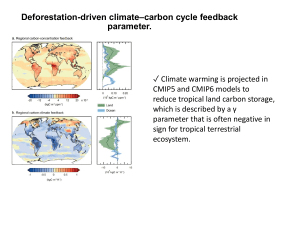
This presentation is included for reflection by
advertisement

This presentation is included for reflection by practitioners in planning for learning and teaching. It is intended for exemplification purposes only. It may be appropriate for some teachers/lecturers to adapt these materials for use within their own context. Causes It is very important in geography that we can categorise causes of climate change into two subgroups. We need to group them into: 1. physical causes 2. human causes. Try the card sort activity, which your teacher will explain. Volcanic dust Ice cap melting Sunspot activity Changing ocean circulation (El Nino/La Nina) Permafrost melting Deforestation Burning fossil fuels Aircraft contrails Cattle farming (methane) Nitrous oxides from power stations CFCs from refrigerators and aerosols Sea level rise Melting ice caps and glaciers. Flooding of low-lying areas such as UK fenlands, Shetland Islands, Bangladesh, Maldives and Japan. Higher water temperatures mean that water expands further, compounding the problem. Polar bear habitats in the northern hemisphere are shrinking. Tourism problems for snow areas. The Mediterranean may become too hot for some tourists. Crop failures. Extinction of species. Bleaching of coral reefs. Tropical diseases such as malaria spreading. Weather becoming less predictable. More flooding, droughts, tropical storms and heat waves. Alternative forms of energy Solar Tidal Wind (on-shore and off-shore) Hydroelectric Electrical cars. Reduce deforestation and increase afforestation. Control population. Reduce energy consumption at school and at home. World summits.