Trig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and Identities
advertisement
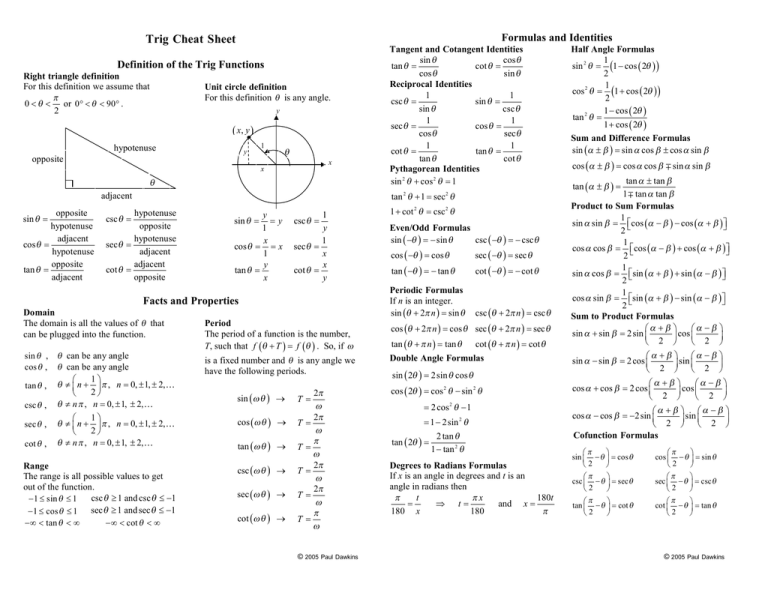
Formulas and Identities Trig Cheat Sheet Definition of the Trig Functions Right triangle definition For this definition we assume that ! 0 < " < or 0° < " < 90° . 2 Unit circle definition For this definition " is any angle. y ( x, y ) hypotenuse y opposite 1 " x x " tan " + 1 = sec " adjacent opposite hypotenuse adjacent cos " = hypotenuse opposite tan " = adjacent sin " = 2 hypotenuse opposite hypotenuse sec" = adjacent adjacent cot " = opposite csc " = y =y 1 x cos " = = x 1 y tan " = x sin " = 1 y 1 sec " = x x cot " = y csc " = Facts and Properties Domain The domain is all the values of " that can be plugged into the function. sin " , cos " , tan " , csc " , sec " , cot " , Tangent and Cotangent Identities sin " cos " tan " = cot " = cos " sin " Reciprocal Identities 1 1 csc " = sin " = sin " csc " 1 1 sec " = cos " = cos " sec " 1 1 cot " = tan " = tan " cot " Pythagorean Identities sin 2 " + cos 2 " = 1 " can be any angle " can be any angle 1" ! " # $ n + % ! , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… 2' & " # n ! , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… 1" ! " # $ n + % ! , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… 2' & " # n ! , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… Range The range is all possible values to get out of the function. csc " * 1 and csc " ) (1 (1 ) sin " ) 1 sec " * 1 and sec " ) (1 (1 ) cos " ) 1 (+ < tan " < + (+ < cot " < + Period The period of a function is the number, T, such that f (" + T ) = f (" ) . So, if # is a fixed number and " is any angle we have the following periods. sin ( #" ) , T cos (#" ) , T tan (#" ) , T csc (#" ) , T sec (#" ) , T cot (#" ) , T 2! = # 2! = # ! = # 2! = # 2! = # ! = # © 2005 Paul Dawkins 2 1 + cot 2 " = csc 2 " Even/Odd Formulas sin ( (" ) = ( sin " csc ( (" ) = ( csc " cos ( (" ) = cos " sec ( (" ) = sec " tan ( (" ) = ( tan " cot ( (" ) = ( cot " Periodic Formulas If n is an integer. sin (" + 2! n ) = sin " csc (" + 2! n ) = csc " cos (" + 2! n ) = cos " sec (" + 2! n ) = sec " tan (" + ! n ) = tan " cot (" + ! n ) = cot " Double Angle Formulas sin ( 2" ) = 2sin " cos " cos ( 2" ) = cos 2 " ( sin 2 " = 2 cos 2 " ( 1 = 1 ( 2sin 2 " tan ( 2" ) = 2 tan " 1 ( tan 2 " Degrees to Radians Formulas If x is an angle in degrees and t is an angle in radians then ! t !x 180t = - t= and x = 180 x 180 ! Half Angle Formulas 1 sin 2 " = (1 ( cos ( 2" ) ) 2 1 cos 2 " = (1 + cos ( 2" ) ) 2 1 ( cos ( 2" ) 2 tan " = 1 + cos ( 2" ) Sum and Difference Formulas sin ($ ± % ) = sin $ cos % ± cos $ sin % cos ($ ± % ) = cos $ cos % ! sin $ sin % tan $ ± tan % 1 ! tan $ tan % Product to Sum Formulas 1 sin $ sin % = .0 cos ($ ( % ) ( cos ($ + % ) /1 2 1 cos $ cos % = .0 cos ($ ( % ) + cos ($ + % ) /1 2 1 sin $ cos % = .0sin ($ + % ) + sin ($ ( % ) /1 2 1 cos $ sin % = .0sin ($ + % ) ( sin ($ ( % ) /1 2 Sum to Product Formulas !$ + % " !$ ( % " sin $ + sin % = 2 sin $ % cos $ % 2 & ' & 2 ' !$ + % " !$ ( % " sin $ ( sin % = 2 cos $ % sin $ % & 2 ' & 2 ' tan ($ ± % ) = !$ + % " !$ ( % " cos $ + cos % = 2 cos $ % cos $ % 2 & ' & 2 ' !$ + % " !$ ( % " cos $ ( cos % = (2 sin $ % sin $ % & 2 ' & 2 ' Cofunction Formulas !! " sin $ ( " % = cos " &2 ' !! " csc $ ( " % = sec " &2 ' !! " cos $ ( " % = sin " &2 ' !! " sec $ ( " % = csc " &2 ' !! " tan $ ( " % = cot " 2 & ' !! " cot $ ( " % = tan " 2 & ' © 2005 Paul Dawkins Unit Circle y ! 3 1" $( , % & 2 2' 3! 4 ( 0,1) ! 2 ! 1 3" $( , % & 2 2 ' ! 2 2" , $( % & 2 2 ' Inverse Trig Functions 2! 3 ! 3 90° 120° 45° 30° ! 180° y = cos ( 1 x is equivalent to x = cos y sin ( sin (1 ( x ) ) = x sin (1 ( sin (" ) ) = " tan ( tan ( 1 ( x ) ) = x tan (1 ( tan (" ) ) = " y = tan x is equivalent to x = tan y ! 2 2" , $$ %% & 2 2 ' ! 6 Domain and Range Function Domain ! 3 1" $$ 2 , 2 %% & ' y = sin (1 x (1 ) x ) 1 y = cos x (1 ) x ) 1 y = tan (1 x (+ < x < + (1 150° ( (1,0 ) Inverse Properties cos ( cos (1 ( x ) ) = x cos (1 ( cos (" ) ) = " (1 ! 4 60° 135° 5! 6 !1 3" $$ , %% &2 2 ' Definition y = sin ( 1 x is equivalent to x = sin y 0° 0 360° 2! (1,0 ) ! 3 1" $ ( ,( % 2' & 2 ! 2 2" ,( $( % 2 ' & 2 210° 330° 225° 5! 4 4! 3 240° ! 1 3" $ ( ,( % & 2 2 ' 270° 3! 2 315° 7! 300° 4 5! 3 ( 0,(1) 11! 6 !1 3" $ ,( % &2 2 ' For any ordered pair on the unit circle ( x, y ) : cos " = x and sin " = y a & Law of Sines sin $ sin % sin & = = a b c Law of Tangents a ( b tan 12 ($ ( % ) = a + b tan 12 ($ + % ) Law of Cosines a 2 = b 2 + c 2 ( 2bc cos $ b ( c tan 12 ( % ( & ) = b + c tan 12 ( % + & ) c = a + b ( 2ab cos & 2 ! 5! " 1 cos $ %= & 3 ' 2 % b b 2 = a 2 + c 2 ( 2ac cos % Example tan ( 1 x = arctan x $ ! 3 1" $ ,( % & 2 2' ! 2 2" ,( $ % 2 ' & 2 cos ( 1 x = arccos x Law of Sines, Cosines and Tangents x c 7! 6 Alternate Notation sin (1 x = arcsin x Range ! ! ( ) y) 2 2 0) y )! ! ! ( < y< 2 2 2 2 a ( c tan 12 ($ ( & ) = a + c tan 12 ($ + & ) Mollweide’s Formula a + b cos 12 ($ ( % ) = c sin 12 & 3 ! 5! " sin $ %=( 2 & 3 ' © 2005 Paul Dawkins © 2005 Paul Dawkins


