Immune system Lecture(8 ) Dr.Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi
advertisement

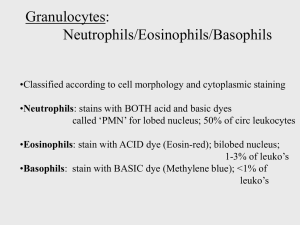
Immune system Lecture(8 ) Dr.Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology Immune system :The Immune system comprise a network cells with each other cooperates directly to reach the effectors mechanism. and defense the body .against invaders , back to the 1960 the immune system has been structurally and functionally confined to lymphoid organs .Recently however immune system may be of six component as in the following Component of immune system 1-genetic component 2-Haemopietic component 3-Reticulo endothelial component 4-complement component 5-Lymphoid component 6-mucosal component genetic component: The immune system structures &functions are encoded by set of genes like control Immune response, GVHR ,immunoglobulin synthesis and The genes of MHC system involved in rejection of foreign tissue from a region known as the Major histocompatability complex (MHC) that contain several Polymorphic genes which expressed on the surface of all nucleated cells consist of two classes (class I and class II) .These act as peptide receptors and are important in Antigen presentation after processing the Antigen . T-Cell receptors complex T-Cell asurface MHC I&MHC II These epitopes peptides bind to MHC molecules and present on the cell surface of antigen presenting cells like macrophage, dendric cells Class I + epitopes peptide(APC)= recognized by CD-8 T- Cell (Intracellular infection ) Class II + epitopes peptide(APC) =recognized by CD-4 T- Cell (Extracelluler infection ) Processing and presentation of antigens Lymphoid component: The Lymphoid component consist of primary and secondary Lymphoid organs. The primary Lymphoid organs consist of Thymus, Bone marrow and Bursa of fabricious while the secondary Lymphoid organs consist of Spleen and peripheral — Lymphoid nodes. : Lymphoid System organs l- primary lymphoid organs Thymus Bursa 2-Secoundary lymphoid organs Spleen lymph Nodes Lymphoid system Thymus: It is so- called because shape it resemble the leaf of thymus plant .each lobe can be seen divide by septa of connective tissue into series of lobular sub - compartments the outer region of densely packed and rapidly dividing lymphocyte called cortex the central area of more loosely arrange of lymphoid and reticular cell called medulla lymphocytes differentiation in thymus are called T- lymphocyte Thymus Bursa: it is epithelial & lymphoid organ that is found only in bird it is very similar to the thymus it is composed of numerous lobes each which has cortical and medullar area. The medullar and the cortical regions are separated by layer of epithelial cells. Bursa play role in birds in differentiation of. B- lymphocytes.In mammals the Bursa equivalent is not known. It is suggested that bone marrow may do this function. The peripheral lymphoid s stem organ: The peripheral lymphoid system organ: Spleen : It is abright-red organ lying in the upper left quadrant of the a abdominal cavity it is capsulated by coating of connective tissue the spleen have two function. 1-It is the major site for removal and destruction of dead red blood cells. 2-It is important organ of immune system it has red pulp and white pulp ,there is lymphocyte cuff around central arterioles in spleen for production antibodies - also it contain B- lymphocyte seeded sit in white pulp of spleen while the red pulp of spleen is site for seeded T- lymphocyte Lymph node 2- Lymph Nodes: It is small lees than 1cm,it is bean-shape ,it is distributed through the entire body it is linked to ether by lymphatic vessels .the principle function of lymph nodes are captured the foreign matter in the lymph circu1ation and as a site for maturation of lymphocyte with in lymphoid follicles in the cortical region of lymph node the afferent lymphatic vessel is the site of entering of foreign antigens to the lymph node. The Lymphopoiesas happened in bone marrow B-cells processed and matured in bone marrow ,While T-cells initially developed in Thymus in mammals Bursa equivalent as site of B- cell development, bone marrow has been suggested, There are several structural difference between B-cell and T-cell and are summarized in table. Lymphocytes: They are small round cells found in peripheral blood ,lymph .lymphoid organs and other tissue .They have the function of the *Storage of immunological memory *immune responses to specific antigens *T-cells produce activation produce (lymphokines) and induce cells mediated response . T-Cell Receptor molecule (TCR) which are associated with the Cluster of differentiation marker(CD3) Which are transmits signal to produce lymphokines when (TCR) binds an antigen that regulate the function of other lymphocytes . T-Cell divided into several subsets with different function : The T-cell Receptor 1-TH1 Helper cells or TH2 express CD4 molecules on their surface and function by secreting cytokine( 1L4 , 1L5, 1L6 and IL 10) that promote B-cell to produce antibody 2-CD8 + T cells function as cytotoxic (TC) cells and can kill other cell , primarily these infected by Virus. Characters 1-Origin 2-Differentiation 3-Role 4-Mediater 5-Surface Immunoglobulin 6-T-surface marker(E-Rosett) 7-Antigen recogonition B-Lymphocytes T-Lymphocytes Bone marrow Bone Marrow Bon marrow Thymus Humeral immune Cells mediated Response Immune respons + + - _ + +CD T Cells Cytotoxic T Cells (TC) • Possess CD8 receptors on the surface. • activated into cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). – CTLs recognize Ag + MHC I. – Kills target cell.(virus-infected or tumor cells) – Releases perforin or granzyme to kill. Figure B-cells divide and transform into plasma cells which recognize Antigen through synthesize Antibody molecule on their surface Lymphocyte Functions: •B cells secrete their antigen receptors: antibodies. Natural killer cells: Small percentage of lymphocytes 3% of peripheral lymphocytes lack features of B&T cells but have significant immunological roles. * They are killing target cells without antibody and independent M.H.C * They are killing malignant cells and virus infected cells Reticuloendothelial system: it s a System of cells and tissues whose function include principally phagocytosis and degradation and antigen presentation on the surface of the cells which including fixed macrophage and Circulation in blood. It is filter particular matter from blood. The cells of Reticuloendothelial system organized into dense sheet and fibers form sructura1 matrix of spleen ,bone marrow and lymph nodes The cells are mononuclear leukocytes in blood in liver is kuppfar cells in spleen is denderitic cells in lung is alveolar cells… ect. Haemopietic component: Macrophages and microphages: Macrophages of lymphoid system captured the particulate antigen such as bacteria it is large of lymphoid cells in blood (monocytes) they are produced by bone marrow .tissue macrophages are denderic cells in spleen alveolar cells in lung…. etc Macrophages have function phagocytosis for the invading microbes. Microphages are leukocytes of blood: Neutrophile :active phagocytic in acute inflammation. Esinophile: are phagocytic in condition like allergic inflammation, parasitic inflammation Basophiles :cells will release of. pharmacologically active agents in anaphylactic and a topic allergy. Neutrophile Monocyte Esinophile Basophile The End