Introduction to Space Weather Program D.N. Baker University of Colorado, Boulder
advertisement

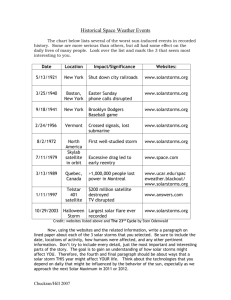
Introduction to Space Weather Program D.N. Baker University of Colorado, Boulder “Change of weather is the discourse of fools.” -Thomas Fuller “Don’t knock the weather; nine-tenths of the people couldn’t start a conversation if it didn’t change once in a while.” -Kin Hubbard “Space Weather” refers to conditions on the sun and in the solar wind, magnetosphere, ionosphere, and thermosphere that can influence the performance and reliability of space-borne and ground-based technological systems and endanger human life and health. Adverse conditions in the space environment can cause disruption of satellite operations, communications, navigation, and electronic power grids, leading to a panoply of socio-economic losses. National Space Weather Program Strategic Plan (March 1995) Sun-Earth Relationships Understanding of Sun-Earth Connections Sunspots and Magnetic Storms Major Magnetic Storms: 1932-2000 Annual Sunspot Number: 1930-2000 Different parts of the solar cycle contribute to different types of activity that can adversely affect technology and humans. Yohkoh Soft X-rays: The 11-Year Solar Activity Cycle Earth’s Space Environment The Solar Wind (Interplanetary Medium) The Magnetosphere Magnetospheric Current Systems Bow Shock Cusp Solar Wind SOHO: Ultraviolet Picture of the Sun TRACE: Detailed Solar Structure The Disturbed Solar Wind: Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) • Occur most often near the peak of the Sun’s 11-year activity cycle • Propel >109 tons of matter into interplanetary space • Can travel at speeds as high as 1700 km/s • Drive interplanetary shocks • Can trigger geomagnetic storms when they impact Earth’s magnetosphere Coronal Mass Ejection CME Relative to the Earth The size of Earth compared to the size of a large Coronal Mass Ejection from the sun Courtesy SDAC, NASA Goddard CME-Earth Impact Space Environment Effects spacecraft (a) Single Event Upset Mechanism Direct Ionization ion track electronics box penetrating radiation sensitive region charge collected in this region during particle transit can trigger a change of state of the memory induced ionization along the particle track Background Produced by Solar Energetic Particles SOHO – EIT, 2000/07/14 @ 13:28 UT Geomagnetic Storm—March 1991 Impact of Solar Flares During March 1991 Satellite Effects MARECS-A Satellite failure INTELSAT 602 GOES 7 Permanent power degradation (Decrease of satellite lifetime by 2-3 years) TDRSS INTELSAT CRRES Single Event Upsets Soft errors (Increase from 1 per day to 10-20 per day) DOD Spacecraft charging Deep dielectric charging DMSP NOAA 11 Loss of automatic attitude control NORAD Satellite drag (Loss of 200 vehicles from catalogue) The Earth’s Radiation Belts Contours of the omnidirectional flux (particles per square centimeter per second) of protons with energies greater than 10 MeV Contours of the omnidirectional flux of electrons with energies greater than 0.5 MeV UOSAT-2 Memory Upsets Space Environment Effects spacecraft (a) Single Event Upset Mechanism Direct Ionization ion track electronics box penetrating radiation sensitive region sensitive component floating circuit trace can collect charge and discharge charge buried in insulator can discharge (b) Deep-Dielectric Charging charge collected in this region during particle transit can trigger a change of state of the memory induced ionization along the particle track Star Tracker Anomalies at GEO Baker et al. (1987) High-Energy Electrons: Deep-Dielectric Charging 1. Electrons bury themselves in the insulator 2. Electrons slowly leak out of the insulator 3. Influx of electrons increases to levels higher than the leakage rate 4. Electrons build up faster than they leak off 5. Discharge (electrical spark) that damages or destroys the material ANIK Spacecraft Failures Anomalies Due to Dielectric Charging Probability of discharges goes up dramatically with increasing electron fluence. surface interactions photoemission Space Environment Effects (c) Surface Charging incident particle surface currents backscattered secondary particles spacecraft (a) Single Event Upset Mechanism Direct Ionization ion track electronics box penetrating radiation sensitive region sensitive component floating circuit trace can collect charge and discharge charge buried in insulator can discharge (b) Deep-Dielectric Charging charge collected in this region during particle transit can trigger a change of state of the memory induced ionization along the particle track SCATHA (Reagan et al., 1981) Surface Charging: SCATHA Spacecraft Local Time Plot of Various Satellite Disruptions and Anomalies March 1989: Hydro Quebec Blackout 0745 UT March 1989: Transformer Failure Courtesy John Kappenman, Metatech March 1991: Ground-Induced Currents The Active Sun: July 2000 SOHO-EIT, 2000/07/14 @ 07:00 UT Close-up from SOHO EIT Sensor Bastille Day 2000 Event (2 hours later) Shock-induced Global Auroral Brightening at 14:40 and 17:04 UT on July 15, 2000 Bastille Day Storm POLAR: Another View of the Aurora Courtesy John Kappenman, Metatech July 15, 2000: Auroral Currents and GICs Plot of ground-level magnetic field disturbances at time 14:38:15 UT on July 15, 2000 Thermospheric Heating and Satellite Drag Long Term Variability • Climate (Space, Earth) and its causes (natural, anthropogenic) • Solar-Climate relationships and Applications Space Weather and Airlines • Passengers feel relatively safe when flying on 747’s and comparable aircraft, but the aircraft’s safe operation has aspects the passenger seldom knows about. • Navigation can be a problem – GPS signals can be scrambled – radio signals from LORAN and OMEGA systems can be distorted and made unusable – zones along critical air routes can be made unsafe for use Courtesy Gene Cameron, United Airlines Arctic Radio HF Polar Route Radio Coverage Arctic Radio VHF Edmonton Ctr Winnipeg Minneapolis Ctr Chicago Ctr Polar Routes North Pole Courtesy Gene Cameron, United Airlines Polar 1 Polar 2 HKG Polar 3 Polar 4 Courtesy Gene Cameron, United Airlines Chicago Space Weather Has Many Forms Civilian Spacecraft at Geostationary Orbit News Accounts of Galaxy-4 Failure It is not always possible to prove that conditions in the space environment cause problems with communication devices such as cell phones and pagers, but it is one explanation. Galaxy-4 Satellite Failure April-May 1998 Special Analysis Interval SAMPEX and POLAR Popular Books About Space Weather Scientific Themes Three basic themes can be used to span the activities: Quests Campaigns – 1. Long-Term Variability of SunEarth phenomena. – 2. Cross-coupling between Long-Term Variability and Space Weather establish Space Climate. – 3. Limits/Extremes including examples from other planets. Advanced Numerical Simulations NASA: Living With a Star Possible Geospace Network and Missions of Opportunity Geospace Missions Network Radiation Environment Mission - GTO Ionospheric Mission - LEO Geospace Imaging Mission - Polar Missions of Opportunity SET - GTO SDO - GEO Leveraged Missions C/NOFS - CINDI - LEO DMSP, GOES, POES, GPS POES, NPOES, METOP CISM Vision: Center for Integrated Space Weather Modeling GOAL: Create a physics-based numerical simulation model that describes the space environment from the Sun to the Earth. USES: • Scientific tool for increased understanding of the complex space environment. • Specification and forecast tool for space weather prediction. • Education tool for teaching about the space environment. MANDATE: in the National Space Weather Program plan CISM Institutions Dartmouth College Boston University University of California NCSA Stanford University University of Colorado NCAR/HAO NOAA/SEC Alabama A&M University SAIC University of Texas, El Paso Rice University Knowledge Transfer • Transition to Forecasting Tools – NOAA/SEC and Air Force Weather Agency. • Knowledge Transfer within Space Physics Community – community access to models. • Industrial Partners – Lockheed Martin, Ball Aerospace, Boeing, Metatech and NOAA/SEC’s user community • Educational knowledge transfer – disseminate educational information and materials to non-CISM institutions CISM Integrated Timeline Code and Model Development Version I Version II Version III Validation/ Assimilation Knowledge Transfer Education Faculty Professional Development 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 MOD NRC MOD DREA NSF NASA NOAA SCOSTEP DOD DOE ESA IKI IZMIRAN Sib-IZMIRAN AARI CNES CAST CMMP INPE EMBRATEL ISAS NASDA STELAB MRST IPS ISES Future Planetary and Human Exploration Testing Limits: Extreme Cases • Earth • Planets