Onsite Exhibit March 2, 2015 Conceptual Framework Data Locations
advertisement

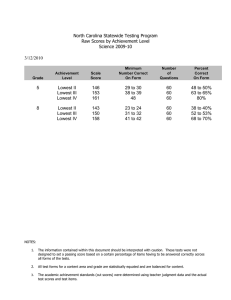
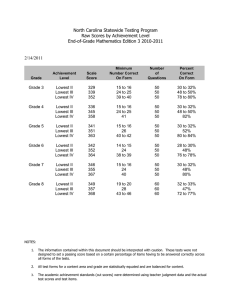
American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Onsite Exhibit March 2, 2015 Conceptual Framework Data Locations This exhibits provides the location for the key assessments in the Conceptual Framework Overview document. All data has been previously report in other exhibits except for the Task Analysis and Case Study. We included the data for these assessments to this exhibit. ! American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Excellence (knowledge of Evidencedbased practice relative to content knowledge and pedagogical practice) & Equity (practices that ensure equitable access to education) Professional Dispositions Developed Through the Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Principles of excellence in combination with equity produces a disposition that centers on a commitment to teaching practices that promote each learner’s growth in the most informed way possible. This includes valuing that all learners need to be taught in ways that best support their diverse learning needs and strengths. This encompasses a belief in fairness and ethics. This disposition encompasses a belief that content knowledge is not a fixed body of facts but is complex, culturally situated, and ever evolving. This means a commitment to keeping abreast of new ideas and understandings in the field. This also includes a commitment to helping learners build literacy and thinking skills to address multiple perspectives in exploring ideas and solving problems both locally and globally. Further at the intersection of excellence and equity is a commitment to work toward every learner’s mastery of disciplinary content and skills. As part of this, teacher candidates value knowledge beyond her/his own content area and values how such knowledge enhances student learning. Key Assessments Impact on Student Learning On-Site Exhibit 3.1.15 Philosophy of Teaching On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Disposition Data, Portfolio Score Report INTASC Standards NCATE Standards 1: Learner Development 2: Learning Differences 4: Content Knowledge 5: Application of Content 7:Planning for Instruction 9:Professional Learning and Ethical Practice 1a: Content Knowledge for Teacher Candidates 1c: Professional and Pedagogical Knowledge and Skills for Teacher Candidates 3c: Candidates’ Development and Demonstration of Knowledge, Skills, and Professional Dispositions To Help All Students Learn 5a: Qualified Faculty American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Excellence (knowledge of Evidencedbased practice relative to content knowledge and pedagogical practice) & Diversity (Belief that all children, regardless of social class, race and ethnicity, disability, are able to learn) Professional Dispositions Developed Through the Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles At the intersection of excellence and diversity, candidates come to understand the need for disrupting the exclusionary forces of dominant discourses and ideologies creating a space for ensuring that all learners are taught using the best practices possible. This includes the belief that all learners can learn and a commitment to valuing social justice and equity for all. This encompasses a commitment to create content that is accessible to all learners regardless or race, class, religion, ability or life orientation and across disciplines and content areas. As a way to further support diverse learners. Teacher candidates are committed to an ongoing exploration of how to use disciplinary knowledge as a lens to address local and global issues. Key Assessments Cultural Issues in Your Classroom Data is available in the TESOL SPA Report. Next set of data will be collected in Spring 2015 during TESL527 Class. Content Based Unit Plan On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Technology (Math, Science, TESOL) and Dispositions (Social Studies) Task Analysis Included in this On-Site Exhibit INTASC Standards NCATE Standards 1: Learner Development 2: Learning Differences 4: Content Knowledge 5: Application of Content 1a: Content Knowledge for Teacher Candidates 1c: Professional and Pedagogical Knowledge and Skills for Teacher Candidates 3c: Candidates’ Development and Demonstration of Knowledge, Skills, and Professional Dispositions To Help All Students Learn 5a: Qualified Faculty American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Professional Dispositions Developed Through the Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Key Assessments INTASC Standards NCATE Standards 3: Learning Environments 5: Application of Content 7: Planning for Instruction 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice. 10: Leadership and Collaboration. 1b: Pedagogical Content Knowledge and Skills for Teacher Candidates 3a: Collaboration between Unit and School Partners 3b: Design, Implementation, and Evaluation of Field Experiences and Clinical Practice 4d: Experiences Working with Diverse Students in P–12 Schools 5b: Modeling Best Professional Practices in Teaching Conceptual Framework within the Special Education Portfolio Report Excellence (knowledge of Evidencedbased practice relative to content knowledge and pedagogical practice) & Community (reflection on the outcomes for students within the greater context of their relation with the communities in which they exist). At the intersection of excellence and community, candidates come to understand what it means to draw from a theoretical and practical knowledge base in constructing supportive learning environments for all learners. This encompasses a belief in creating caring communities, which includes the need for good communication and interpersonal skills as well as an understanding of the impact and use of technology in community building. This also encompasses a belief in creating collaborative partners with parents and community members to inform teaching and learning. Further, teacher candidates value flexible learning environments, which include the use of technology that encourages learner exploration, discovery, and Parent Teacher Conference Evaluation On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Dispositions Student Teaching Evaluation Exhibit 1.4.d Final Evaluation of Student Teaching Data Undergradu ate Initial & Exhibit 1.4.d American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Professional Dispositions Developed Through the Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles expression across content areas. Teacher candidates respect diverse learners’ various strengths and needs and are committed to using this information to plan effective and rigorous instruction across the content areas, within supportive learning environments. Teacher candidates welcome and value collaboration with and contributions and input from families, colleagues, and other professionals in understanding how to best support the learning needs of diverse children. Key Assessments Final Evaluation of Student Teaching Data Graduate Initial Content Based Unit Plan On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Technology (Math, Science, TESOL) and Dispositions (Social Studies) Task Analysis Included in this On-Site Exhibit Conceptual Framework within the Special Education Portfolio Report INTASC Standards NCATE Standards American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Diversity (Belief that all children, regardless of social class, race and ethnicity, disability, are able to learn) & Equity (practices that ensure equitable access to education) Professional Dispositions Developed Through the Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Principles of diversity in combination with equity produce dispositions of commitment to the belief that all children can learn when their diverse learning needs are used to inform curricular decision-making including assessment and evaluation. Encompassing this disposition is a belief in fairness and valuing social justice for all. Subsequently candidates are committed to making accommodations in the assessment and evaluation conditions, especially for learners with disabilities and language learning needs. Key Assessments Creating and Evaluating Assessments On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Dispositions INTASC Standards NCATE Standards 2: Learning Differences 6: Assessment 7: Planning for Instruction 8: Instructional Strategies 1g: Professional Dispositions for All Candidates 4a: Design, Implementation, and Evaluation of Curriculum and Experiences 3c: Candidates’ Development and Demonstration of Knowledge, Skills, and Professional Dispositions To Help All Students Learn 4b: Experiences Working with Diverse Faculty 4c: Experiences Working with Diverse Candidates 3: Learning Environments 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice 10:Leadership and Collaboration 3a: Collaboration between Unit and School Partners 4b: Experiences Working with Diverse Faculty 5b: Modeling Best Professional Practices in Teaching Impact on Student Learning On-Site Exhibit 3.1.15 Further, candidates are committed to the ethical use of multiple types of assessment processes to support, verify, and document the learning of diverse learners and promote their growth. Community (reflection on the outcomes for students within the greater context of their relation with the communities in At the intersection of community and equity, candidates believe that all children can learn in respectful environments where their diverse learning needs are used to inform curricular decision-making and where their families and caregivers are part of the teaching/ learning process. Philosophy of Teaching On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Disposition Data, Portfolio Score Report American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles which they exist). & Equity (practices that ensure equitable access to education) Community (reflection on the outcomes for students within the greater context of their relation with the communities in which they exist). & Diversity (Belief that all children, regardless of social class, race and ethnicity, disability, are able to learn) Professional Dispositions Developed Through the Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles This encompasses a commitment to fairness and a belief in responsible and compassionate citizenry. At the intersection of community and diversity, candidates value the understanding that all learners need healthy, safe, and engaging environments for learning whereby the children’s families and caregivers are part of the educational process. As part of this disposition candidates believe that all learners can learn and that collaborating with parents, caregivers and community members is valuable in developing supportive learning environments for diverse learners. Further teacher candidates value planning as a collegial activity that takes into consideration the input of learners, colleagues, families, and the larger community. Key Assessments INTASC Standards NCATE Standards 3: Learning Environments 6: Assessment 7: Planning for Instruction 8: Instructional Strategies 9: Professional Learning and Ethical Practice 10:Leadership and Collaboration 2c: Use of Data for Program Improvement 3b: Design, Implementation, and Evaluation of Field Experiences and Clinical Practice Impact on Student Learning On-Site Exhibit 3.1.15 Parent Teacher Conference Evaluation On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Dispositions Reflection/ Case Study Included in this On-Site Exhibit Conceptual Framework within the Special Education Portfolio Report American University – School of Education, Teaching, and Health Conceptual Framework Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Professional Dispositions Developed Through the Conceptual Framework Organizing Principles Key Assessments Lesson Plan Analysis On-Site Exhibit 3.2.15 under Dispositions INTASC Standards NCATE Standards Score Report Final Semester from: Fall 2013 Final Semester to: Summer 2014 Portfolio Type: Special Ed Portfolio 1a. Content Knowledge for Teacher Candidates and 4a. Design, Implementation, and Evaluation of Curriculum and Experiences (InTASC 2) 1b. Pedagogical Content Knowledge and Skills for Teacher Candidates 1c. Professional and Pedagogical Knowledge and Skills for Teacher Candidates 1g. Professional Dispositions for All Candidates Standard 1: Foundations -­ Philosophy of Education Mean: 2.2703 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 3 Scores of 2: 21 Scores of 3: 13 Standard 2: Development & Characteristics of Learners / Standard 3: Individual Learning Differences -­ LD 1 & 2 Exams Mean: 2.3649 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 3 Scores of 2: 41 Scores of 3: 30 Standard 2: Development & Characteristics of Learners / Standard 3: Individual Learning Differences -­ Case Study or Research Project Mean: 2.2895 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 8 Scores of 2: 38 Scores of 3: 30 Case Study Data Standard 7: Instructional Planning -­ Task Analysis Mean: 2.4595 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 1 Scores of 2: 18 Scores of 3: 18 Standard 4: Instructional Strategies / Standard 5: Learning Environments & Social Interactions -­ Reading Takeover Week Mean: 2.3649 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 5 Scores of 2: 37 Scores of 3: 32 Task Analysis Data Mean: 2.3514 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 3 Scores of 2: 18 Scores of 3: 16 2.3553 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 6 Scores of 2: 37 Scores of 3: 33 Mean: 2.4595 Median: 3 Scores of 1: 2 Scores of 2: 16 Scores of 3: 19 Mean: Mean: 2.4324 Median: 3 Scores of 1: 4 Scores of 2: 13 Scores of 3: 20 Mean: 2.3026 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 9 Scores of 2: 35 Scores of 3: 32 Mean: 2.4595 Median: 2 Scores of 1: 0 Scores of 2: 20 Scores of 3: 17