Obstetric Ultrasound Scanning Technique Harry Gee (teaching materials provided
advertisement

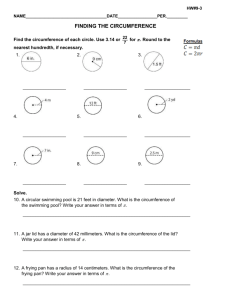
Obstetric Ultrasound Scanning Technique Harry Gee (teaching materials provided by David Cole, Lecturer at City University, Birmingham) 2nd & 3rd Trimester Scans • Identify fetus – Orientation – Fetal heart beat • Placental site • Biometry – – – – Bi-Parietal Diameter (BPD) Head Circumference (HC) Abdominal Circumference (AC), Femur length (FL) • Liquor Estimation 2nd & 3rd Trimester Scans • Place probe longitudinal on lower abdomen superior to symphysis pubis • Slide probe superiorly using sweeping movements to locate fetus 2nd & 3rd Trimester Scans • Slide probe superiorly - sweeping side to side up to uterine fundus. FH + Orientation Fetal Orientation • Lie – longitudinal – Transverse – Oblique • Presentation – cephalic – breech Cephalic Breech Breech legs extended Transverse lie Placental localisation • • • • Full bladder Midline sagittal section Placental position anterior or posterior Low placenta - measure distance between lower edge and internal os * Fundal placenta Major placenta praevia Minor placenta praevia Liquor volume • Subjective assessment • Maximum deepest pool (MPD) • Amniotic fluid index Subjective Assessment Normal liquor volume Maximum deepest pool Deepest pool in cm Do not include cord or fetal limbs Amniotic Fluid Index Sum of the deepest pools in each of four quadrants Oligohydramnios MPD < 3 cm up to 36 weeks MPD < 2 cm 36 weeks - term Polyhydramnios MPD > 8 cm Fetal Biometry • • • • Biparietal diameter BPD Head circumference HC Abdominal circumference AC Femur length FL BPD Measurement ROCK Biparietal diameter BPD BPD Errors • Few (best inter-observer error) • Oblique section (increases measurement) • Not at BPD (decreases measurement) Head Circumference Trans-ventricular choroid Plane plexus anterior horn posterior horn CSP falx cerebri Trans-ventricular Plane Measurement Criteria BPD & HC •Landmarks: CSP, Falx, thalami •Alignment: symmetrical –midline no orbits, no cerebellum •Calipers: BPD widest distance 90o midline. •HC bony perimeter of skull Abdominal Circumference • • • • Long Axis of fetus (Spine) Fetal trunk parallel to transducer Rotate transducer at right angles Move up and down until landmarks identified. • Repeat to consistency Abdominal Circumference spine Ao UV stomach Abdominal Circumference AC Sources of Error • • • • Oblique Section (Salami Effect) Too high Too low Abdominal compression (oligohydramnios) • Fetal Breathing FL Measurement • Identify femur close to fetal bladder/pelvis. FL Measurement • Slide probe so that femur is central FL Measurement • Rotate probe to obtain full length image of femur. Femur Length Source of Error • Oblique image (shortens measurement)