Dynamics Worksheet 3 John Paul George
advertisement

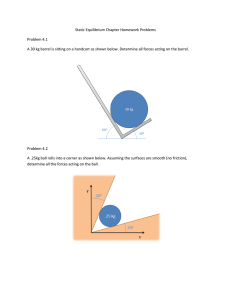
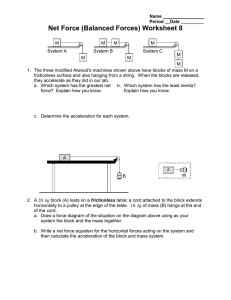
Name Period Date Dynamics Worksheet 3 John Ringo Paul Tension = 150 N George 12.0 kg 20.0 kg 15.0 kg Tension = 222 N 1. Four penguins (John, Paul, George, and Ringo) are being playfully pulled along very slippery (frictionless) ice by a curator as in the diagram above. The masses of three of the penguins and the tension in two of the cords are given. Remember, objects that are moving together can be analyzed as a system. Draw and label the forces acting on the chosen system in each part. a. Calculate the acceleration of the b. What is John’s mass? penguins. c. What is the tension in the rope that pulls Ringo? d. What is the tension in the rope between George and Paul? Dynamics Worksheet 3 page 2 m1 m2 2. A block of mass m1 on a frictionless inclined plane of angle is connected by a cord over a massless, frictionless physics pulley to a second block of mass m2 hanging vertically as in the diagram above. a. On the system diagram below, draw and label the forces (not components) that act on the system as it accelerates. m2 m1 b. What is the acceleration of each block? If you need to draw anything besides what you have shown in part (a) to assist in your solution, use the space below. Do NOT add anything to the figure in part (a). Express your answer in terms of m1 , m2 , , and g . m2 m1 c. Calculate the acceleration if m1 3.70 kg , m2 2.30 kg , 30.0 and g 9.80 N . kg d. In what direction is block m2 moving and how do you know? Dynamics Worksheet 3 page 3 e. Draw a separate force diagram for each box and calculate the tension acting on each. m2 m1 3. A 4.0 kg block is put on top of a 5.0 kg block. The 4.0 kg coefficient of static friction between the blocks is 0.306 . The assembly of blocks is now placed on a horizontal, 5.0 kg F frictionless table and a force F is applied to the bottom Frictionless block as shown so that the blocks move together. a. Draw a force diagram of b. What is the maximum acceleration the blocks can the top block. achieve if they are to remain together? 4.0 kg c. What is the magnitude of the maximum horizontal force F that can be applied to the lower block so that the blocks will move together? Remember, objects that are moving together can be analyzed as a single system. 4.0 kg 5.0 kg Dynamics Worksheet 3 page 4 Fapplied mA mB mC 4. Three boxes of mass m A 2.0 kg , mB 4.0 kg and mC 6.0 kg are side-by-side on a frictionless surface as in the diagram. A force of Fapplied 60. N is applied horizontally to the 2.0 kg box. a. Draw and label the forces acting on b. Calculate the acceleration of the boxes. the system of three boxes. mA mB mC c. Draw a quantitative force diagram for each box. Remember, the length of a force arrow represents the magnitude of the force. Use the following interaction notation. FAB Force of A acting on B FBA Force of B acting on A FBC Force of B acting on C FCB Force of C acting on B mA mB d. Explain why FAB FBA and FBC FCB . mC e. Explain why Fapplied FBA and FAB FCB .