A sociological theory is a set of ideas that provides... Theories of sociology Sociological Theories
advertisement

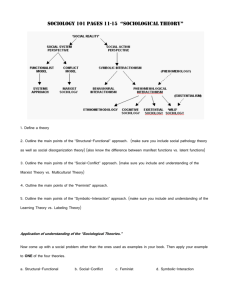
Theories of sociology: Sociological Theories A sociological theory is a set of ideas that provides an explanation for human society. Theories are selective in terms of their priorities and perspectives and the data they define as significant. As a result they provide a particular and partial view of reality. Sociological theories can be grouped together according to a variety of criteria. The most important of these is the distinction between Structural and Social action theories. Structural, or macro perspectives analyses the way society as a whole fits together. Structural theory sees society as a system of relationships that creates the structure of the society in which we live. It is this structure that determines our lives and characters. Structured sets of social relationships are the 'reality' that lie below the appearance of 'the free individual' of western individualism. Structuralism focuses on the particular set of 'structural laws' that apply in any one society. 1. Symbolic Interaction Theory The symbolic interaction perspective, also called symbolic interactions, is a major framework of sociological theory. This perspective relies on the symbolic meaning that people develop and rely upon in the process of social interaction. 2. Conflict Theory Conflict theory emphasizes the role of coercion (force) and power in producing social order. This perspective is derived from the works of Karl Marx, who saw society as fragmented into groups that compete for social and economic resources. Social order is maintained by domination, with power in the hands of those with the greatest political, economic, and social resources. 3. Functionalist Theory The functionalist perspective, also called functionalism, is one of the major theoretical perspectives in sociology. It has its origins in the works of Emile Durkheim, who was especially interested in how social order is possible or how society remains relatively stable. 4. Feminist Theory Feminist theory is one of the major contemporary sociological theories, which analyzes the status of women and men in society with the purpose of using that knowledge to better women's lives. Feminist theory is most concerned with giving a voice to women and highlighting the various ways women have contributed to society. 1 5. Critical Theory Critical theory is a type of social theory oriented toward critiquing and changing society as a whole, in contrast(difference) to traditional theory oriented only to understanding or explaining it. Critical theories aim to dig beneath the surface of social life and uncover the assumptions that keep us from a full and true understanding of how the world works. 6. Labeling Theory Labeling theory is one of the most important approaches to understanding deviant and criminal behavior. It begins with the assumption that no act is intrinsically(basically) criminal. Definitions of criminality are established by those in power through the formulation of laws and the interpretation of those laws by police, courts, and correctional institutions. 7. Social Learning Theory Social learning theory is a theory that attempts to explain socialization and its effect of the development of the self. It looks at the individual learning process, the formation of self, and the influence of society in socializing individuals. Social learning theory is commonly used by sociologists to explain deviance and crime. 8. Structural Strain Theory Robert K. Merton developed the structural strain theory as an extension of the functionalist perspective on deviance. This theory traces the origins of deviance to the tensions that are caused by the gap between cultural goals and the means people have available to achieve those goals. 9. Rational Choice Theory Economics plays a huge role in human behavior. That is, people are often motivated by money and the possibility of making a profit, calculating the likely costs and benefits of any action before deciding what to do. This way of thinking is called rational choice theory. 10. Game Theory Game theory is a theory of social interaction, which attempts to explain the interaction people have with one another. As the name of the theory suggests, game theory sees human interaction as just that: a game. 2