4/28/2016 Sea Level Changes • Why Important? • Time Orders
advertisement

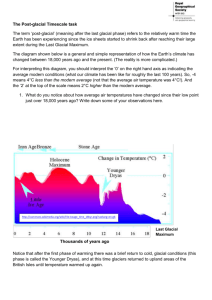
4/28/2016 5 Billion Years of Earth’s Climate History Sea Level Changes • Why Important? • • • • • The dark blue areas indicate periods of continental glaciations or Glacioeustatic Sea Level Changes Possible driving forces for climate and S.L. change: Time Orders Eustacy Recognizing Eustacy? Glacioeustatic S.L. Change Geoeustatic S.L. Changes •Plate Tectonics (location of continents / ocean currents + long term changes in SFS rates) •Greenhouse Gases (anthropogenic or natural) •Milankovitch Cycles Future Estimates of Sea Level Rise .5 meters / 50cm / 1.64ft or 5mm/yr 0.2 meters / 20cm / .72ft or 2mm/yr Milutan Milankovic, 1879 – 1958 Serbian geophysicist, Civil Engineer GLACIOUESTATIC SEA LEVEL CHANGES These changes in sea level have been occurring for the last ~2.8 MY. This Epoch of time is called the Pleistocene. Many refer to the Pleistocene as “The Ice Ages”. The Pleistocene consists of both “Glacial Maximums” = cold times, larger polar caps, low stands of sea Level, AND “Interglacials” = warmer times, less ice and high stands of sea level. Some people regard Glacial Maximums & Ice Ages as Synonyms We are currently in an Interglacial, a high stand of SL, warmer. Most of the Pleistocene consisted of Glacial Maximums, colder. GLACIOUESTATIC SEA LEVEL CHANGES 1. Very important for coastal landforms. 2. They result from advancing and retreating glaciers and the polar ice caps. A long term climatic puzzle ??? 3. There is a change in volume of seawater and ice (polar caps) 4. Last Glacial Maximum was approximately 16,000 to 18,000 years B.P. Sea level has been rising ever since.......... most places....... Sea level is still slowly rising in 5. During glacial episodes as much as 50 million cubic kilometers (12 million cubic miles) of sea water were removed from the oceans and transformed into glacial ice – sea level dropped 350 – 410 feet. 6. During the last Glacial Maximum sea level was approximately 120 meters lower than today. San Francisco Bay was mostly dry..... much of Monterey Bay Continental Shelf was exposed...... 7. If all the ice in Greenland and Antarctica melted in one week, sea level would rise approximately 70 meters worldwide. 1 4/28/2016 Some Evidence of Climatic Instability and past Glacioeustatic Sea Level Changes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Glacial Deposits on Continents / Cont. Shelves Pluvial Lakes Relic River Sediments Tidal Gauge Data and Satellite Altimetry Wave Cut Terraces near shorelines Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Isotopes preserved in Glacial Ice and Planktonic oozes. 7. Seismic Reflection Profiling Continental Shelves...... onlapping and offlapping sediments 8. Estuarine stratigraphy U-shaped Valley in Alaska Glacial Grooves at Kellys Island Lake Erie and Manhatten NY Glacial Events recorded in the Mid-continent region of North America during the Pleistocene • • • • • • • Postglacial Age (Holocene) WISCONSIN STAGE (late Pleistocene) Sangamon Interglacial Age ILLINOIAN STAGE Interglacial Age KANSAN STAGE Interglacial Age • NEBRASKAN STAGE (early Pleistocene) 2 4/28/2016 Some Evidence of Climatic Instability and past Glacioeustatic Sea Level Changes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Glacial Deposits on Continents / Cont. Shelves Pluvial Lakes Relic River Sediments Tidal Gauge Data and Satellite Altimetry Wave Cut Terraces near shorelines Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Isotopes preserved in Glacial Ice and Planktonic oozes. 7. Seismic Reflection Profiling Continental Shelves...... onlapping and offlapping sediments 8. Estuarine stratigraphy Some Evidence of Climatic Instability and past Glacioeustatic Sea Level Changes Glacial Maximum 17,000 years B.P. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Glacial Deposits on Continents / Cont. Shelves Pluvial Lakes Relic River Sediments Tidal Gauge Data and Satellite Altimetry Wave Cut Terraces near shorelines Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Isotopes preserved in Glacial Ice and Planktonic oozes. 7. Seismic Reflection Profiling Continental Shelves...... onlapping and offlapping sediments 8. Estuarine stratigraphy Relic River Deposits Tidal Gauge Data 3 4/28/2016 The San Francisco tide station has measured the rise and fall of tides continuously since June 30, 1854 Some Evidence of Climatic Instability and past Glacioeustatic Sea Level Changes San Clemente Island 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Glacial Deposits on Continents / Cont. Shelves Pluvial Lakes Relic River Sediments Tidal Gauge Data and Satellite Altimetry Wave Cut Terraces near shorelines Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Isotopes preserved in Glacial Ice and Planktonic oozes. 7. Seismic Reflection Profiling Continental Shelves...... onlapping and offlapping sediments 8. Estuarine stratigraphy Greenland Ice Sheet Project 2 (GISP2) Drilling Station Oxygen naturally occurs in 3 isotopes: 16O (99.763%) 17O (0.0375%) 18O (0.1995%) 4 4/28/2016 Temperature Change for the Past 160,000 years from the Vostok Ice Core in Eastern Antarctica (3,623m) Oxygen-18 is decreasing (proportionately) in the ice as more O-16 is evaporating from the world’s oceans Glacial ice around the world will have less O-18 proportional to O-16 during glacial maximums A decrease in 1 part per million of Oxygen-18 in glacial ice reflects a 1.5 degree Celsius drop in air temperature at the time the H20 originally evaporated from the oceans. 1ppm decrease= 1.5 degree C drop 2ppm decrease = 3 degree C drop 3 ppm decrease = 4.5 degree C drop 4ppm decrease = 6 degree C drop 5ppm decrease = 7.5 degree C drop Planktonic Organisms Average temperature over past 900,000 years Cold periods, less O-16, more O-18 in shells Average surface temperature (°C) Warm periods, more O-16, less O-18 in shells 17 16 15 Today’s Temperature 14 13 12 11 10 9 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 Thousands of years ago 200 100 Present 5 4/28/2016 Today’s sea level 0 0 –130 –426 250,000 200,000 150,000 100,000 Years before present Some Evidence of Climatic Instability and past Glacioeustatic Sea Level Changes Height below present sea level (feet) Height above or below present sea level (meters) Variations in Earth’s Temperature over the past 850,000 years 50,000 0 Present Seismic Reflection Profiling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Glacial Deposits on Continents / Cont. Shelves Pluvial Lakes Relic River Sediments Tidal Gauge Data and Satellite Altimetry Wave Cut Terraces near shorelines Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Isotopes preserved in Glacial Ice and Planktonic oozes. 7. Seismic Reflection Profiling Continental Shelves...... onlapping and offlapping sediments 8. Estuarine stratigraphy Some Evidence of Climatic Instability and past Glacioeustatic Sea Level Changes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Glacial Deposits on Continents / Cont. Shelves Pluvial Lakes Relic River Sediments Tidal Gauge Data and Satellite Altimetry Wave Cut Terraces near shorelines Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Isotopes preserved in Glacial Ice and Planktonic oozes. 7. Seismic Reflection Profiling Continental Shelves...... onlapping and offlapping sediments 8. Estuarine stratigraphy 6 4/28/2016 Geouestatic Sea Level Changes @18cm/yr for 20 mill yrs = 3,600km @4cm/yr for 20 mill yrs = 800km 20 7 4/28/2016 Rising Sea Level………. 8