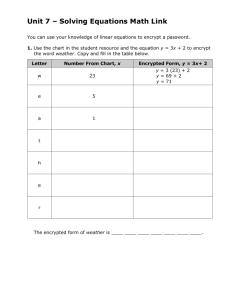
Design Patterns
advertisement

Design Patterns
Design Patterns
Fundamental Design Patterns
Creational Design Patterns
Partitioning Patterns
Behavioral Patterns
Concurrency Patterns
Fundamental Design Patterns (FDP)
Delegation **
Interface
Marker Interface
Immutable
Proxy
FDP - Delegation
Synopsis:
Delegation is a fundamental method to extend and
reuse a classes functionality ( behavior or methods)
Context:
Allows instances of a class to play multiple roles.
Solution:
Reuse and extend behavior using delegation
FDP - Delegation
class x
public void methodforx () {
}
class y
x _x = new x();
……
_x.methodforx ( )
DELEGATION
FDP - Delegation - Example
Delegator
Class or
Instance
uses
1
1
Delegatee
Instance
FDP - Delegation - Example
1. checkluggage()
FlightSegment
Instance
1.1 checkluggage() 1
1
LuggageCompartment
FDP - Delegation - Example
// Instance of this class represent a flight segment.
class FlightSegment {
LuggageCompartment luggage;
/**
* Check a piece of luggage
* @param piece The piece of luggage to be checked.
* @exception LuggageException if piece cannot be checked.
*/
void checkLuggage(Luggage piece) throws LuggageException {
luggage.checkLuggage(piece);
} // checkLuggage(Luggage)
} // class FlightSegment
DELEGATION
Fundamental Design Patterns (FDP)
Delegation **
Interface - Allows classes with some similar data to
use polymorphism to execute behavior.
Marker Interface - used for utilities – allows
investigation into class information without
knowing they are an instance of a particular class.
Immutable – forbids any of an object’s state
information to change after the object is created.
Proxy - forces method calls to an object indirectly.
Creational Design Patterns
Factory Method **
Abstract Factory
Builder
Prototype
Singleton
Object Pool **
CDP - Factory Method
Synopsis:
Need for a class to reuse with arbitrary data types.
Reusable class remains independent of the classes it
instantiates by delegating the choice of which class to
instantiate to another object and referring to the
newly created object through a common interface.
Context:
Creates a framework to support instantiations of
various data types.
CDP - Factory Method
Solution:
Proxy object and the service providing object must
either be instances of a common super class or
implement a common interface.
CDP - Factory Method - Example
You have an application such as MS Office.
You want to perform some common functions with all the files.
Example of common functions might be open file, save file, etc.
The only difference is that the functions are done on different file
types such as word doc files, excel xls files and PowerPoint ppt files.
You could write several independent functions for each of the
different types but the code would be very similar with only the data
type as a difference.
Factory method allows you to build a framework for common
functions with only a few classes that reuse methods for each type.
CDP - Factory Method - Example
Manage
Doc
Files
doc file commands
xls file commands
Manage
Xls
Files
ppt file commands
file commands
Manage
Files
Manage
Ppt
Files
Make
one Function
CDP - Factory Method - Example
Document
MyDocument
edits
*
1
Application
May be doc,
xls, or ppt.
CDP - Factory Method - Example
Suppose you have a process which reads and writes
a DataStream to a socket.
string
Write to
Socket
stream
Socket
string
Read from
Socket
stream
Socket
But you also wish to have strings in which you encrypt the data.
And you write an encrypted DataStream and read back an
encrypted Data Stream decrypt it.
CDP - Factory Method - Example
encrypted
string
string
Encrypt
Data
decrypted
string
Decrypt
Data
Write to
Encrypted
Socket
encrypted
string
encrypted
string
encrypted
stream
Write to
Encrypted
Socket
Read from
Socket
EncryptedSocket
encrypted
stream
encrypted
stream
EncryptedSocket
Socket
But now you realize that there are several different encryption
algorithms and codes you wish to use.
CDP - Factory Method - Example
The process to encrypt differs in using many different different
algorithms (function/method) and type of string output must be
written for each type.
string
Encrypt
Data
encrypted
String #1
Write to
Encrypted
Socket
algorithm # 1
string
Encrypt
Data
encrypted
String #2
Write to
Encrypted
Socket
encrypted
stream
encrypted
stream
EncryptedSocket
EncryptedSocket
algorithm # 2
string
algorithm # n
Encrypt
Data
encrypted
String #n
Write to
Encrypted
Socket
encrypted
stream
EncryptedSocket
CDP - Factory Method - Example
The factory pattern allows you to have a framework that will
handle any type of algorithm and encrypted data.
concrete
product
string
encrypted
String
Encrypt
Data
algorithm # 1
algorithm # n
algorithm # 2
Write to
Encrypted
Socket
encrypted
stream
EncryptedSocket
CDP - Factory Method - Example
Socket
Socket
4
Product
6
encrypt, decrypt
Encryption
1
EncryptedSocket
1
*
Creation Requester
DESEncryption
1
5
*
Concrete Product
Transcription
*
1
creates
1
EncryptedSocket
creates
EncryptionFactory
3
Factory
EncryptionFactoryIF
2
* requestCreation
Interface
CDP - Object Pool
Synopsis:
Manages reuse of objects when a type of object is
expensive to create or only limited number needed.
Context:
You wish to limit access to a resource.
Solution:
Create a reusable class to collaborate with other
objects for a limited amount of time.
Create a reusable pool to manage reusable objects for
use by client objects.
CDP - Object Pool
Suppose you have a database systems that need to allow only a
limited number of accesses to the database at one time.
database access requested
Allow
Database
Access
database access
You must write a counting semaphore to protect this resource from
having more than the limited access.
CDP - Object Pool
manage objects
Client
uses
Reusable
ReusablePool
Reusable Pool
Partitioning Patterns
Layered Initialization **
Filter
Composite
PP - Layered Initialization
Synopsis:
You need multiple implementations with common
logic in super and specialized in subs.
However the common logic decides which
specialized subclass to create.
Therefore layered initialization encapsulates
common and specialized logic to create the multiple
implementations.
PP - Layered Initialization
Context:
You have a piece of logic that requires partial
execution prior to determining which subclass
methods might be used.
You need to layer the initializations of the objects to
process the complex logic or complex data.
PP - Layered Initialization
Forces:
A specialized class must be chosen to process complex
data.
Constructor of the specialized classes and their sub
classes are invoked after it has been decided which
specialized class to instanciate.
Solution:
Essence of this pattern is to layer the initializations of
the objects participating in the pattern.
PP - Layered Initialization
1.
Objects that performs logic common to all cases is initialized
2.
Initialization concludes by determining the class to instantiate
3.
Specialized class constructor performs next layer of initialization logic.
4.
After all initialization, one top-level object exist for logic
5.
If method needs more specialized logic, it calls method one layer down
Consequences:
Complexity of initialization of objects using data
requires analysis before initialization can proceed.
PP - Layered Initialization
Suppose you have a business rule engine which must select a type
of database on which to query to resolve issues in the rule base.
trigger
to resolve
business rule
Oracle
query
Resolve
Business
Rules
query
request
Select
Database
DB2
query
n
query
Perform
Oracle
Query
Perform
DB2
Query
Perform
n
Query
You cannot perform query until you know what type of database
PP - Layered Initialization
You need to initialize the database prior to query.
Initialize
Database
trigger
to resolve
business rule
Oracle
query
Resolve
Business
Rules
query
request
Select
Database
DB2
query
n
query
Perform
Oracle
Query
Perform
DB2
Query
Perform
n
Query
PP - Layered Initialization
ServiceImpFactoryIF
DataQueryFactoryIF
request creation
DataQuery
ServiceImpFactory
uses
DataQueryImplFactory
creates
Service
OracleQuery
ServiceImpIIF
DB2Query
…..
DataQueryImplIF
Data Query factory method object appears like this.
Behavioral Patterns
Chain of Responsibility
State
Command
Null Object
Little Language
Strategy **
Mediator
Template Method
Snapshot
Visitor
Observer **
BP - Observer
REDO Suppose you have a process which reads and writes
a DataStream to a socket.
string
Write to
Socket
stream
Socket
string
Read from
Socket
stream
Socket
But you also wish to have strings in which you encrypt the data.
And you write an encrypted DataStream and read back an
encrypted Data Stream decrypt it.
BP - Observer
Document
MyDocument
edits
*
1
Application
May be doc,
xls, or ppt.
Concurrency Patterns
Single Threaded Execution
Guarded Suspension
Balking
Scheduler
Read/Write Lock
Producer-Consumer
Two-Phase Termination