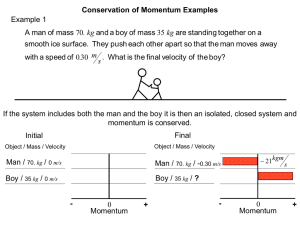
Example 1 Conservation of Momentum Bar Graph Examples
advertisement

Conservation of Momentum Bar Graph Examples Example 1 A man of mass 70. kg and a boy of mass 35 kg are standing together on a smooth ice surface. They push each other apart so that the man moves away with a speed of 0.30 m . What is the final velocity of the boy? s If the system includes both the man and the boy it is then an isolated, closed system and momentum is conserved. Initial Final Object / Mass / Velocity Object / Mass / Velocity Man / 70. kg / 0 m/s Man / 70. kg / -0.30 m/s Boy / 35 kg / 0 m/s Boy / 35 kg / ? - 0 Momentum + 21kgm 21 kgm - s s 0 Momentum + Conservation of Momentum Bar Graph Examples Example 1 A man of mass 70. kg and a boy of mass 35 kg are standing together on a smooth ice surface. They push each other apart so that the man moves away with a speed of 0.30 m . What is the final velocity of the boy? s Final Initial Object / Mass / Velocity Object / Mass / Velocity Man / 70. kg kg / 0 m/s kg / -0.30 m/s Man / 70. kg kg / 0 m/s Boy / 35 kg Boy / 35 kg kg / ? - 0 Momentum pbf mbvbf pbf vbf mb 21 kgm - + vbf 21kgm 21kgm s 0 Momentum s 35 kg vbf 0.60 m s s Notice the boy has half the mass so twice the velocity! + Example 2 Conservation of Momentum Bar Graph Examples A bullet of mass 10. g moves horizontally with a speed of 400. m and embeds s itself in a block of wood of mass 0.39 kg that is initially at rest on a frictionless table as shown below. a. What is the final velocity of the bullet and the block after the collision? If the system includes both the bullet and the wood it is then an isolated, closed system and momentum is conserved. Initial Final Object / Mass / Velocity Object / Mass / Velocity Bullet / 0.010 kg / 400. m/s 4.0 kgm 4.0 kgm Combo / 0.40 kg / ? s s Wood / 0.39 kg / 0 m/s - 0 Momentum + - 0 Momentum + Example 2 Conservation of Momentum Bar Graph Examples A bullet of mass 10. g moves horizontally with a speed of 400. m and embeds s itself in a block of wood of mass 0.39 kg that is initially at rest on a frictionless table as shown below. a. What is the final velocity of the bullet and the block after the collision? Initial Final Object / Mass / Velocity Object / Mass / Velocity kgm Bullet / 0.010 kg kg / 400. m/s 4.0 4.0 kgm kg / ? Combo / 0.40 kg s s kg / 0 m/s Wood / 0.39 kg - 0 Momentum p f mb mw v f p f vf mb mw + vbf 4.0 kgm - 0 Momentum s 0.010 kg 0.39 kg v f 10. m s Notice that more mass is moving at a slower velocity! + Example 2 Conservation of Momentum Bar Graph Examples A bullet of mass 10. g moves horizontally with a speed of 400. m and embeds s itself in a block of wood of mass 0.39 kg that is initially at rest on a frictionless table as shown below. b. What are the initial and final kinetic energies of the bullet, wood block system? 1 Ekf mb mw v 2f 2 1 Eki mbvbi2 2 1 Eki 0.010 kg 400. m s 2 Eki 8.0 102 J 2 1 Ekf 0.010 kg 0.39 kg 10. m s 2 Ekf 20. J This is an inelastic collision. Most of the energy is dissipated and is stored as increased thermal energy in the bullet/block system. 2