Use of Outside Experts in FDA’s Premarket Evaluation of Medical Devices
advertisement

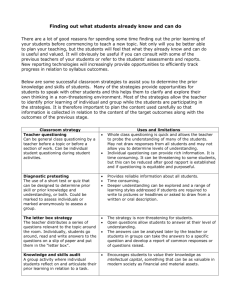
Use of Outside Experts in FDA’s Premarket Evaluation of Medical Devices An Action Learning Project Donna-Bea Tillman AU/OPM II December 2004 “Man’s rational life consists in those moments in which reflection not only occurs but proves efficacious.” George Santayana FDA Mission: Historical Basis Protect the public from unsafe products FDA Mission Today Promote Protect FDA Organizational Chart Department of Health and Human Services Center for Veterinary Medicine Center for Food Safety And Applied Nutrition Food and Drug Administration Office of the Commissioner National Center for Toxicological Research Center for Drug Evaluation And Research (CDER) Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) Devices are Different from Drugs Drugs Yesterday Drugs Today Drugs Tomorrow Devices HHS/FDA/CDRH Challenges Facing CDRH Rapid technological changes Increasing complexity of devices Public demand for more control over healthcare Global marketplace and global regulation Shrinking staff numbers … and we are being asked to make decisions more quickly than ever. Medical Device User Fees to the Rescue! CDRH’s New Challenge: Turning dollars into shorter review times… …while maintaining our commitment to good science. How are we going to make this happen? Office of In Vitro Diagnostic Device Evaluation and Safety Office of Surveillance & Biometrics Office of Compliance Office of Device Evaluation Center for Devices and Radiological Health Office of Management Operations Office of Science & Engineering Laboratories Office of Communication, Education, and Rad Health CDRH Medical Device Fellowship Program CDRH established the Medical Device Fellowship Program to increase the range and depth of collaborations between CDRH and the outside scientific community. The MDFP offers short and long-term fellowship opportunities for individuals interested in learning about the regulatory process and sharing their knowledge and experience with medical devices. Initial MDFP Goals Bring in experts in a range of disciplines. Develop a cadre of outside experts. Incorporate outside expertise into decisionmaking. Where do outside experts come from? Academia Device advisory panels Practicing clinicians, engineers, others Other parts of FDA Other government agencies Nature of appointments Short term (3 months) to longer term (2 years) Part-time or full-time Federal employment or government contract On-site or off-site Office Director Division of Anesthesiology General Hospital, Infection Control, and Dental Devices Division of General, Restorative & Neurological Devices Office of Device Evaluation Division of Reproductive, Abdominal, & Radiological Devices Division of Cardiovascular Devices Division of Ophthalmic & ENT Devices The (Initial) Problem How can CDRH most effectively use outside scientific resources to improve the premarket evaluation of medical devices? The Group Examine pilot program in the Division of Cardiovascular Devices (DCD) Team members: BZ – Director of DCD MM – Branch chief in DCD MB – Reviewer in DCD SH – Director of MDFP LD – ODE Program Management Specialist The Coach Explained the principles of action learning at Meeting #1, including the role of the coach Other team members were uncomfortable with assuming the role of Coach Lack of familiarity with principles of AL “Too touchy/feely” Donna-Bea agreed to be the permanent Coach The Questioning and Reflection Process Team meeting #2: SH presents her understanding of mission and goals of MDFP program Team members engage in the “questioning process” Meeting #2: The Questioning Process The Questioning and Reflection Process Team asked to reflect at the end of the meeting on how things had gone Agreed that: Would work harder to keep it friendly Would build on each others questions Would refrain from asking “questions” that were opinions in disguise Subsequent Meetings: The Questioning Process The Questioning and Reflection Process, cont’d Medical Device review process involves lots of questions But the purpose of these questions is to get an answer “Science has promised us truth … It has never promised either peace or happiness.” Gustave Le Bon The Questioning and Reflection Process, cont’d Action Learning has a different perspective on questions: “… seeking to go deeper, to understand, to respond to what is being asked, to give it thought. Asking questions is not only a quest for solutions but also an opportunity to explore” (Marquardt, p.31) Core Issues How do we identify resource needs that can be appropriately filled using outside resources? How do we find the appropriate people to fill the need? What should be our selection criteria? How do we address real or apparent conflicts of interest? How do we determine the appropriate hiring mechanism and salary to use in each case? Core Issues What do we need to do to train outside resource? What are the infrastructure needs (e.g., computers, space) required to support the program? How do we evaluate the impact of the program on our decision-making process? How do we foster staff acceptance of outside experts? How do we ensure confidentiality of proprietary information obtained by outside experts? The Commitment to Learning Team spent time at the end of each meeting talking about how we had done as a team Particularly helpful after first few meetings Refined questioning process People’s behavior changed as a result! Demonstrated Kurt Lewin theory that the group is a powerful shaper of individual behavior The Commitment to Learning The Commitment to Taking Action Taking action is linked to the questioning and reflection process Need to reframe the question and get at root causes in order to determine appropriate action to take Finding the right people Core Issues: How do we identify resource needs that can be appropriately filled using outside resources? How do we find the appropriate people to fill the need? Why are other divisions not interested in MDFP? Questioning process lead to root cause and development of actions to move forward Medical Device Fellowship Program at end of FY04 Physicians* - 15 Engineers* - 42 Visiting Scholar – senior level clinicians, surgeons Fellow - physician during fellowship training Resident – physician during residency training Visiting Scholar – senior level engineer Co-op students Interns Physicists* - 2 Scientists* - 5 *includes students The Commitment to Taking Action A number of issues were raised that team did NOT take action on Core Issue: How will we determine if the program is a success? Summative evaluation Objective of the program will determine the evaluation questions “It is the mark of a good action that it appears inevitable in retrospect.” Robert Louis Stevenson Outcomes: MDFP Current Status of MDFP Next Steps Determine objectives Conduct evaluation What I learned My role in the organization changed significantly over the course of this project Deputy Director, DCD Deputy Director, ODE Acting Director, ODE Director, ODE What I learned What you see depends on where you stand Leader needs to be able to see things from all perspectives “Every man takes the limits of his own field of vision for the limits of the world.” Schopenhauer What I learned The skills that I needed to be successful in the early part of my career were very different from the skills I would need to be successful in the later stages of my career “We run carelessly to the precipice, after we have put something before us to prevent us from seeing it.” Pascal What I learned Questions? Man who say it cannot be done should not interrupt man doing it. Chinese proverb