REDUCED ORDER METHODS Elisa SCHENONE Legato Team Computational Mechanics
advertisement

REDUCED ORDER METHODS
Elisa SCHENONE
Legato Team
Computational Mechanics
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
1
team at
and
of
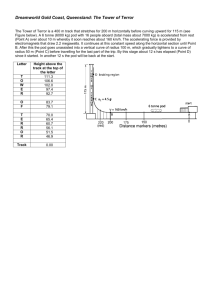
Numerical simulation of biological flows
Respiration modelling
Blood flow modelling
Cardiac electrophysiology
aVR
I
2
2
1
1
0
0
1
1
2
0
200
400
600
2
0
200
2
2
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
200
400
600
2
0
200
2
2
1
1
0
0
1
1
Elisa SCHENONE
0
200
600
0
200
400
600
2
0
400
200
RUES Seminar
V4
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
V3
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
400
600
400
600
400
600
V5
V2
aVF
III
2
400
aVL
II
2
V1
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
V6
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
April, 16th 2015
2
team at
and
of
Numerical simulation of biological flows
Respiration modelling
Blood flow modelling
Cardiac electrophysiology
aVR
I
2
2
1
1
0
0
1
1
2
0
200
400
600
2
0
200
2
2
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
200
400
600
2
0
200
2
2
1
1
0
0
1
1
Elisa SCHENONE
0
200
600
0
200
400
600
2
0
400
200
RUES Seminar
V4
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
V3
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
400
600
400
600
400
600
V5
V2
aVF
III
2
400
aVL
II
2
V1
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
V6
400
600
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
0
200
April, 16th 2015
2
PhD project:
Inverse problems and reduced models in cardiac electrophysiology
✓ Supervisors:
Muriel BOULAKIA and Jean-Frédéric GERBEAU
✓ Subjects:
➡Simulation of realistic Electrocardiograms
➡Parameters estimation
➡Reduced order models (RB, POD, ALP, EIM)
➡Inverse problems
Post-Doc project:
Reduced models in computational mechanics
✓ Supervisors:
Stéphane BORDAS and Lars BEEX
✓ Subjects:
➡Simulation of hyperelastic materials with reduced order models
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
3
PhD project:
Inverse problems and reduced models in cardiac electrophysiology
✓ Supervisors:
Muriel BOULAKIA and Jean-Frédéric GERBEAU
✓ Subjects:
➡Simulation of realistic Electrocardiograms
➡Parameters estimation
➡Reduced order models (RB, POD, ALP, EIM)
➡Inverse problems
Post-Doc project:
Reduced models in computational mechanics
✓ Supervisors:
Stéphane BORDAS and Lars BEEX
✓ Subjects:
➡Simulation of hyperelastic materials with reduced order models
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
3
Summary
✓ PDEs numerical approximation
➡ Finite
Element Methods (overview)
➡ Reduced
Order Methods
•
Reduced-Basis
•
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition
✓ Numerical Results
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
4
A numerical approximation
Overview on Finite Element Method (FEM)
FEM space
u = u(x)
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
5
A numerical approximation
Overview on Finite Element Method (FEM)
FEM space
ui
ui
ui+1
1
u = u(x)
xi
Elisa SCHENONE
1
xi xi+1
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
5
A numerical approximation
Overview on Finite Element Method (FEM)
FEM space
u(x) '
N
X
i
ui
ui vi (x)
ui
1
u = u(x)
xi
Elisa SCHENONE
ui+1
1
xi xi+1
vi
1
vi vi+1
xi
1
xi xi+1
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
5
A numerical approximation
Overview on Finite Element Method (FEM)
FEM space
u(x) '
N
X
i
ui
ui vi (x)
ui
'2 (x)
1
u(x) ' ũ1 '1 (x) + ũ2 '2 (x)
u = u(x)
'1 (x)
xi
Elisa SCHENONE
ui+1
1
xi xi+1
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
5
FEM versus ROM
FEM space
ROM space
VN ⌘ span{v1 , . . . , vN } ⇢ V
dim(VN ) = N
N
X
u=
ui vi (x), ui = hu, vi i
VN ⌘ span{'1 , . . . , 'N } ⇢ VN
dim(VN ) = N ⌧ N
N
X
e=
u
ũi 'i (x), ũi = hu, 'i i
i
i
x1
x2
N
Elisa SCHENONE
= ['1 . . . 'N ] 2 R
e=
u
T
Nu
RUES Seminar
N ⇥N
x3
April, 16th 2015
6
General ROM formulation
Diffusion problem
FEM
Ku = f
Linear case
⇢
d
r · ( ru) = f, ⌦ ⇢ R
B.C. @⌦
= ['1 , . . . , 'N ] 2 R
Weak formulation 8v 2 V
Z
Z
rurv + B.C. =
fv
⌦
Elisa SCHENONE
K2R
N
u2R
N
f 2R
N ⇥N
⌦
RUES Seminar
ROM
eu
e =e
K
f
e =
K
e=
u
e
f=
N ⇥N
N ⇥N
e
K , K2R
T
N
e2R
u,
u
T
N
e
f,
f 2R
T
April, 16th 2015
7
Reduced-Basis Method
A “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
Elisa SCHENONE
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
8
Reduced-Basis Method
A “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
1.Solve with FEM the (linear) problem(s)
(n)
d
@t u = F (u, @x , ⇡), in ⌦ ⇥ [0, T ] ⇢ R ⇥ R+
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
8
Reduced-Basis Method
A “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
1.Solve with FEM the (linear) problem(s)
(n)
d
@t u = F (u, @x , ⇡), in ⌦ ⇥ [0, T ] ⇢ R ⇥ R+
2.Collect snapshots of FEM solution(s) in2a matrix 3
1
p
S = (u , . . . , u ) 2 R
Elisa SCHENONE
N ⇥p
u(x1 , ti )
6
7
.
i
N
..
u =4
5 2 R , 8i = 1, . . . , N
u(xN , ti )
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
8
Reduced-Basis Method
A “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
1.Solve with FEM the (linear) problem(s)
(n)
d
@t u = F (u, @x , ⇡), in ⌦ ⇥ [0, T ] ⇢ R ⇥ R+
2.Collect snapshots of FEM solution(s) in2a matrix 3
1
p
S = (u , . . . , u ) 2 R
N ⇥p
u(x1 , ti )
6
7
.
i
N
..
u =4
5 2 R , 8i = 1, . . . , N
u(xN , ti )
3.Orthonormalization of the matrix
= orthonorm(S)
‣ Can reproduce events described by the FEM solution(s)
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
8
RB application
Diffusion problem
1.Solve with FEM the (linear) problem(s) for different f
⇢
u = f,
u = 0,
⌦ = (0, 1)
@⌦
2
2.Collect snapshots of FEM solution(s)
3.Orthonormalization of the matrix
=[
1, . . . ,
4]
0.0
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
6. x 10-2
April, 16th 2015
9
RB application
Diffusion problem
RB basis functions
-0.05
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
0.15
April, 16th 2015
10
RB application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
RB (N=4)
6. x 10-2
0.0
6. x 10-2
ERROR
0.0
5. x 10-7
NB the solution is “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
11
RB application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
RB (N=4)
6. x 10-2
2. x 10-2
0.0
ERROR
0.0
1.0
NB the solution is NOT “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
12
RB application
Diffusion problem
FEM snapshots
25 sources
0.0
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
6. x 10-2
April, 16th 2015
13
RB application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
RB (N=25)
6. x 10-2
6. x 10-2
0.0
ERROR
0.0
0.25
NB the solution is NOT “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
14
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD)
Another “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
Elisa SCHENONE
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
15
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD)
Another “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
1.Solve with FEM the problem(s)
(n)
d
@t u = F (u, @x , ⇡), in ⌦ ⇥ [0, T ] ⇢ R ⇥ R+
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
15
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD)
Another “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
1.Solve with FEM the problem(s)
(n)
d
@t u = F (u, @x , ⇡), in ⌦ ⇥ [0, T ] ⇢ R ⇥ R+
2.Collect snapshots of FEM solution(s) in2a matrix 3
1
p
S = (u , . . . , u ) 2 R
Elisa SCHENONE
N ⇥p
u(x1 , ti )
6
7
.
i
N
..
u =4
5 2 R , 8i = 1, . . . , N
u(xN , ti )
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
15
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD)
Another “classical” approach to Reduced Order Models
‣ Use information
given by FEM solution(s) to build a suitable basis
1.Solve with FEM the problem(s)
(n)
d
@t u = F (u, @x , ⇡), in ⌦ ⇥ [0, T ] ⇢ R ⇥ R+
2.Collect snapshots of FEM solution(s) in2a matrix 3
1
p
S = (u , . . . , u ) 2 R
N ⇥p
u(x1 , ti )
6
7
.
i
N
..
u =4
5 2 R , 8i = 1, . . . , N
u(xN , ti )
3.Compute Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of the matrix
T
S= ⌃
, ⌃ = diag( i )
4.Keep first eigenvectors as ROM basis functions
‣ Can reproduce events described by the FEM solution(s)
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
15
RB application
Diffusion problem
1.Solve with FEM the (linear) problem(s) for different f
⇢
u = f,
u = 0,
⌦ = (0, 1)
@⌦
2
2.Collect snapshots of FEM solution(s)
3.SVD of the matrix
T
S= ⌃
, ⌃ = diag( i )
4.Keep first eigenvectors
=[
1, . . . ,
4]
0.0
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
6. x 10-2
April, 16th 2015
16
POD application
Diffusion problem
POD basis functions
-0.1
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
0.1
April, 16th 2015
17
POD application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
POD (N=4)
6. x 10-2
0.0
6. x 10-2
ERROR
0.0
5. x 10-7
NB the solution is “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
18
POD application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
POD (N=4)
6. x 10-2
2. x 10-2
0.0
ERROR
0.0
1.0
NB the solution is NOT “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
19
POD application
Diffusion problem
FEM snapshots
25 sources
0.0
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
6. x 10-2
April, 16th 2015
20
POD application
Diffusion problem
POD basis functions
0.0
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
0.05
April, 16th 2015
21
POD application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
POD (N=10)
6. x 10-2
6. x 10-2
0.0
ERROR
0.0
0.3
NB the solution is NOT “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
22
POD application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
POD (N=15)
6. x 10-2
6. x 10-2
0.0
ERROR
0.0
0.3
NB the solution is NOT “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
23
POD application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
POD (N=20)
6. x 10-2
6. x 10-2
0.0
ERROR
0.0
0.3
NB the solution is NOT “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
24
POD application
Diffusion problem
FEM
0.0
POD (N=25)
6. x 10-2
6. x 10-2
0.0
ERROR
0.0
0.3
NB the solution is NOT “in” the basis
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
25
POD application
Diffusion problem
EIGENVALUES
6
ERROR
1
0.5
0.45
5
0.95
0.4
4
0.9
0.35
0.3
3
0.85
0.25
2
0.8
0.2
0.15
1
0.75
0.1
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
0.7
0
5
10
N
X
NT
X
Elisa SCHENONE
15
i
i
RUES Seminar
20
25
0.05
0
5
10
15
20
25
kuFEM uPOD k2
kuFEM k2
April, 16th 2015
26
POD application in Cardiac Electrophysiology
‣ Infarcted tissue: damaged area which cannot be activated
➡ to build the POD basis, we use a FEM solution with NO infarction
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
[Boulakia, Schenone, Gerbeau - 2012]
Simulation of a myocardial infarction
27
POD application in Cardiac Electrophysiology
‣ Infarcted tissue: damaged area which cannot be activated
➡ to build the POD basis, we use a FEM solution with NO infarction
FEM (79,537 basis)
Elisa SCHENONE
[Boulakia, Schenone, Gerbeau - 2012]
Simulation of a myocardial infarction
POD (100 basis)
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
27
POD application in Cardiac Electrophysiology
Simulation of a myocardial infarction
aVR
V1
V4
‣ Infarcted tissue: damaged area which cannot be activated
➡ to build the POD basis, we use a FEM solution with
4
4
4
4
2
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
2
2
2
2
4
4
4
4
0
100
200
300
400
0
100
II
200
300
400
0
100
aVL
200
300
400
0
V2
4
4
4
2
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
2
2
2
2
4
4
4
4
100
200
300
400
0
100
III
200
300
400
0
100
aVF
200
300
400
0
4
4
2
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
2
2
2
2
4
4
4
4
200
300
400
0
100
200
300
400
0
FEM (79,537 basis)
Elisa SCHENONE
100
200
300
400
200
300
400
300
400
V6
4
100
100
V3
4
0
200
V5
4
0
100
FEM
300
400
0
100
200
[Boulakia, Schenone, Gerbeau - 2012]
I
POD (100 basis)
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
27
POD application in Cardiac Electrophysiology
‣ An efficient POD to simulate an infarction in any point of the heart
➡ to build the POD basis, we use many FEM solutions with infarction
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
[Boulakia, Schenone, Gerbeau - 2012]
Simulation of a myocardial infarction
28
POD application in Cardiac Electrophysiology
‣ An efficient POD to simulate an infarction in any point of the heart
➡ to build the POD basis, we use many FEM solutions with infarction
⇥ 1 2
⇤
NT
N ⇥NT
๏ healthy FEM solution
Sh = ⇥uh |uh | . . . |uh 2
R
⇤
NT
1
2
N ⇥NT
uI1 |uI1 | . . . |uI1 2 R
๏ infarct 1 FEM solution SI1 =
⇥ 1 2
⇤
NT
N ⇥NT
๏ infarct 2 FEM solution SI
=
u
|u
|
.
.
.
|u
2
R
I 2 I2
2
I2
... ... ...
⇥ 1
⇤
NT
2
N
⇥N
T
๏ infarct m FEM solution S
Im = uIm |uIm | . . . |uIm 2 R
➡ compute
the
SVD
on
an
enlarged
matrix
h
i
N ⇥(m+1)NT
S = Sh |SI1 |SI2 | . . . |SIm 2 R
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
[Boulakia, Schenone, Gerbeau - 2012]
Simulation of a myocardial infarction
28
POD application in Cardiac Electrophysiology
‣ An efficient POD to simulate an infarction in any point of the heart
➡ to build the POD basis, we use many FEM solutions with infarction
FEM (79,537 basis)
Elisa SCHENONE
[Boulakia, Schenone, Gerbeau - 2012]
Simulation of a myocardial infarction
POD (100 basis)
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
28
POD application in Cardiac Electrophysiology
Simulation of a myocardial infarction
aVR
V1
V4
‣ An efficient POD to simulate an infarction in any point of the heart
➡ to build the POD basis, we use
4
4
4
4
2
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
2
2
2
2
4
4
4
4
0
100
200
300
400
0
100
II
200
300
400
0
100
aVL
200
300
400
0
V2
4
4
4
2
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
2
2
2
2
4
4
4
4
100
200
300
400
0
100
III
200
300
400
0
100
aVF
200
300
400
0
4
4
2
2
2
2
0
0
0
0
2
2
2
2
4
4
4
4
200
300
400
0
100
200
300
400
0
FEM (79,537 basis)
Elisa SCHENONE
100
200
300
400
200
300
400
300
400
V6
4
100
100
V3
4
0
200
V5
4
0
100
300
400
0
100
200
[Boulakia, Schenone, Gerbeau - 2012]
I
POD (100 basis)
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
28
Non-linear problems
Example
⇢
r · ( (u)ru) = f,
B.C.
⌦⇢R
@⌦
d
Weak
formulation
Z
Z
(u)rurv + B.C. =
f v, 8v 2 V
n
⌦
⌦
K(u)u
possible solution
Empirical Interpolation Methods
Ingredients:
• a reduced- basis approximation space, e.g. RB or POD
• an interpolation procedure tho choose some points where
the PDE is solved in its strong form
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
29
References
Reduced Basis
• Y. Maday, A. T. Patera, D.V. Rovas. A blackbox reduced-basis output bound method for noncoercive
linear problems. Studies in Math. and its Appl., 31:533–569, 2002
• Y. Maday, E.M. Rønquist. A reduced-basis element method. J. of scient. comp., 17(1):447–459, 2002
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition
• L. Sirovich. Low dimensional description of complicated phenomena. Contemp. Math., 99:277–305, 1989
• L. Lumley. The structure of inhomogeneous turbulence. Atmospheric turbulence and radio wave
propagation, pp. 166–178, 1967
Empirical Intermpolation Method
• M. Barrault,Y. Maday, N. C. Nguyen, A. T. Patera. An “empirical interpolation” method: Application to
efficient reduced-basis discretization of partial differential equations. C. R. Math. Acad. Sci. Paris,
339:667–672, 2004
• S. Chaturantabut, D. Sorensen. Nonlinear model reduction via discrete empirical interpolation. SIAM J.
of Scient. Comp., 32(5):2737–2764, 2010
Elisa SCHENONE
RUES Seminar
April, 16th 2015
30