UVIS OBSERVATION DESCRIPTION HANDBOOK
advertisement

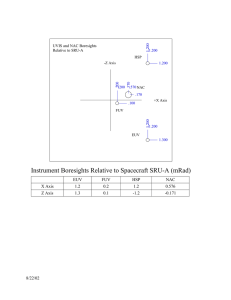
UVIS OBSERVATION DESCRIPTION HANDBOOK COLOR FIGURES 6 January 1994 Revised: 9/97, 1/98, 9/98, 6/99 LIST OF COLOR FIGURES URSTAR Figure 1. Shadowed ring stellar occultation..................................................................3 UISTAR Figure 1. Setup and slit orientation prior to occultation.................................................4 UHIGHSN Figure 1. Iapetus raster.................................................................................................5 ULIMDRFT Figure 1. EUV, FUV slits cross terminator at beginning of drift to obtain airglow temporal properties. .........................................................................................................6 ULIMDRFT Figure 2. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Titan disk. ............................7 ULIMDRFT Figure 3. Titan limb scan. .........................................................................................8 ULIMDRFT Figure 4. Enceladus limb drift...................................................................................9 ULIMDRFT Figure 5. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Saturn dayside atmosphere to determine local time structure of dayglow. ...........................................................10 ULIMDRFT Figure 6. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Saturn terminator to measure local time decay of dayglow into the darkside. S/C range 7 RS , 0.40 x 106 km. ..........11 ULIMDRFT Figure 7. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Saturn dayside. ..................12 USTARE Figure 1. EUV, FUV high resolution deep exposure of Saturn dayside noon local time emission. .......................................................................................................................13 USTARE Figure 2. EUV, FUV high resolution deep exposure of Saturn dayside early evening local time emission..................................................................................................14 USTARE Figure 3. EUV, FUV high resolution deep exposure of Saturn dayside early evening local time emission. ...............................................................................................15 USTARE Figure 4-A. EUV, FUV high resolution exposures of Saturn darkside south pole. .....................................................................................................................16 USTARE Figure 4-B. EUV, FUV high resolution exposures of Saturn dayside south pole..........................................................................................................................17 USTARE Figure 5. EUV, FUV high resolution exposures of Saturn darkside / dayside north pole. ........................................................................................................18 USTARE Figure 6. EUV, FUV high and low resolution exposures of Titan darkside emission. ........................................................................................................................19 USYSCAN Figure 1. Raster pattern. ..........................................................................................20 URSTAR Figure 1. Shadowed ring stellar occultation. 3 UISTAR Figure 1. Setup and slit orientation prior to occultation. 4 UHIGHSN Figure 1. Iapetus raster. 5 ULIMDRFT Figure 1. EUV, FUV slits cross terminator at beginning of drift to obtain airglow temporal properties. Slit crosses (tangent) limb near south pole to obtain transition from airglow to aurora. Drift continues above the limb to obtain emission scale. Slit orientation minimizes off-axis scattering. Spatial resolution 150 to 200 km in both dimensions of the slit. S/C range 4Rs , 0.2 x 106 km. Spectrum will be dominated by H2 and H emission. Possible heavy ion capture spectra. 6 ULIMDRFT Figure 2. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Titan disk. Obtain spectra of darkside and airglow emissions. Slit makes near tangent crossing of terminator to obtain transition from dark to solar stimulated atmosphere. S/C range 4RT , 0.34 x 106 km. Spectrum dominated by N2, N, and N+ emissions. Possible detection of argon. Drift must start and end at impact parameters of at least 2 RT. 7 ULIMDRFT Figure 3. Titan limb scan. 8 ULIMDRFT Figure 4. Enceladus limb drift. 9 ULIMDRFT Figure 5. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Saturn dayside atmosphere to determine local time structure of dayglow. S/C range 11 RS , 0.65 x 106 km. Rings are edge-on to minimize obscuration and scattering, allowing measurement close to equator. Obtain H2, H, and solar reflection spectrum defining upper atmosphere properties. 10 ULIMDRFT Figure 6. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Saturn terminator to measure local time decay of dayglow into the darkside. S/C range 7 RS , 0.40 x 106 km. 11 ULIMDRFT Figure 7. EUV, FUV low resolution slits drift across Saturn dayside. S/C range 20 RS , 1.1 x 106 km. Length of slit on planet allows measurement of latitudinal structure of dayglow. Rings are edge-on to minimize obscuration and scattering. 12 USTARE Figure 1. EUV, FUV high resolution deep exposure of Saturn dayside noon local time emission. S/C range 24 RS , 1.4 x 106 km. Rings are edge-on. This observation is designed to obtain accurate excitation mechanism, thermal and altitude structure of H2 dayglow emission. The data will include latitudinal distribution structure. 13 USTARE Figure 2. EUV, FUV high resolution deep exposure of Saturn dayside early evening local time emission. S/C range 28 RS , 1.4 x 106 km. Spectrum will include some ring reflection. This observation is designed to obtain accurate excitation mechanism, thermal and altitude structure of H2 dayglow emission. The data will include latitudinal distribution structure. 14 USTARE Figure 3. EUV, FUV high resolution deep exposure of Saturn dayside early evening local time emission. S/C range 28 RS , 1.7 x 106 km. Spectrum will include some ring reflection. This observation is designed to obtain accurate excitation mechanism, thermal and altitude structure of H2 dayglow emission. The data will include latitudinal distribution structure. The ends of the slit will contain north and south pole auroral emission. 15 USTARE Figure 4-A. EUV, FUV high resolution exposures of Saturn darkside south pole. S/C range 3.7 - 4.7 RS , 0.22 - 0.28 x 106 km. This observation is designed to obtain high resolution auroral spectra over as large a range in longitude as allowed by the fly-by period in order to characterize longitudinal precipitation structure, penetration depth, and search for heavy ion emissions. 16 USTARE Figure 4-B. EUV, FUV high resolution exposures of Saturn dayside south pole. S/C range 3.7 - 4.7 RS , 0.22 - 0.28 x 106 km. This observation is designed to obtain high resolution auroral spectra over as large a range in longitude as allowed by the fly-by period in order to characterize longitudinal precipitation structure, penetration depth, and search for heavy ion emissions. 17 USTARE Figure 5. EUV, FUV high resolution exposures of Saturn darkside / dayside north pole. S/C range 6.4 RS , 0.39 x 106 km. This observation is designed to obtain high resolution auroral spectra over as large a range in longitude as allowed by the fly-by period in order to characterize longitudinal precipitation structure, penetration depth, and search for heavy ion emissions. 18 USTARE Figure 6. EUV, FUV high and low resolution exposures of Titan darkside emission. S/C range 31 RT , 0.08 x 106 km. This observation is designed to obtain as large a range in longitude as allowed by the fly-by period in order to characterize longitudinal precipitation structure. The projected slit is the diameter of the body, providing latitudinal distribution in a single exposure. 19 USYSCAN Figure 1. Raster pattern. 20