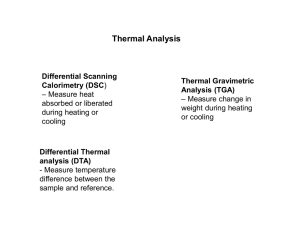
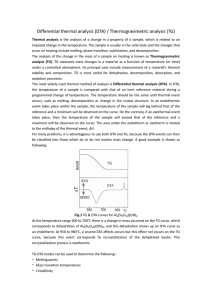
Differential Thermal Analysis
advertisement

Differential Thermal Analysis Differential Thermal Analysis – (Also DTA) – One of the methods used to study the thermal properties of energetic materials. DTA is a technique in which the difference in temperature between a sample and an inert reference substance is measured, as the two specimens are subjected to an identical temperature program. If the test sample generates heat, its temperature will be higher than the reference sample. If the sample absorbs heat, its temperature will be lower than the reference sample. During the temperature program, the specimens are most often heated at a constant rate (typically ranging from 2 to 20°C per minute) or held at constant temperature (isothermal). One of the advantages of the DTA technique is that the instrument design can be made relatively robust so that much higher temperature than that achievable in differential scanning calorimetry can be attained (typically 1400-1500°C). A schematic diagram of a typical DTA apparatus is shown in Fig. 1, below. Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of a typical DTA instrument.