Projectile Motion Review Worksheet - Physics
advertisement

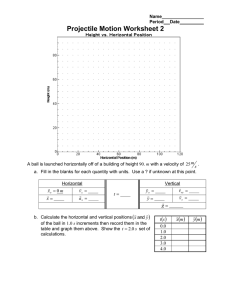
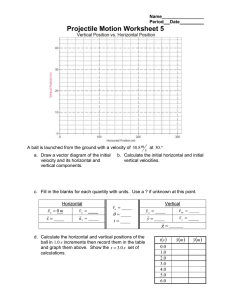
Name Period Date Projectile Motion Review 1. The acceleration due to gravity acts: a. upward. b. depending on the motion of the object. c. downward. d. toward outer space. 2. A bullet is fired at an angle of 45°. Neglecting air resistance, what is the direction of acceleration during the flight of the bullet? Draw a force diagram of the bullet in flight. a. Downward. b. Dependent on the initial velocity. c. Upward. d. At a 45° angle. 3. A golfer drives her golf ball from the tee down the fairway in a high arcing shot. When the ball is at the highest point of its flight a. the velocity and acceleration are both zero. b. the horizontal velocity is zero and the vertical velocity is zero. c. the velocity is non-zero and the acceleration is zero. d. the horizontal velocity is non-zero and the vertical velocity is zero. 4. In the first practicum the ball was shot horizontally. What was the initial vertical velocity v oy of the ball when it was shot? a. It depends on the initial horizontal velocity. b. Unknown; it must be measured. c. It depends on the mass of the ball. d. 0 m s 5. A soccer ball is kicked at a 55° angle with an initial velocity of 8 m . What is the s vertical velocity of the ball as it hits the ground? a. 8 m s b. 8 m s c. 6.6 m s 6. Approximately how far will an object near Earth's surface fall in 3.0 s? a. 44 m b. 29 m c. 9.8 m d. 88 m Projectile Motion: Review Worksheet page 2 7. For a projectile, what is the acceleration in the horizontal direction? Draw a force diagram for the projectile anywhere in its path. a. It depends on its initial velocity. b. It depends on how long it is in the air. c. 0 m 2 s d. It depends on its vertical acceleration. 8. A bullet is fired horizontally from a gun. At the same time a similar bullet is dropped from the same height. In the absence of air resistance, the fired bullet will a. hit the ground first. b. hit at the same time as the dropped bullet. c. hit the ground second. d. never hit the ground. 9. A 10 kg stone and a 100 kg stone are dropped from the roof of a building. Which will hit the ground first? (Neglect air resistance) a. They will hit at the same time. b. The 10 kg stone. c. The 100 kg stone. d. It cannot be determined from given information. 10. A ball thrown vertically upward reaches a maximum height of 30. m above the surface of the Earth. At its maximum height, the speed of the ball is a. 24 m s b. 0 m s c. 3.1 m s d. 9.8 m s 11. A red ball and a green ball are simultaneously thrown horizontally from the same height. The red ball has an initial speed of 40. m and the green ball has an initial s m speed of 20. . Compared to the time it takes the red ball to reach the ground, the s time it takes the green ball to reach the ground will be a. half as much b. the same c. twice as much d. four times as much Projectile Motion: Review Worksheet page 3 The rider and his bicycle in the diagram above are traveling to the right at a constant speed. A ball is dropped from the hand of the cyclist. 12. Which set of graphs best represents the horizontal motion of the ball as it falls? a. x b. x vx t c. x t t d. x vx t vx t t vx t t 13. Which set of graphs best represents the vertical motion of the ball as it falls? a. y b. y vy t t c. y vy t vy t t t d. y vy t t Projectile Motion: Review Worksheet page 4 14. Which of the following statements are true of projectiles? a. A projectile is a free-falling object. b. A projectile experiences negligible or no air resistance. c. A projectile must be moving in the downward direction. d. A projectile must be accelerating in the downward direction. e. A projectile does not have to have horizontal motion. f. A projectile could begin its projectile motion with a downward velocity. 15. Which of the following statements are true of the horizontal motion of projectiles? a. A projectile does not have a horizontal velocity. b. A projectile with a rightward component of motion will have a rightward component of acceleration. c. The horizontal velocity of a projectile changes by 9.8 m each second. s d. A projectile with a horizontal component of motion will have a constant horizontal velocity. e. The horizontal velocity of a projectile is 0 m at the peak of its trajectory. s f. The horizontal velocity of a projectile is unaffected by the vertical velocity; these two components of motion are independent of each other. g. The horizontal displacement of a projectile is dependent upon the time of flight and the initial horizontal velocity. h. The final horizontal velocity of a projectile is always equal to the initial horizontal velocity. i. As a projectile rises towards the peak of its trajectory, the horizontal velocity will decrease; as it falls from the peak of its trajectory, its horizontal velocity will decrease. j. Consider a projectile launched from ground level at a fixed launch speed and a variable angle and landing at ground level. The horizontal displacement (i.e., the range) of the projectile will always increase as the angle of launch is increased from 0 degrees to 90 degrees. k. Consider a projectile launched from ground level at a fixed launch angle and a variable launch speed and landing at ground level. The horizontal displacement (i.e., the range) of the projectile will always increase as the launch speed is increased. 16. A football is kicked into the air at an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal. At the very top of the ball's path, its velocity is _______. a. entirely vertical b. entirely horizontal c. both vertical and horizontal d. not enough information given to know. 17. A football is kicked into the air at an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal. At the very top of the ball's path, its acceleration is _______. (Neglect the effects of air resistance.) a. entirely vertical b. entirely horizontal c. both vertical and horizontal d. not enough information given to know. Projectile Motion: Review Worksheet page 5 18. A football is kicked into the air at an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal. At the very top of the ball's path, the net force acting upon it is _______. (Neglect the effects of air resistance.) a. entirely vertical b. entirely horizontal c. both vertical and horizontal d. not enough information given to know. 19. Which of the following statements are true of the vertical motion of projectiles? a. The vertical component of a projectile's velocity is a constant value of 9.8 m . s b. The vertical component of a projectile's velocity is constant. c. The vertical component of a projectile's velocity is changing. d. The vertical component of a projectile's velocity is changing at a constant rate. e. A projectile with an upward component of motion will have a upward component of acceleration. f. A projectile with a downward component of motion will have a downward component of acceleration. g. The magnitude of the vertical velocity of a projectile changes by 9.8 m each s second. h. The vertical velocity of a projectile is 0 m at the peak of its trajectory. s i. The vertical velocity of a projectile is unaffected by the horizontal velocity; these two components of motion are independent of each other. j. The final vertical velocity of a projectile is always equal to the initial vertical velocity. k. The vertical acceleration of a projectile is 0 m 2 when it is at the peak of its s trajectory. l. As a projectile rises towards the peak of its trajectory, the vertical acceleration will decrease; as it falls from the peak of its trajectory, its vertical acceleration will increase. m. As a projectile rises towards the peak of its trajectory, the vertical acceleration is directed upward; as it falls from the peak of its trajectory, its vertical acceleration is directed downward. n. The peak height to which a projectile rises above the launch location is dependent upon the initial vertical velocity. o. As a projectile rises towards the peak of its trajectory, the vertical velocity will decrease; as it falls from the peak of its trajectory, its vertical velocity will decrease. p. Consider a projectile launched from ground level at a fixed launch speed and a variable angle and landing at ground level. The vertical displacement of the projectile during the first half of its trajectory (i.e. the peak height) will always increase as the angle of launch is increased from 0 degrees to 90 degrees. q. Consider a projectile launched from ground level at a fixed launch angle and a variable launch speed and landing at ground level. The vertical displacement of the projectile during the first half of its trajectory (i.e. the peak height) will always increase as the launch speed is increased. Projectile Motion: Review Worksheet page 6 20. At what point in its path is the horizontal component of the velocity v x of a projectile the smallest? a. The instant it is thrown. b. Halfway to the top. c. At the top. d. As it nears the top. e. It is the same throughout the path. 21. At what point in its path is the vertical component of the velocity v y of a projectile the smallest? a. The instant it is thrown. b. Halfway to the top. c. At the top. d. As it nears the top. e. It is the same throughout the path. 22. Which of the following statements are true of the time of flight for a projectile? a. The time that a projectile is in the air is dependent upon the horizontal component of the initial velocity. b. The time that a projectile is in the air is dependent upon the vertical component of the initial velocity. c. For a projectile which lands at the same height that it is projected from, the time to rise to the peak is equal to the time to fall from its peak to the original height. d. For the same upward launch angles, projectiles will stay in the air longer if the initial velocity is increased. e. Assume that a kicked ball in football is a projectile. If the ball takes 3 seconds to rise to the peak of its trajectory, then it will take 6 seconds to fall from the peak of its trajectory to the ground. 23. Roll a bowling ball off the edge of a table. As it falls, the horizontal component of its velocity ___. a. decreases b. remains constant c. increases 24. A bullet is fired horizontally and hits the ground in 0.5 seconds. If it had been fired with twice the speed in the same direction, it would have hit the ground in ____. (Assume no air resistance.) a. less than 0.5 s. b. more than 0.5 s. c. 0.5 s. 25. A projectile is launched at an angle of 15 degrees above the horizontal and lands down range. For the same speed, what other projection angle would produce the same downrange distance? a. 30 degrees. b. 45 degrees. c. 50 degrees. d. 75 degrees e. 90 degrees. 26. Two projectiles are fired at equal speeds but different angles. One is fired at an angle of 30 degrees and the other at an angle of 60 degrees. The projectile to hit the ground first will be the one fired at (neglect air resistance) ____. a. 30 degrees b. 60 degrees c. both hit at the same time Projectile Motion: Review Worksheet page 7 27. An egg is thrown horizontally off of a 20. m high roof with an initial velocity of 6.5 m . s a. How long is the egg in the air? b. How far from the base of the building does the egg land? 28. A car drives horizontally off a cliff 80. m high. The car lands 100. m from the base of the cliff. a. How long is the car in the air? b. How fast was the car traveling when it left the cliff? 29. A cannonball is fired from the ground at an angle of 60.° with an initial velocity of 200. m . s a. Calculate the horizontal and vertical b. How long is the cannonball in the air? components of the initial velocity. c. How far will the cannonball travel before returning to the ground? d. What is the maximum height reached by the cannonball? Projectile Motion: Review Worksheet page 8 30. Suppose that in the first practicum, a ball was shot horizontally from a height of 1.10 m into a can of height 15 cm. It took the ball 0.0240 s to pass through the photogates which are 10. cm apart. a. What is the initial b. What is the initial c. What is the ball’s velocity of the ball? vertical velocity v oy of horizontal velocity v x 0.20 s after the ball is the ball? shot? d. How long does it take the ball to reach the can? e. How far away from the launcher should the can be placed so that the ball lands into the can? f. Suppose a ball with twice the mass was shot from the launcher at the same height. How long would it take this more massive ball to reach the can?