless access application in which the location of the end-user termination may be in different places but it must be stationary while in use. 3 Mapping of Wireless Access Mobility and Bit rate of 3 types of Wireless Access Mobility Systems beyond IMT-2000 High IMT-2000 Enhanced IMT-2000 Mobile Wireless Access Low Nomadic Wireless Access No Fixed Wireless Access 1 10 100 1000 (Mbit/s) Peak Transmission Data Rate (The Figure is based on Recommendation ITU -R M.1645.) 4 2 Studies on Wireless Access in ITU-R IMT-2000 & beyond P r e-IM T sys tems Mobile Service Study Group 8 Working Party 8A NWA Fixed Service WP 8F Working Party 8F MWA FWA WP 8A RLA Ns -deriv Mobile A FW ed General FWA Joint Rapporteur Group 8A-9B (* ) Working Party 9B WP 9B Study Group 9 ( * ) JRG 8A-9B was disbanded in November 2003 . 5 ITU-R Recommendations recently developed in relation to FWA systems Rec. ITU-R Terminology Performance & Availability Characteristics Short title F.1399 Vocabulary of terms for wireless access F. 757 Basic system requirements and performance objectives for FWA using mobile -derived technologies F.1400 Performance and availability objectives for FWA to PSTN F.1490 Generic requirements for fixed wireless access (FWA) systems F.1499 Radio transmission systems for fixed BWA based on cable modem standards F.1401 Considerations for the identification of possible frequency bands for fixed wireless access and related sharing studies F.1488 Frequency block arrangements for FWA systems in the range 3 400-3 800 MHz F.1496 Radio-frequency channel arrangements for fixed wireless systems operating in the band 51.4-52.6 GHz Radio frequency arrangement F.1497 Radio-frequency channel arrangements for fixed wireless systems operating in the band 55.78-59 GHz F.1519 Guidance on frequency arrangements based on frequency blocks for systems in the fixed service F.1567 RF channel arrangement for digital fixed wireless systems operating in the frequency band 406.1 to 450 MHz F.1568 RF block arrangements for FWA systems in the range 10.15-10.3/10.5-10.65 GHz F.1402 Sharing & Compatibility F.1489 F.1613 Others F.1671 Frequency sharing criteria between a land MWA system and a FWA system using the same equipment type as the MWA system A methodology for assessing the level of operational compatibility between FWA and radar systems when sharing the band 3.4-3.7 GHz Operational and deployment requirements for FWA systems in Region 3 to ensure the protection of systems in the EESS (active) and the SRS (active) in the band 5 250-5 350 MHz Guidelines for a process to address the deployment of area-licensed fixed wireless systems operating in neighbouring countries Note: Application of some Recommendations include short range ba ck-haul systems 6 3 Development of FWA systems in various environments FWA application Other access media Preferred frequency bands Urban area FWA (Last-1000 m connection) Residential area FWA (Last-100m connection) Upper SHF Lower SHF 10.5 GHz F.1568 18 GHz F. 595 26-28 GHz F. 748 38 GHz F.749 2.4 GHz - 3.4 GHz F.1488 5.3 GHz - 5.5 -5.7GHz - 450 MHz Rural area FWA UHF Below 1 GHz Factors to be considered · High-density deployment · Sharing with space services Optical fibre · Optical fibre · DSL · Wireless LAN · Compatibility with ISM application · Line-of-sight condition · License-exempt use of nomadic wireless access systems for FWA F.1567 Cellular phone - · Line-of-sight condition · Sharing/compatibility with other radio services 7 New 5 GHz frequency allocations approved at WRC-03 5000 5100 5200 5300 5400 5500 Mobile service ( RLAN) 5600 5700 5800(MHz) Mobile service ( RLAN) Fixed service ( FWA) (*) (*) 12 countries in Region 3 only (5.447E) Fixed-satellite service Aeronautical radionavigation service Earth exploration-satellite( active) and Space research service Radionavigation service Radiolocation service ( meteorological, defense, etc) New allocations Existing allocations 8 4 Requirements for RLANs specified in Resolution 229 ( WRC-03) Frequency band Maximum Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power ( EIRP ) 5150-5250 MHz 200 mW ( 10 mW/MHz, 0.25 mW/25 kHz) Indoor use only 200 mW ( 10 mW/MHz ) Basically indoor use*1 5250-5350 MHz Mitigation measures No specification or subject to the elevation angle EIRP must be in accordance mask specified in Rec.ITU - R M.1653 with the mask for outdoor use 2W for FWA*3 5470-5725 MHz Operational restriction 1W ( 50 mW/MHz ) Deployment restriction is subject to Rec.ITU -R F.1613 TPC*2 and DFS are required Indoor / outdoor use *1 Each country is requested to take appropriate measures so that t he predominant number of RLAN terminals are used indoors. *2 EIRP is reduced by 3 dB if not equipped with TPC. *3 12 Countries in Region 3 9 Recent study topics on the fixed service including BWA Application Characteristics Multipoint -to-multipoint systems BWA conveying IP packets or ATM cells Exploitation of bands above 57GHz RF arrangement & spectrum use Future vision of the FS 10 5 Future vision of the Fixed Service ( 1) Draft new Recommendation ; Technology developments and application trends in the FS Exploitation of high frequency bands Increase of frequency utilization efficiency (GHz) ( (bit/sec/Hz) 100 (bit/sec/Hz) 10 20 F.1496 38GHz F.749 F.1497 30 23GHz F.748 18GHz 20 F.595 13GHz F.497 10 1970 15 7.5 1980 1990 2000 2010 512QAM 512 ( Narrow spectrum system) 256 QAM 5 10 (Wide spectrum system) 64QAM 64 2.5 5 (4 PSK) (8 PSK) 1970 16 QAM 1980 Year 1990 2000 2010 Year ( when the ITU -R Recommendation was adopted ) ( when the ITU -R Recommendation was adopted) 11 Future vision of the Fixed Service ( 2 ) Development of FS applications including future vision (GHz) 50 Frequency bandwidth for FS Frequency Single polarization system 52/56GHz 50 Dual polarization system (CCCP) Frequency Utilization Efficiency of multi-state modulation schemes 40 30 access access access access 20 access access 10 access RRS RRS access access RRS RRS RRSRRS RRS RRS RRS RRS 1980 1990 2000 200 2003 2010 Year ( when the ordinate bandwidth has become available) RRS: radio-relay systems, access: FWA and back-haul systems, and HAPS systems in some countries 12 6 Toward Refarming of 4 & 5GHz Bands (Example) Frequency allocation in the R.R. Use of the band in many countries 4200 ? Fixed wireless systems (point-topoint application) 3600 4GHz band FIXED (3600-4200MHz) Fixed-satellite links (space-to-earth direction) ? FIXED-SATELLITE ? MOBILE FS and FSS are sharing the frequency band under the criteria specified in Recommendation ITU-R F.1565 or SF.1485. ? 4400 5000 5GHz band (4400-5000MHz) FIXED FIXED-SATELLITE ? Use of the mobile service has not been reported. ? MOBILE Draft Recommendation ITU-R F.[Trend] (Document 9/9) One administration has reported that in its network use of 4 and5 GHz frequency bands by radio relay systems will be terminated by 2012 with a view to utilize these bands for terrestrial wireless systems for access networks including systems beyond IMT -2000. 13 Scope of Standardization Protocol stack Higher Layer Application - TCP Network layer (IP) Data Link Layer Specified items DLC Sub-layer · Network routing · Mobility management De facto Standard · Send-receive flow control · ARQ control ETSI · QoS control IEEE · Medium access control MAC · Error detection & Sub-layer correction ARIB · Radio frequency arrangement Physical Layer ( PHY) · Modulation/Demodulation Transmission bit rate ·· Necessary bandwidth · Frequency sharing criteria TCP : Transmission Control Protocol IP : Internet Protocol MAC : Medium Access Control DLC : Data Link Control ITU-R Recommendation 14 7 Recommendation on fixed broadband wireless access ( approved in 2000) Recommendation ITU-R F . 1499 Radio transmission systems for fixed broadband wireless access ( ITU-T Recommendation J.112, Annex B) based on cable modem standards ? Complementary Recommendation PHY Layer BWA specifications ITU-R F.1499 MAC Layer and above ? ITU-T J.116 CONTENTS 1. General system requirements 2. Functional assumptions 3. Communication protocols 4. PMD sublayear specifications 5. Downstream transmission convergence sublayer 15 New ITU-R Recommendation on fixed BWA ITU-R Study Group 9 ( Working Party 9B) is developing a draft new Recommendation on fixed BWA, whose specifications are based on the standards agreed at regional standardization development organizations . Candidate specifications for the radio interface for this Recommendation PHY Layer IEEE 802.16 Hiper MAN ETSI BRAN Hiper Access ARIB (Japan) MAC Layer IEEE Std. Part 16 : Air interface for fixed BWA ETSI TS 102 177 ETSI TS 102 178 ETSI TS 101 999 ETSI TS 102 000 ARIB STD T 58 ( P-P) ARIB STD T 59 ( P-M P) - These specifications in this Recommendation will become available electronically through the website. 16 8 Summary Broadband Wireless Access systems ; - are important media in access networks, - will operate in different environments and in various frequency bands, - will be more developed under efficient cooperation between SDOs and ITU-R. 17 9