SourceRank: Trust and Relevance based Ranking of 0.78 S
advertisement
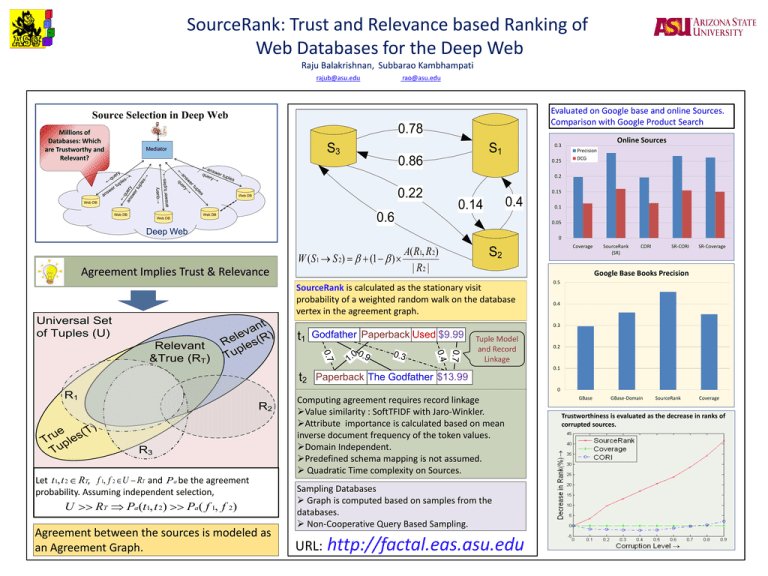
SourceRank: Trust and Relevance based Ranking of Web Databases for the Deep Web Raju Balakrishnan, Subbarao Kambhampati rajub@asu.edu rao@asu.edu Evaluated on Google base and online Sources. Comparison with Google Product Search Source Selection in Deep Web 0.78 Millions of Databases: Which are Trustworthy and Relevant? S3 Mediator S1 0.86 0.3 0.25 Online Sources Precision DCG 0.2 0.22 Web DB 0.15 Web DB 0.4 0.14 Web DB 0.6 Web DB Web DB 0.05 Deep Web 0 W (S1 S 2) (1 Agreement Implies Trust & Relevance SourceRank (SR) CORI SR-CORI SR-Coverage Google Base Books Precision 0.5 0.4 0.3 t1 Godfather Paperback Used $9.99 0.3 0.7 0 0 . . 9 1 0.4 0.7 Relevant &True (RT) t n a v ) e l R e ( R les p u T Coverage S2 A( R1, R 2) ) | R2 | SourceRank is calculated as the stationary visit probability of a weighted random walk on the database vertex in the agreement graph. Universal Set of Tuples (U) 0.1 Tuple Model and Record Linkage 0.2 0.1 t2 0 R1 R2 ) T e ( u les r T p u T R3 Let t1, t 2 RT, f 1, f 2 U RT and P a be the agreement probability. Assuming independent selection, U Paperback The Godfather $13.99 RT Pa (t1, t 2) Pa ( f 1, f 2) Agreement between the sources is modeled as an Agreement Graph. Computing agreement requires record linkage Value similarity : SoftTFIDF with Jaro-Winkler. Attribute importance is calculated based on mean inverse document frequency of the token values. Domain Independent. Predefined schema mapping is not assumed. Quadratic Time complexity on Sources. Sampling Databases Graph is computed based on samples from the databases. Non-Cooperative Query Based Sampling. URL: http://factal.eas.asu.edu GBase GBase-Domain SourceRank Coverage Trustworthiness is evaluated as the decrease in ranks of corrupted sources.




