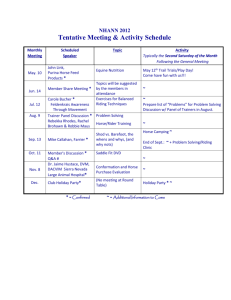
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
advertisement

Newton’s Third Law of Motion In any interaction between two objects, the forces exerted are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction” Newton’s Third Law of Motion In any interaction between two objects, the forces exerted are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. The Horse and the Wagon: A Newton’s Third Law Story "Newton's Third Law says that if I pull on the wagon, the wagon exerts an equal and opposite force on me,” says the Horse. "If these two forces are equal and opposite, they will cancel, so that the net force is zero, and I won’t move. So why should I even bother?” FWagon pulling FHorse pulling backwards on the Horse forward on the wagon Earth Newton’s Third Law pairs do not cancel because they act on different objects! But if I pull forward on the wagon, it will pull backwards on me, so how can I move forward to market? Fg of the Earth pulling FN of the ground pushing down on the Horse upward on the Horse F f of the surface pushing forward on the Horse Fg of the Horse F f of the Horse pushing backwards on the Surface pulling up on the Earth Earth FN of the Horse pushing downward on the ground As long as the ground pushes forward harder on the Horse than the wagon pulls backwards, the net force and therefore the resulting motion is forward! The Tug-of-War Fof the rope pulling Fof me pulling backwards on the rope forward on me Fof the ground pushing backwards on me Fof me pushing forward on the ground I must push harder on the ground than I pull on the rope, so that the ground pushes back on me harder than the rope pulls forward! It’s all about how hard you can push!