Vectors Practicum II Goal:
advertisement

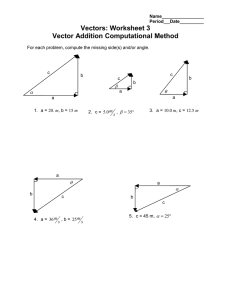
Name Name Name Name Period Vectors Practicum II Goal: The purpose of this practicum is to gain experience in adding three (3) vector quantities experimentally and computationally. Apparatus: Force Table Masses Protractor Ruler Graph Paper Procedure For each case, hang the given masses at the stated angles. Be sure to include the mass hanger m 5.0 g 0.0050 kg in the total mass. All directions are measured using counter-clockwise from 0 notation. Adjust the pulleys downward until the strings are close to but not touching the top surface of the force table. By trial and error, find the angle for the fourth super pulley clamp and the mass that must be suspended over the pulley so that its weight will balance the forces exerted on the strings by the other two masses. This fourth force is called the equilibriant because it establishes equilibrium. Remember that the equilibriant is the same size as the resultant, but in the opposite direction. Experimental Method of Finding Equilibrium The knot should be centered over the hole in the middle of the center post when the system is in equilibrium. The anchor string should be slack. Pull the knot slightly to one side and let it go. Check to see that the knot returns to the center. If not, adjust the mass and/or the angle of the super pulley clamp until the knot always returns to the center when pulled slightly to one side. Compute the resultant both computationally and graphically (chose a scale). Record the results and calculate the percent error for each compared to the experimental value. Everyone should complete the worksheet, with one set for the group to be turned in at the end of the hour. PSYW % Error Theoretical Experimental 100 Theoretical Vectors Practicum II page 2 Do not forget to include the mass hanger m 5.0 g 0.0050 kg in the total mass Trial 1 Mass (kg) Force (N) Direction (degrees) 0.055 15 0.075 80. 0.105 160 Force (N) Experimental Equilibriant Mass Force Direction (kg) (N) (degrees) Experimental Resultant Force Direction (N) (degrees) Computational Resultant % Error Direction (degrees) Force Direction Sketch a vector diagram of the situation and then compute the resultant in the space below using the component method. Record the results above and calculate the % error between this result and the experimental result. PSYW Vectors Practicum II page 3 Trial 2 Mass (kg) Force (N) Direction (degrees) 0.055 0 0.075 90. 0.105 300. Experimental Equilibriant Mass Force Direction (kg) (N) (degrees) Experimental Resultant Force Direction (N) (degrees) Computational Resultant % Error Force Direction (N) (degrees) Force Direction Sketch a vector diagram of the situation and then compute the resultant in the space below using the component method. Record the results above and calculate the % error between this result and the experimental result. PSYW